How Does Solar Affect Climate Change?
Solar energy, as a renewable power source, plays a vital role in combating climate change by curbing greenhouse gas emissions, thereby safeguarding humans, wildlife, and ecosystems. Moreover, solar energy contributes to enhanced air quality, reduced water consumption in energy production, and can even play a role in land use conservation. Therefore, solar power is set to play a fundamental role in the world’s transition to a low-carbon and sustainable future. This article will examine how does solar affect climate change and discuss the various environmental benefits that can be derived from deploying solar panels. It will also discuss the strategies that can be employed at the individual, community, corporate, and governmental levels to boost the adoption of solar power worldwide.
So, how does solar affect climate change? Here are the seven key ways:
1) Solar Power Is A Carbon-Free Energy Source
Unlike conventional fossil fuels, solar energy is both clean and renewable. Solar panels generate electricity or heat without emitting any greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, such as CO2. This characteristic makes solar power, along with other renewable energy sources, a potential game-changer in our efforts to combat global climate change.
Furthermore, while lifecycle emissions from solar panels are not zero emissions, they are significantly lower than emissions from fossil fuels and the technology has a generally lower carbon footprint. Lifecycle emissions of solar panels include production, transportation, installation, and disposal. Over a solar panel’s lifespan (25 to 30 years), it offsets CO2 emissions compared to fossil fuel electricity. The “carbon payback period” is relatively short, with emissions-free electricity delivered for decades.
2) Solar Power Will Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Offsetting Fossil Fuels
For several decades, energy markets and the global electricity system have revolved mainly around thermal sources, with oil, gas, and coal taking center stage. These fossil fuels have been pivotal in meeting the world’s energy demand owing to their historical abundance, comparatively low costs, and well-established infrastructure for extraction, transportation, and power generation.
However, by harnessing the power of solar panels to generate electricity or provide heating, individuals, businesses, and policymakers can effectively diminish their dependency on fossil fuels and counterbalance their energy consumption. As solar energy usage increases, the reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity decreases. This deliberate shift leads to a tangible reduction in CO2 emissions, contributing positively to the global fight against climate change.
Many people have asked us: How Do Solar Panels Reduce CO2 Emissions? The answer is simple can be found in that article.
3) Solar Power Will Decrease Air Pollutants
Another solar affect on climate change is by decreasing air pollutants. Solar panels offer significant benefits to air and water quality. In sharp contrast to fossil fuel power plants, solar panels do not release harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, or particulate matter, all of which are notorious for contributing to air pollution and respiratory problems. By eliminating these emissions, solar power directly leads to enhanced air quality, resulting in healthier communities.
This positive impact manifests in various ways, including fewer hospital admissions, reduced healthcare expenses, and an overall enhancement in the quality of life for those living near solar installations. Solar energy’s clean and sustainable nature makes it a transformative force for environmental and public health.
4) Solar Power Helps Mitigate the Urban Heat Island Effect
Solar panels are vital in mitigating the urban heat island effect, a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural regions. This effect is primarily caused by heat-absorbing surfaces like concrete and asphalt, coupled with the lack of vegetation in urban environments.
