Solar Panels 101: Types, Costs, Savings & Tax Credits ☀️
In today’s world, solar panels have become a practical and accessible solution for homeowners and businesses, thanks to the growing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility. They are now a symbol of progress and change as the world increasingly adopts renewable energy sources.
In this article, “Solar Panels 101: Types, Costs, Savings & Tax Credits,” we delve into the world of solar energy, shedding light on the diverse array of solar systems and panels available, the costs involved, the substantial savings they offer, and the financial support provided by government incentives and tax credits. Whether you’re a seasoned environmental enthusiast or someone simply seeking to reduce their energy bills, this article will serve as your roadmap to understanding the essentials of solar panels, empowering you to make informed decisions about embracing solar energy.
Understanding Solar Panels
The PV Effect
Solar panels operate on the fundamental principle of converting sunlight into electricity. This process is made possible through photovoltaic cells, which are the core components of a solar panel. Photovoltaic cells, often referred to as solar cells, are semiconductor devices that absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity.
A standard solar panel typically consists of several layers. The top layer is composed of a protective cover made of tempered glass, which shields the underlying layers from external elements. Beneath the glass, there is an anti-reflective coating that helps maximize light absorption. Below the coating are the photovoltaic cells, interconnected by conducting wires. These cells are responsible for capturing the sunlight and converting it into electricity. The frame of the solar panel provides structural support and protection to the internal components.
Solar panels work by allowing photons from sunlight to knock electrons loose from the atoms within the photovoltaic cells. This creates an electric current, which is then captured and converted into usable electricity.
Solar PV technology finds common application in various settings, including rooftop installations, solar farms and arrays, as well as small-scale setups.
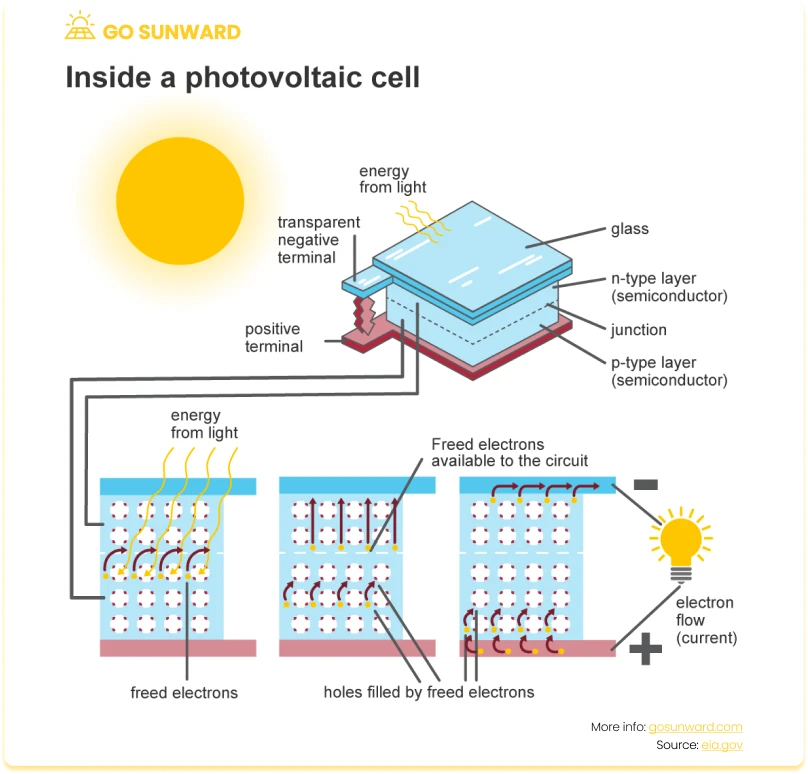
The efficiency of a solar panel is a critical factor in determining its overall performance. It is essentially a measurement of how efficiently the panel can convert sunlight into usable electricity, and it is expressed as a percentage. Various factors influence the efficiency of a solar panel, and modern panels exhibit a wide range of efficiency levels, typically falling between 15% and 22%, although some advanced technologies can achieve even higher rates.
