What Do Solar Panels Cost?
Solar panels have emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against climate change and rising energy costs, offering clean, renewable energy harnessed from the sun. However, investing in solar power often hinges on understanding the financial aspects, with many businesses, homeowners and policymakers questioning, “What do solar panels cost?“.
This article looks closely into the world of solar panel pricing, exploring the factors that influence costs, examining recent trends, and shedding light on what to expect in the future.
Whether you’re a homeowner looking to make the switch to solar, a business considering renewable energy options, or simply curious about the economics of solar power, this article aims to provide the answers you need to make informed decisions.
What Do Solar Panels Cost?: Average Price In US
Over the past decade, we’ve witnessed a remarkable decline in the cost of solar panels, ushering in an era of increased accessibility to solar energy for a broader spectrum of consumers. Over the past decade, residential solar panel costs have dropped by 70%, with a 3% decrease over the last four years.
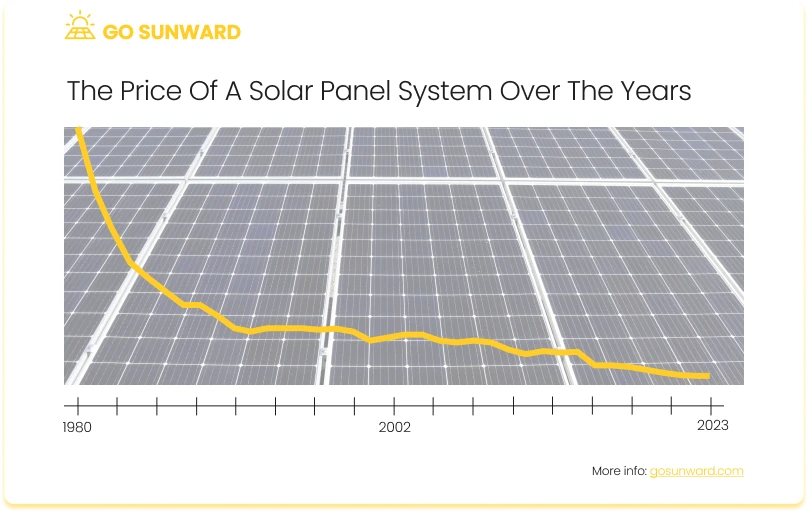
Average prices are typically quantified in terms of dollars per watt or kilowatt-hour (kWh). Our research suggests that, in the United States, the average cost of solar panels currently falls between $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. This pricing encompasses not only the expenses associated with the solar panels themselves but also the costs related to their installation.
In terms of an entire residential solar panel system, it’s worth noting that a typical system may range from approximately $15,000 to $25,000, prior to any application of incentives, rebates and net metering schemes.
When examining average pricing, our reference primarily pertains to residential solar systems rather than utility-scale installations. Utility-scale solar projects distinguish themselves by their larger size and capacity compared to residential counterparts. This substantial disparity in scale exerts a profound influence on the overall cost structure of solar installations. Utility-scale projects enjoy economies of scale, translating to lower per-unit costs for equipment, labor, and materials. Recognizing this distinction is instrumental in accurately gauging the cost-effectiveness and competitiveness of solar energy across diverse contexts.
What Do Solar Panels Cost? Panel Perspective
Solar panels come in various types, each offering different levels of durability, efficiency, and size, tailored to specific needs. For more information on the various types of panels on the market, click here.
