Can Solar Fully Power a House?
In an era marked by an increasing commitment to sustainability and renewable energy sources, the adoption of residential solar power is on the rise across the world. And no more so than in the US. As homeowners across the US seek ways to reduce their carbon footprint and reduce their energy bills, the appeal of solar power has risen exponentially. Yet, a crucial question persists: Can solar fully power a house? It’s a query that promises economic savings, environmental responsibility, and energy independence.
Data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) indicates that residential solar power installations surged by 34% in 2021, increasing from 2.9 gigawatts in 2020 to 3.9 gigawatts. Furthermore, our research indicates that in 2022, the market size of residential solar PV in the US reached USD 14.21 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.3% anticipated from 2023 to 2030.
In this comprehensive article on residential solar power, we look into the intricacies of solar systems and inverters and their potential to fulfil the energy demands of a modern household. We will explore topics such as the equilibrium between energy generation and consumption. We’ll also cover, the critical significance of energy storage solutions, and gain insights into the evolving landscape of solar energy trends and the technology’s feasibility. This article will shed light on the opportunities and considerations that come with investment in solar power for your home and determine whether or not solar can really fully power a house.
Is It Possible For Solar To Fully Power A House?
The simple answer is a resounding “yes.”
Solar energy can indeed be harnessed to power an entire household. In fact, some individuals have implemented extensive solar systems and solar arrays, allowing them to achieve complete energy independence. This approach aligns with ‘net-zero’ energy homes which aim to achieve a harmonious balance between energy production and consumption. These homes are designed and equipped to generate as much energy as they consume. Which effectively erases their carbon footprint in terms of energy use.
Nonetheless, for many homeowners, retaining a connection to the local energy grid serves as a practical backup during cloudy days or extended inclement weather periods. Depending on your location, utility companies may levy a modest fixed charge to maintain this grid connection, ensuring continuous access to electricity.
In certain regions, solar installers can configure your solar panels to feed surplus energy back into the grid. In return, energy providers offer you credits that can be redeemed to access free electricity from the grid during nighttime hours or overcast days. This process is known as net metering.
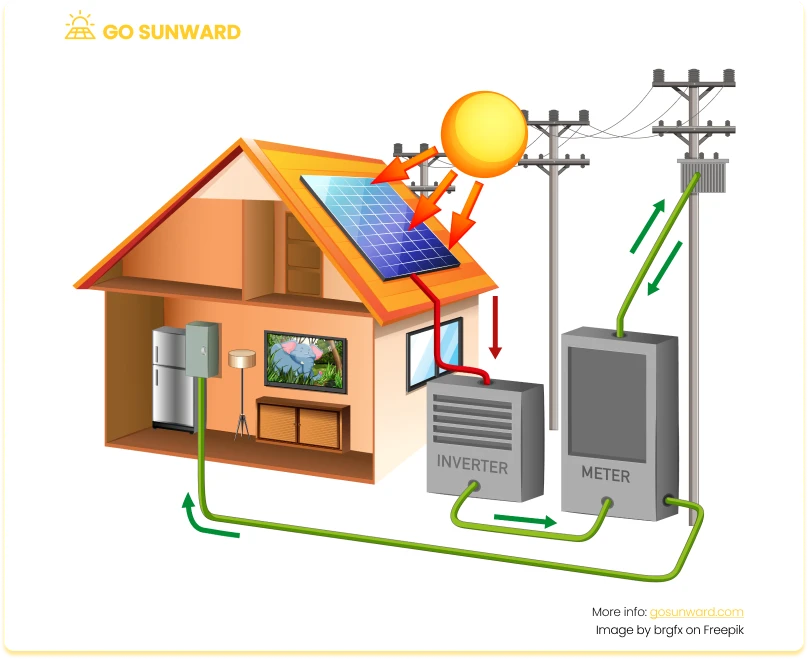
Residential Solar: Factors To Consider When Using Solar To Fully Power a House
While solar power can indeed meet a substantial portion, or in fact, all of a household’s energy requirements, several factors need to be considered when exploring options for solar power in your home.
- Energy Consumption: Begin by assessing your household’s energy consumption. Analyze your past electricity bills to determine your average daily and monthly energy usage. Understanding your energy needs is the foundation for sizing a solar panel system accurately.
- Sunlight Availability & Location: The amount of sunlight your location receives is a pivotal factor. Areas with more sunshine, such as regions closer to the equator, are better suited for solar power. However, even in less sunny regions, solar can still be a viable option, albeit with potentially larger solar panel arrays.
- Panel Efficiency: The efficiency of solar panels matters. More efficient panels can generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. Consider the type and quality of panels you intend to install.
- Roof Space: Assess the available roof space for solar panel installation. The size of your roof will impact the number of panels you can install and their orientation for optimal sunlight exposure.
- Budget and Financial Incentives: Evaluate your budget for solar installation. Explore available financial incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs, which can significantly offset initial costs.