One of the primary factors affecting efficiency is the type of solar cell technology used in the panel. For instance, monocrystalline solar cells tend to have higher efficiency levels than polycrystalline or thin-film cells. Additionally, the design and manufacturing quality of the panel plays a significant role in determining its efficiency.
Environmental conditions can also impact efficiency. High temperatures can reduce a panel’s voltage and, consequently, its efficiency. Shading, whether from nearby structures, trees, or debris, can create localized efficiency losses. Proper maintenance, including regular cleaning to remove dirt and dust, is essential to maintaining peak efficiency.
The geographic location of the solar panel installation is another crucial factor. Areas with abundant sunlight will generally yield higher energy production and, therefore, greater efficiency. Proper installation, including the orientation and tilt angle of the panels, can optimize their exposure to the sun and enhance efficiency over the long term.
Overall, understanding these efficiency variables is vital when selecting and maintaining solar panels to ensure they meet your energy production needs and maximize your return on investment. This is a detailed guide that covers everything you need to know including how solar panels work, what they cost, and how much you can save with solar.
Types of Solar Panels
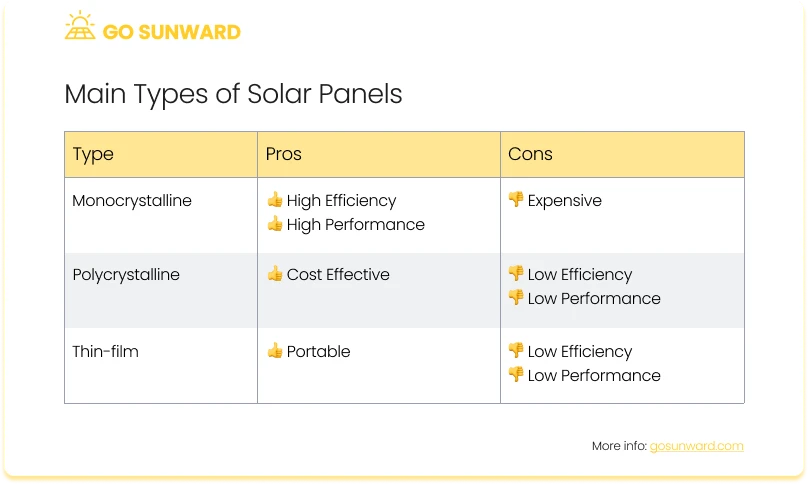
At present, photovoltaics is one of the most recognizable methods for capturing solar energy and mainly utilizes three technology panel types: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline and Thin-Film Solar Panels. Navigate here to see how these solar panels are made.
These options each bring with them distinct advantages and disadvantages. The choice of the most suitable solar panel type for your installation and which brands you choose depends on your preferences and the particular characteristics of your property.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from single-crystal silicon, producing an exceptionally efficient and uniform structure. The production process involves slicing cylindrical silicon ingots into thin wafers, which are the foundation for individual solar PV cells. Thanks to the high purity of monocrystalline silicon, these panels outperform other types in terms of converting sunlight into electricity.
Their distinctive dark black hue and rounded edges set monocrystalline solar panels apart. Their superior efficiency means they occupy less space to achieve the same power output, making them ideal for installations with limited rooftop or ground area. However, it’s worth noting that their higher manufacturing costs can result in slightly elevated prices.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels feature multiple crystal structures of silicon, giving them a distinctive bluish tint. The production process entails melting raw silicon and casting it into moulds to form square-shaped wafers. Polycrystalline panels are known for their cost-effectiveness, as they are easier and more economical to manufacture compared to monocrystalline panels.
Although slightly less efficient than monocrystalline counterparts, ongoing technological advancements have narrowed the efficiency gap between the two types. Polycrystalline panels now offer good performance while remaining a popular choice for both residential and commercial installations due to their cost-effectiveness and durability.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made from thin layers of semiconductor materials, such as amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). This technology yields solar panels that are lightweight, flexible, and adaptable, capable of integration into various surfaces, including those with curves or irregular shapes.