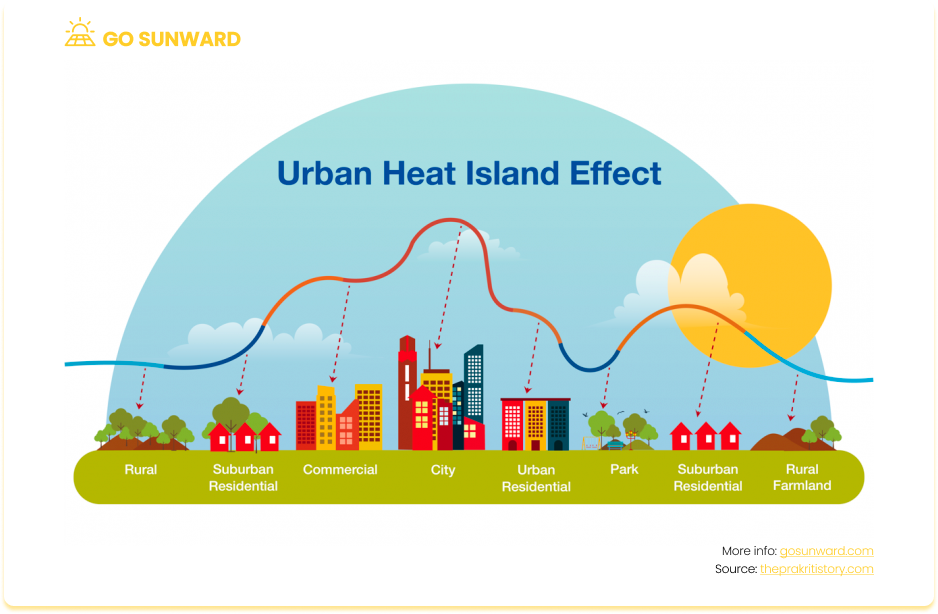
One of the key ways solar panels counteract the urban heat island effect is through surface cooling. When installed on rooftops, parking lots, and structures, solar panels provide shade, reducing direct exposure to sunlight and lowering heat absorption by buildings and pavements. This leads to surface cooling and helps lower overall temperatures in urban areas.
Additionally, solar panels possess heat absorption and reflection properties. While they absorb solar radiation to produce electricity, their reflective surfaces bounce back a portion of incoming sunlight, reducing overall heat absorption by urban surfaces.
Integrating solar panels with green rooftops is another effective strategy. Green rooftops involve planting vegetation, providing an extra insulation layer that reduces heat conducted into buildings, thereby lowering indoor temperatures and enhancing the urban landscape. Furthermore, solar panels influence air circulation by creating gaps between the panels and rooftops, promoting ventilation and heat dissipation, thus reducing surface temperatures.
5) Solar Power Supports Water Conservation
Solar panels not only promote clean air but also boast a remarkable advantage when it comes to water usage compared to conventional energy sources. Unlike traditional power plants, which demand substantial water volumes for cooling purposes, solar panels operate without any water requirement, alleviating stress on local water resources and mitigating water scarcity concerns. This water-saving characteristic of solar energy proves particularly beneficial in regions grappling with water stress or facing drought conditions, challenges that are exacerbated further by climate change. By embracing solar energy, such regions can ease the burden on limited water supplies, providing much-needed relief to local communities and agriculture.
Moreover, solar energy’s water-saving benefits extend beyond electricity generation. In applications like solar water heaters and desalination systems, solar power directly supplies hot water and fresh water, bypassing the need for water-intensive heating methods or desalination processes that traditionally rely on fossil fuels. This multifaceted approach demonstrates the versatility and sustainability of solar energy as a solution for cleaner air and for preserving and efficiently utilizing our invaluable water resources.
6) Solar Power Encourages Positive Land Use Change
Solar panels offer an environmental advantage by actively conserving natural habitats and landscapes. Unlike conventional energy sources like coal mining and natural gas extraction, which often necessitate extensive land clearance and ecosystem disruption, solar panels operate without causing deforestation, habitat loss, or irreversible damage to biodiversity. This remarkable attribute stems from solar panels’ capacity to harness clean energy while minimizing harm to the natural world. Their adaptability allows for installation in various locations, including urban areas and previously disturbed lands, thereby reducing the need for new infrastructure development and safeguarding undisturbed wilderness.
By strategically deploying solar installations on rooftops, parking lots, and brownfields, we can optimize land use efficiency and alleviate the pressure to convert pristine landscapes into industrial zones. This approach ensures the preservation of critical habitats for wildlife, protects native plant species, and sustains the ecological balance essential for a healthy and resilient environment. Furthermore, promoting solar projects on unused or degraded lands presents land restoration and reclamation opportunities. Former mining sites or abandoned industrial areas can be ingeniously repurposed for solar energy generation, transforming once-scarred lands into productive and environmentally responsible assets.