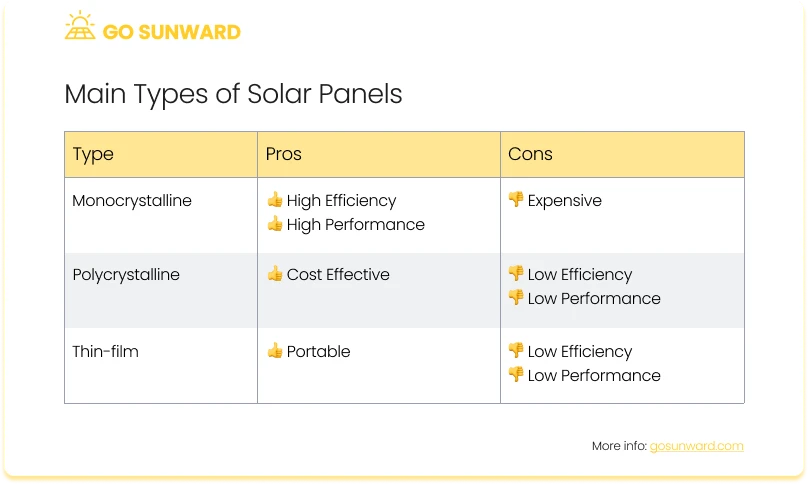
There are three main panel types, with a different cost per watt.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Monocrystalline solar panels are renowned for their exceptional energy efficiency, making them a popular choice for those with limited roof space. These panels typically cost between $1 to $1.50 per watt. Monocrystalline panels boast an impressive lifespan of up to 40 years, making them a long-lasting investment. When compared to polycrystalline panels, monocrystalline panels are the more efficient option.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Polycrystalline solar panels, while slightly less energy-efficient than their monocrystalline counterparts, offer an attractive cost advantage. They typically range from $0.75 to $1 per watt. Polycrystalline panels are commonly used in residential settings due to their affordability. While they may not match the efficiency of monocrystalline panels, their average lifespan of 25 to 30 years ensures a reliable performance over time.
Thin-Film Solar Panels: Thin-film solar panels are the cost-effective choice, with an average price ranging from $0.75 to $1.10 per watt. These panels are more budget-friendly but come with a trade-off. They require a larger amount of space, which makes them suitable for industrial applications or smaller projects such as RVs or sheds. However, they have a shorter lifespan, lasting approximately 10 to 20 years, and offer a shorter warranty compared to other panel types.

What Do Solar Panels Cost?: Factors Affecting Price
Besides technology type, many other factors influence the cost of solar panels, and each factor plays a crucial role in determining the overall price of solar energy systems.
- Raw Materials: The availability and cost of raw materials used in solar panel production are primary drivers of solar panel prices. Silicon, for instance, is a key component in most solar modules, and fluctuations in silicon prices can significantly impact solar panel costs. The supply and demand dynamics of materials such as glass, aluminum, and conductive materials also contribute to pricing variations.
- Economies of Scale: The scale of production matters. Large-scale manufacturing facilities benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to produce solar panels more efficiently and cost-effectively. As production volumes increase, per-unit manufacturing costs decrease, often leading to lower consumer prices.
- Supply Chain Factors: The global supply chain for solar panels can introduce pricing variations. Factors such as shipping costs, import/export tariffs, and trade regulations can impact the final cost of solar panels in different regions. The resilience and efficiency of the supply chain also influence the overall cost structure.
- Labor Costs: Labor is a significant component of solar panel installation costs. Local labor costs and the complexity of the installation process can vary widely, impacting the overall price of solar energy systems.
- Quality and Performance: High-quality solar panels with better performance characteristics often come at a premium price. Solar panel manufacturers invest in research and development to enhance their products’ efficiency, durability, and reliability. While these advancements can contribute to higher upfront costs, they may result in a greater long-term rate of return (ROI) and energy production.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Government incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs, can significantly reduce the upfront cost of solar panel installations. These incentives can vary by region and greatly affect solar energy adoption’s overall cost-effectiveness. The Solar Energy Industries Association (seia) is a good resource for information of federal, state and regulatory policy.
- Manufacturing Processes: The efficiency and sophistication of manufacturing processes play a critical role in solar panel pricing. Improvements in manufacturing technologies can reduce production costs, resulting in more affordable solar panels. Innovations in techniques like thin-film and multi-junction solar cell manufacturing have the potential to drive down costs and boost the efficiency of solar panels.
Regional Variations : Factors such as sunlight intensity and local market conditions can lead to substantial differences in pricing. For instance, regions with abundant sunlight and strong solar incentives, such as the southwestern United States, tend to have lower solar panel prices compared to less sunny regions.
Cost Considerations: Size & Quantity
Wattage size and the number of solar panels required are critical factors to consider when evaluating solar panel costs and planning your solar installation. These aspects not only impact the upfront expenses but also influence the overall performance and feasibility of your solar energy system.
To make informed decisions about your solar panel purchase, it’s essential to research just how many panels you will need to meet your energy demands, and what that means regarding system sizing and the associated costs.