While thin-film panels exhibit lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, they offer distinct advantages in specific scenarios. They excel in low-light conditions and demonstrate resilience to high temperatures. Their ease of integration makes them well-suited for applications like building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), solar shingles, and other innovative solar designs.

Other Technologies To Consider
While we’ve explored thin-film, polycrystalline, and monocrystalline solar panels, the solar panel landscape offers a diverse range of options, each with its unique features and applications.
Bifacial Solar Panels: Bifacial panels are notable for their dual-sided light capture capabilities, efficiently harnessing sunlight from both the front and rear. By reflecting light from surrounding surfaces, they excel in scenarios where sunlight bounces off reflective surfaces, such as white roofs or snowy environments.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): BIPV represents a synergy between solar panels and building materials like roofing, windows, or facades. This integration seamlessly merges solar power generation with architectural design. Beyond clean energy production, BIPV enhances both the aesthetic and functional aspects of buildings, showcasing the limitless potential of solar technology in the construction industry.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that companies like Tesla have been pioneering innovative solar solutions, such as solar roof tiles, which combine solar technology with roofing materials, further highlighting the integration of clean energy into our everyday lives. For more information on Tesla’s solar offering and the company’s innovative approach, click here.

Costs, Costs, Costs
When contemplating the adoption of solar panels, it’s vital to grasp the various costs linked to procuring and installing a solar panel system.
The primary consideration revolves around the initial expenditure, encompassing the purchase of solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and other essential components, as well as the installation cost. This upfront outlay can fluctuate significantly, contingent on the system’s size and intricacy, underscoring the importance of evaluating your specific requirements and financial resources.
Installation expenses typically make up a substantial portion of the initial investment. These costs encompass labor, materials, and equipment needed to establish the solar panels on your property. The details of the installation, whether it involves roof-mounted or ground-mounted systems or necessitates additional electrical work, can have an impact on the overall installation cost.
Numerous factors contribute to the cost of a solar panel system. The system’s size, quantified in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW), holds a central role in this regard. Larger systems, equipped with more panels, generally entail higher initial costs. The geographical location serves as another pivotal factor, influencing expenses through the lens of local regulations, permitting requirements, and installation conditions. Furthermore, the selection of a solar panel brand and the quality of components can exert an influence on the overall cost.
Average Prices
Over the past decade, we’ve witnessed a remarkable decline in the cost of solar panels, ushering in an era of increased accessibility to solar energy for a broader spectrum of consumers. Over the past decade, residential solar panel costs have dropped by 70%, with a 3% decrease over the last four years.
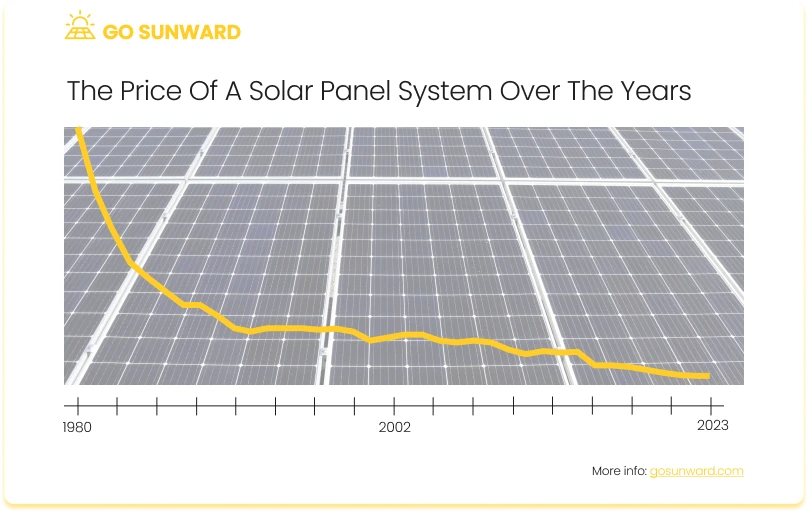
Average prices are typically quantified in terms of dollars per watt or kilowatt-hour (kWh). Our research suggests that, in the United States, the average cost of solar panels currently falls between $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. This pricing encompasses not only the expenses associated with the solar panels themselves but also the costs related to their installation.