These factors will influence the feasibility of installing solar at your home. They will also help you decide whether or not you can use solar to fully power your home. For more help on working out your own panel requirements, click here.
The Balance Between Consumption & Production
Understanding and achieving a delicate balance between energy generation and consumption is paramount before determining if solar power can fully power a house. This equilibrium hinges on matching the intermittent nature of solar energy production with the continuous energy demands of a household. By comprehending their energy consumption patterns, homeowners can size their solar panel systems and energy storage solutions appropriately.
Oversized systems may lead to excess energy generation, which, without efficient storage or utilization, can go to waste. Conversely, undersized systems may leave households reliant on the grid during periods of low solar output. Striking this balance not only ensures efficient use of solar resources but also influences the economic viability and sustainability of a solar-powered household, making it a fundamental consideration in the transition to solar energy.
The Crucial Role of Energy Storage
Energy storage, like a battery, is crucial for fully powering a house with solar because it addresses the fundamental challenge of matching the intermittent nature of solar power generation with the continuous energy demands of a household. Solar panels generate electricity primarily during daylight hours when the sun is shining. However, homes require power around the clock.
Energy storage, usually in the form of batteries, serves as a buffer, allowing excess daytime solar energy to be stored for use during evenings, nights, and cloudy days. This ensures a consistent and reliable power supply. It also reduces reliance on the grid, maximizes self-consumption of solar energy, and contributes to cost savings and environmental sustainability. Without energy storage, fully powering a house with solar alone becomes impractical and less dependable. In fact, according to SEIA (Solar Energy Industries Association), by 2027, nearly 30% of all new behind-the-meter solar systems will be paired with storage, compared to under 10% in 2022.
Costs To Consider But Savings To Be Made
There are numerous benefits associated with solar energy. However, it’s essential to acknowledge one of the primary challenges: the upfront capital costs. This consideration becomes particularly significant when aiming to install a system that can fulfill all your homes energy needs.
One of the primary concerns regarding solar energy is the initial investment required for installation. While solar panel prices have significantly decreased in recent years, the upfront cost can still be substantial for homeowners. However, it’s important to consider solar energy as a long-term investment, which can lead to significant savings on electricity bills over time.
Overall, our research shows that the cost of a solar panel system can vary from a few thousand dollars for a small residential system to tens of thousands of dollars for a larger, high-efficiency system with energy storage. On average, in the United States, a typical residential solar panel installation might cost between $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives and rebates. However, this cost can be significantly lower with incentives and can vary based on regional factors and individual circumstances.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Emerging technologies and trends in the global solar energy sector are helping improve the viability of solar power. This in turn and boosts the potential for solar to be able to fully power your house. This includes improved panel efficiency, smart grid integration, and advanced energy management systems.
One of the key areas of interest is the continuous enhancement of solar panel efficiency. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells and multi-junction photovoltaics are poised to revolutionize the industry, making solar panels more efficient at capturing and converting sunlight into electricity. These breakthroughs promise to significantly increase energy yields from solar installations.
Moreover, the evolving landscape of energy management systems will also boost the residential solar market. These systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, utilizing data analytics and AI algorithms to optimize energy consumption patterns. They automatically adjust power usage to align with solar generation, thus maximizing self-consumption and energy efficiency.Finally, integrating solar power into smart grids will improve its feasibility. Smart grids offer the potential for seamless coordination between energy production, consumption, and storage. By leveraging advanced grid management technologies, we can ensure optimal utilization of solar resources and enhance overall grid stability.
The Future Of Solar
As technological advancements continue, including improvements in solar panel efficiency and the development of advanced energy storage solutions, along with the widespread integration of smart grids, we anticipate a significant reduction in the barriers and costs hindering the adoption of residential solar energy. This progression enhances its potential to meet a household’s full energy needs more effectively.
Government policy and incentives will also be crucial in the market’s future trajectory. Measures such as enhanced net metering and renewable energy mandates play pivotal roles in fostering greater adoption of solar technologies.
Moreover, collaborations between the private sector and research institutions will drive continuous breakthroughs in solar energy technology. This synergy fosters innovation and cost reduction. This makes solar power an even more accessible and cost-effective energy solution for the future.
Conclusion
While solar can absolutely fully power a house, the question is not entirely straightforward. It hinges on many variables, including energy consumption patterns, geographic location, panel efficiency, and energy storage capacity. However, as technological advancements continue and government incentives support solar adoption, the barriers to entry are diminishing. Solar power is becoming an increasingly viable and sustainable option for households.
We recommend that readers to assess their unique circumstances, energy needs, and environmental aspirations. Solar energy represents a clean and renewable power source with the potential for significant long-term cost savings. By considering solar as a primary electricity source, individuals can play a part in fostering a greener future while also potentially reducing their energy bills. It’s a decision that aligns both with environmental stewardship and economic prudence. This makes solar power an increasingly compelling choice for homes in today’s world.