We have several articles to help you with this process, including: ‘How Many Solar Panels Will I Need To Run A House?’, ‘Solar Power: How To Power Your House With The Sun’, and ‘How Many Solar Panels Do I Need For 1000 kWh Per Month?’.
In essence, to calculate how many solar panels you need you should multiplying your household’s hourly energy requirement (in watts) by the peak sunlight hours for your area and dividing that by a panel’s wattage. In other words:
Number of Panels = (Hourly Energy Requirement in watts x Peak Sunlight Hours) / Solar Panel Wattage
Solar installer companies often consider a 20% buffer when planning a solar system to take into consideration system inefficiencies.
Additional Costs To Consider
When planning your solar panel installation, it’s crucial to factor in some potential additional expenses as well.
Maintenance: Solar panels require periodic maintenance, typically recommended twice a year, with some opting for quarterly servicing. For an in-depth looking into the maintenance required for solar panels, have a look at this comprehensive article.
Cleaning: Regular panel cleaning, usually performed annually or semi-annually, is essential for optimal performance.
Home Insurance: Installing solar panels may lead to adjustments in your homeowner’s insurance rates; ensure your coverage accounts for replacement costs.
Solar System Monitoring: Budget for monitoring tools and connectivity, as most installations require some investment.
Roof Repair: Ensure your roof is structurally sound before installation; minor or major repairs may be necessary.
Solar Panel Repair: Repair costs vary depending on the extent of damage; consider warranty options from solar panel companies.
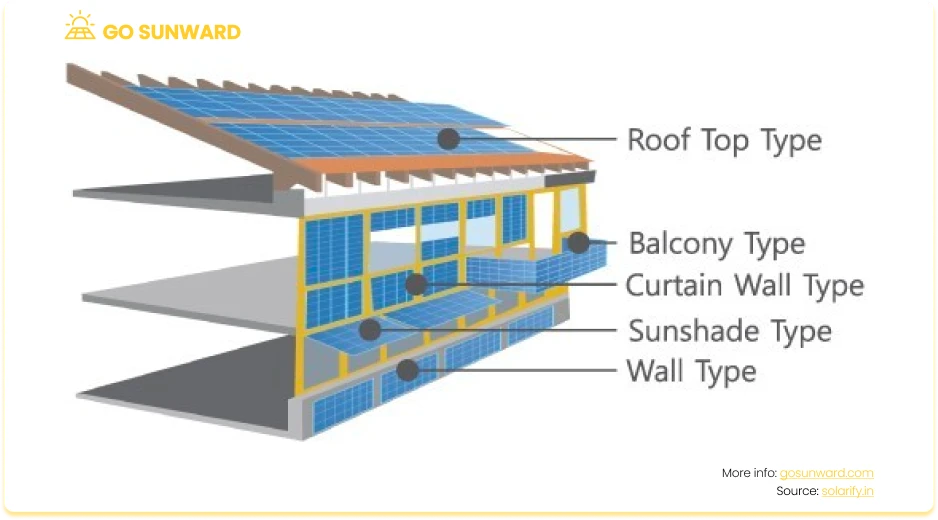
Solar Shingles and Tiles: Premium options like solar shingles and tiles integrate energy generation with roofing; costs depend on material quality. For example, Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) refer to solar panels that are integrated directly into building materials such as roofing, windows, or facades. This approach combines solar power generation with architectural design.
What Are The Financing Options For Buying Solar Panels?
You can buy solar panels outright using your own savings or funds. This option provides the greatest long-term savings because you own the system and can benefit from incentives and energy savings without ongoing monthly payments.
Many banks, credit unions, and solar financing companies offer solar loans. With a solar loan, you borrow money to purchase the solar panels and pay it back over time, often with low-interest rates. You own the system from the beginning and can benefit from the savings on your energy bills.
Meanwhile, solar leasing involves renting the solar panels from a solar company (see the best solar companies here). You pay a fixed monthly lease payment but do not own the system. This can be a good option for those who want to go solar with little or no upfront costs, but you may not be eligible for certain incentives or tax credits.
Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) financing are offered in some areas that allow you to finance your solar installation through a special property tax assessment. This option can make it easier to finance solar with flexible repayment terms.