In terms of an entire residential solar panel system, it’s worth noting that a typical system may range from approximately $15,000 to $25,000, prior to any application of incentives, rebates and net metering schemes.
Maintenance Considerations
Maintaining your solar panel system is a crucial aspect of ensuring its long-term performance and maximizing your return on investment. While solar panels are known for their durability and minimal maintenance requirements, there are still some key considerations to keep in mind.
One of the primary maintenance tasks is regular cleaning. Solar panels are exposed to the elements, and over time, dust, dirt, pollen, leaves, and other debris can accumulate on their surfaces. This buildup can reduce the amount of sunlight the panels can capture, leading to a drop in efficiency. Cleaning your panels a few times a year, or as needed, is essential to keep them operating at their full potential. Typically, a gentle rinse with a hose or a soft brush with soapy water is sufficient for cleaning.

Additionally, it’s essential to inspect your solar panels periodically for any physical damage, such as cracks or scratches. While solar panels are designed to withstand various weather conditions, extreme events like hailstorms can potentially cause damage. If you notice any issues, it’s best to contact a professional for repairs to prevent further deterioration of the system’s performance.
The inverter, a critical component that converts DC electricity generated by the panels into usable AC electricity, may have a shorter lifespan compared to the panels themselves. Depending on the manufacturer’s warranty and the inverter’s age, you may need to plan for its replacement within 10 to 15 years.
Monitoring your solar panel system’s performance is also essential. Many modern systems come with monitoring tools that allow you to track energy production and identify any deviations from expected output. Monitoring can help you quickly identify and address any issues that may arise, ensuring your system operates efficiently over time.
Finally, consider investing in a maintenance plan or warranty coverage offered by your solar panel manufacturer or installer. These plans can provide peace of mind by covering maintenance and repairs for a specified period, reducing the financial burden of unexpected issues.
Long-term Financial Savings
Solar panels offer the potential for significant long-term savings on electricity bills by harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity for your home or business. Here’s how:
Reduced Energy Costs: Solar panels generate clean and renewable electricity from sunlight, which can offset or even eliminate your reliance on grid-supplied electricity. This results in lower monthly electricity bills, especially if your solar system produces more energy than you consume. Excess energy can be credited back to your utility through net metering, further reducing costs.
Return on Investment (ROI): Solar panel installations typically come with an initial upfront cost. However, over time, the solar savings on electricity bills can offset this investment. The ROI for solar panels can be substantial, and many homeowners and businesses see a return on their investment within a few years, depending on factors such as system size, location, and local incentives.
Resale Value Increase: Homes equipped with solar panels often have a higher resale value. Buyers are attracted to the prospect of lower electricity bills and the environmental benefits of solar energy. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels can sell faster and at a premium compared to homes without solar installations. Click here to find out more!
Other Benefits To Consider
Environmental Benefits
Solar panels play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Solar panels generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4). They rely on the abundant and clean energy from the sun, resulting in a significant reduction in the carbon footprint associated with electricity production. This is in stark contrast to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation, which releases substantial amounts of CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
The environmental benefits of solar energy are substantial. On average, every megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity generated by solar panels can reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 0.5 to 1 metric ton. The cumulative impact of widespread solar adoption is remarkable, with solar energy helping to decrease air pollution, combat global warming, and preserve ecosystems.
Solar energy is a prime example of renewable energy, which is crucial in the global effort to combat climate change. Unlike finite fossil fuel resources, renewable energy sources like solar power are sustainable and do not deplete natural reserves. The transition to renewable energy is paramount for reducing the world’s dependence on fossil fuels and achieving a sustainable and environmentally responsible energy future.