7) Solar Power Promotes Energy Storage and Grid Stability
Solar power can play a pivotal role in enhancing grid stability and promoting energy storage, which is highly beneficial and one of the most impactful ways that solar can affect climate change.
Grid Stability: As mentioned, solar power can reduce the reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity generation, which is subject to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Solar power’s inherent diversity, with installations spread across different geographic regions, makes it less susceptible to large-scale outages caused by events like natural disasters or fuel supply interruptions. By diversifying the energy mix and incorporating solar power, grids become more stable and resilient to fluctuations in demand and supply.
Energy Storage: One of the significant challenges with renewable energy sources like solar is their intermittent nature. Solar energy is generated when the sun is shining, but demand for electricity remains constant throughout the day. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, help overcome this intermittency by storing excess solar energy during sunny periods and releasing it when the sun is unavailable. This enables a consistent and reliable power supply, regardless of variations in solar output. Integrating energy storage with solar power helps balance the grid and optimize energy distribution.

How Can We Increase The Use of Solar Energy And The Solar Affect On Climate Change
As we have uncovered from our research, solar energy plays a crucial role in combatting climate change due to its numerous environmental benefits, as listed above. Furthermore, the widespread adoption of solar energy fosters technological advancements, job creation, and economic growth in the renewable energy sector.
But what can be done to increase the use of solar energy to mitigate climate change? To accelerate the adoption of solar energy, several strategies can be employed at the individual, community, corporate, and governmental levels:
- Raise Awareness & Education: Raising public awareness about the benefits of solar energy is essential. Educational campaigns and outreach programs can inform people about the environmental advantages, long-term cost savings, and the potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Financial Incentives, Subsidies & Net Metering: Governments can incentivize the use of solar energy by offering financial benefits, such as tax credits, rebates, grants and net metering. These incentives make solar installations more affordable and encourage greater adoption, especially for those facing financial barriers upfront.
- Streamlining Permitting and Regulations: Simplifying and expediting the permitting process for solar installations can reduce administrative hurdles and costs, making it more attractive for individuals and businesses to invest in solar power.
- Community Solar Projects: Community solar initiatives enable individuals who cannot install solar panels on their own properties to participate in solar energy projects. Shared solar installations allow multiple customers to receive the benefits of clean energy generation and cost savings.
- Corporate and Institutional Commitments: Encouraging businesses, schools, and institutions to commit to renewable energy goals can have a significant impact on increasing solar energy use. Companies can install solar panels on their premises or purchase solar energy through power purchase agreements.
- Integration of Solar in Urban Planning: Urban planners and policymakers can incorporate solar energy considerations into building codes and zoning regulations. This can include requirements for solar-ready buildings and provisions for solar installations in public infrastructure projects.
- Research and Development: Continued investment in solar research and development is crucial to improve solar technologies’ efficiency, affordability, and scalability. Advancements in energy storage solutions, flexible solar panels, and novel materials can revolutionize solar energy adoption.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among nations can facilitate the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and resources to accelerate the global adoption of solar energy. International partnerships can foster innovation and enhance the accessibility of solar technologies in developing countries.
- Transitioning Energy Policies: Governments can gradually phase out subsidies and incentives for fossil fuels and redirect support towards renewable energy sources like solar power. This transition can level the playing field and make renewable energy more competitive in the energy market.
Conclusion
Increasing the use of solar energy is a critical step in transitioning to an environmentally sustainable and low-carbon energy future. As outlined in this article: How does solar affect climate change, we can see the impact is profound. Solar is a carbon-free energy source, it can offset emissions from fossil fuels, decrease air pollution, mitigate the urban heat island effect, boost water conservation, lead to positive land use changes and aid grid stability
Solar power presents an invaluable solution as the global community grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Luckily, there are several ways in which individuals, communities, corporations, and governments can help promote and adopt solar energy.