You can also use the equity in your home to secure a loan or line of credit for solar panel installation. These options may offer competitive interest rates, but your home serves as collateral.
Breaking Even On Solar Panel Costs & Solar Lifespan
Determining how long it will take to recoup your solar panel investment is a key consideration for many homeowners. On average, the annual energy bill in 2022 stood at around $1,650, according to the EIA. Given that the typical solar system costs between $4,600 and $16,000 after applying tax credits, your break-even period can range from three to 10 years. The exact timeframe hinges on various factors, including your electricity expenses and financing options, such as local and federal tax credits.
The typical lifespan of a solar panel is around 25 to 30 years. However, many solar panels continue to generate electricity effectively for well beyond that timeframe. Most reputable solar panel manufacturers offer warranties that guarantee the panels will still produce at least 80% to 90% of their rated power output after 25 years.
The longevity of solar panels is influenced by various factors, including the quality of the panels, the environment in which they are installed, and the maintenance they receive. Properly maintained panels in favorable conditions may exceed their expected lifespan, while panels subjected to harsh environments or poor maintenance may not last as long.
It’s worth noting that the rate of efficiency degradation in solar panels is relatively slow, typically around 0.5% to 1% per year. This means that even after their warranty period, solar panels can continue to produce electricity at a reasonable level for many years, making them a durable and reliable renewable energy investment.
Will Solar Panels Get Cheaper?
The future of solar panel pricing is a topic of great interest with far-reaching implications for renewable energy adoption, and one that we have written extensively on. Predicting future prices involves considering multiple factors. Experts anticipate that solar panel costs will continue to decrease due to technological advancements and economies of scale. By 2030, for instance, the global weighted average levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for solar photovoltaic (PV) is projected to decrease by 58% compared to 2018, further enhancing the affordability and accessibility of solar energy solutions.
Technological innovations, like perovskite and tandem solar cells, hold promise for boosting efficiency and lowering manufacturing expenses.
Market dynamics, driven by increasing demand and policy support, are expected to influence solar panel prices positively. Government policies, including incentives like tax credits and rebates, will influence pricing. Conversely, policy changes such as import tariffs can affect supply chains and competition.
Solar panel pricing can vary by region, influenced by trade policies, local markets, and solar resource availability. Emerging markets may experience slower price decreases, while mature markets with well-established solar industries may see faster declines.
Considering not only panel costs but also overall system expenses, such as installation and inverters, is crucial. As installation processes become more efficient, installation costs may decrease, enhancing the affordability of solar energy.
Looking Beyond Costs, What Are The Wider Benefits Of Solar?
There are some key benefits when switching your energy use to solar power. These are largely focused on environmental benefits, financial benefits and energy independence.
Solar power offers a multitude of environmental and energy security benefits. Firstly, it significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. By harnessing energy from the sun, solar power generates electricity without releasing harmful pollutants, improving air quality and public health.
Moreover, solar energy is a renewable resource, abundant and accessible to most regions, ensuring a reliable and sustainable energy supply. This reduces dependency on finite fossil fuels and lessens exposure to energy supply disruptions, enhancing energy security. It also diminishes reliance on foreign energy sources, decreasing geopolitical tensions associated with resource conflicts.
Solar power is water-efficient, particularly important in areas prone to droughts, as it consumes minimal water compared to traditional power generation methods. Additionally, it reduces transmission losses since it can be generated close to where it’s consumed, improving overall energy efficiency and grid stability.
Furthermore, the solar industry generates employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, fostering economic growth. Lastly, the decentralized nature of solar power enhances grid resilience by diversifying energy sources and minimizing vulnerability to large-scale failures, contributing to a more robust and reliable energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey into understanding the cost of solar panels reveals not just a financial picture, but an interesting narrative of technology innovation and sustainability. Solar panels, once considered a niche technology, have evolved into a practical and accessible solution for homeowners and businesses alike. If you want to know quite simply, are solar panels worth it?, then this article should help you get a better idea.
While we’ve explored the various factors influencing solar panel pricing, from the type of panels to regional variations and incentives, one overarching theme emerges – the undeniable trend of affordability. Over the past decade, solar panel costs have plummeted, and technological advancements continue to drive prices downward.