Energy Independence
Solar panels contribute significantly to energy independence and bolster national security.
Solar panels enable decentralized energy production, allowing homes, businesses, and communities to generate their electricity locally. This decentralization reduces vulnerability to centralized energy systems, making it more resilient in the face of natural disasters, cyberattacks, or other disruptions. It enhances energy security by diversifying energy sources and reducing the risk of widespread power outages.
By harnessing solar energy, individuals and nations can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. This reduces exposure to volatile energy markets and price fluctuations, enhancing economic stability and energy security.
Solar power decreases the need for importing fossil fuels, which can enhance a nation’s energy independence and reduce geopolitical tensions associated with energy supply. Relying on domestically produced solar energy strengthens national sovereignty and decreases reliance on foreign energy suppliers.
Incentives & Tax Credits
Government incentives are pivotal to the global growth of solar energy because they provide crucial support and motivation for individuals, businesses, and communities to embrace clean and sustainable solar solutions. These incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and performance-based programs, reduce the financial barriers associated with solar adoption, making it more accessible and affordable.
In the US, federal tax credits and state/local incentives play a pivotal role in rendering solar panel installations financially feasible and appealing. Leveraging these programs can significantly reduce the initial cost of transitioning to solar energy.
Federal Tax Credits
Ihe Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) stands as a critical financial incentive for those contemplating solar panel installations in the United States, offering a substantial reduction in the overall cost of adopting solar energy.
- Understanding the ITC: The ITC permits taxpayers to claim a federal tax credit equivalent to a percentage of their solar panel system installation’s total cost. In 2023, the ITC currently allows both homeowners and businesses to claim 30% of their solar system costs as a tax credit. The tax credit will stay at 30% for the next 10 years until 2033, at which point it will drop to 26%.
- Savings and Benefits: The ITC delivers substantial savings, enhancing the financial accessibility of solar panel installations. It not only reduces the initial system cost but also expedites the return on investment (ROI). Moreover, it is applicable to both residential and commercial solar installations, rendering it accessible to a wide spectrum of individuals and businesses, thereby promoting solar adoption.
- Recent Changes: Staying informed about any recent changes or updates to federal tax credits is essential. Government policies and incentives are subject to evolution, which may affect the availability and terms of the ITC. To ensure you have the most accurate and up-to-date information, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional or visit the government energy department website for the latest details on federal tax credits for solar panel installations.
State and Local Incentives
In addition to federal incentives, numerous states and localities offer their incentives, rebates, and programs aimed at further promoting the adoption of solar panel installations.
- State-Specific Incentives: Various states feature their incentives and rebate programs that can substantially curtail the costs associated with solar panel installations. These incentives may encompass additional tax credits, cash rebates, or performance-based incentives that reward the generation of solar energy.
- Enhancing Affordability: State and local incentives complement federal programs by enhancing the affordability of solar panel installations. When combined with federal tax credits, these incentives can considerably reduce the overall expense of your solar system, making it an economically appealing choice.
- Research Local Incentives: To optimize your savings, conducting research into the specific incentives available in your locality is essential. Incentive programs can significantly differ from one region to another, underscoring the importance of investigating local opportunities. Initiating this exploration by contacting your state energy office or local utility providers can provide valuable insights into available incentives and rebates.
Conclusion
This article has highlighted the significant advantages of solar panel installations as a sustainable and economically viable choice for individuals and businesses. We’ve explored key topics, including the efficiency of solar panels, long-term savings, environmental benefits, and the importance of government incentives. Solar panels not only reduce electricity bills but also contribute to a cleaner environment by curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
Embracing solar power not only offers immediate financial benefits but also contributes to a more sustainable future. To take the next step, consider contacting a local solar installer for a consultation. They can provide personalized insights, assess your specific needs, and help you embark on a journey towards energy efficiency, cost savings, and a more sustainable energy future.




