Solar Tax Incentives Explained: Pay Less Tax With Solar
In today’s world, where environmental consciousness is on the rise, the concept of solar tax incentives has gained significant attention. As the world faces the pressing challenges of climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, solar energy has emerged as a beacon of hope—a clean, sustainable source of power that can revolutionize the way we generate electricity. It’s a solution that not only benefits the environment but also your wallet. Don’t forget to also consider the option of solar getting cheaper, if you’re trying to pay less money 💡
This article will delve into the world of solar tax incentives, shedding light on how they work, what they entail, and how they can help you pay less in taxes while contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
We will focus on the US residential solar sector as our prime example, but it is important to note that many countries around the world use solar incentives to drive growth in domestic renewable energy capacity.
The Rise Of Solar Energy
In recent years, the world has witnessed a monumental shift towards renewable energy sources, with solar power emerging as a frontrunner in the race towards a low-carbon energy system.
The deployment of solar, both photovoltaic (PV) or concentrated solar power (CSP), residential or utility-scale, has been driven by lowering system costs, the scalability of the technology to meet various energy needs and favourable government policy. Furthermore, the increasing awareness of climate change and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions has spurred a global movement towards renewable energy sources in general. Governments, businesses, and individuals alike have recognized the urgency of transitioning away from fossil fuels, which are not only finite but also responsible for a significant portion of the world’s carbon emissions. Among the various renewable energy options available, solar power has gained prominence for its versatility, scalability, and eco-friendliness.
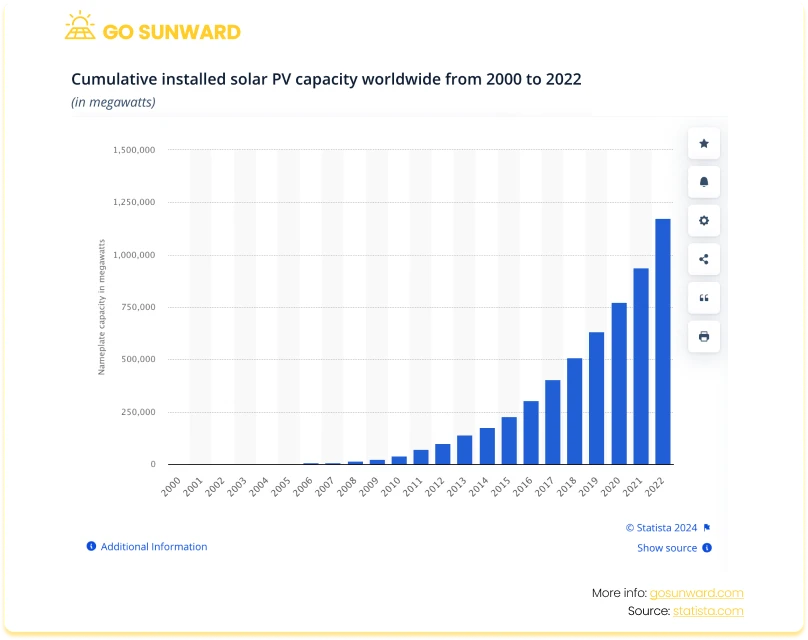
Solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity has seen substantial growth worldwide over the last decade. In 2013, installed global solar capacity was around 139 gigawatts (GW). By 2022, it had surged to over 1177GW. This trend will likely continue as innovations in solar technology will continue to drive the efficiency and performance of solar panels, propelling its expansion and falling costs over the coming decade. Our research shows that the global solar energy market will grow at a CAGR of 7.2% between 2023 to 2030, with the market size totalling nearly USD350 billion by 2030.
Here in the US, the adoption of solar PV has surged in recent years, transforming it into a key component of the country’s energy landscape. According to a report by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie, over the coming five years, the US solar industry is predicted to almost triple in size. From 2023 to 2028, it will grow from 142GW to 378GW, making solar the primary technology driving the clean energy transition. A large part of this growth can be attributed to the favorable policy environment in the country, including federal tax credits, rebates and investment incentives.
Solar Tax Incentives: What Role Do They Play?
Solar tax incentives often form the backbone of renewable energy adoption, offering financial incentives that make going solar an attractive prospect. This is certainly true in the context of the US.
Now we will take a closer look into the world of solar tax incentives to understand what they are, why they exist, and how they can vary depending on your location.
Defining Solar Tax Incentives
Solar tax incentives, also known as solar incentives or solar tax credits, are government-initiated financial incentives designed to bolster the adoption of solar energy systems. Their primary objective is to encourage homeowners, businesses, and organizations to invest in solar power infrastructure. Governments introduce these incentives for several reasons:
- Promoting Renewable Energy: By shifting toward renewable energy sources like solar, governments aim to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating climate change, and minimizing environmental damage.
- Boosting Economic Growth: Solar incentives stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in the renewable energy sector, fostering innovation, and attracting investments in clean energy technologies.
- Enhancing Energy Security: Solar energy reduces dependence on foreign energy sources, enhancing energy security and reducing vulnerability to supply disruptions.
Environmental Benefits: Solar power substantially reduces carbon emissions and pollutants compared to fossil fuel-based energy generation, leading to improved air quality and public health.
Regional Variations In Solar Tax Incentives
Solar tax incentives are not one-size-fits-all; they exhibit significant regional variations depending on the policies and priorities of local, state, and national governments:
- Federal vs. State vs. Local Incentives: Solar incentives are typically offered at multiple government levels. Federal incentives provide overarching support, while state and local incentives are tailored to regional needs and conditions.
- Incentive Types and Amounts: Different regions may offer various types and amounts of incentives, such as investment tax credits (ITCs), rebates, grants, or performance-based incentives.
- Eligibility and Criteria: Eligibility criteria, system size limits, and ownership status requirements can differ from one jurisdiction to another. Some incentives may target residential installations, while others support commercial or industrial projects.
- Expiration Dates: Many solar tax incentives have expiration dates or step-down schedules, reducing the incentives over time. These deadlines can vary significantly between jurisdictions.
Understanding the diverse landscape of solar tax incentives is crucial when considering a solar installation. These incentives can significantly reduce upfront costs, making solar energy an economically attractive and environmentally responsible choice.
Federal Solar Tax Credits
The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) stands as a linchpin of support for solar energy adoption in the United States, offering substantial financial benefits to those who choose to harness the power of the sun.
The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a federal-level solar incentive program aimed at reducing the financial barriers associated with solar energy adoption. It operates as a dollar-for-dollar reduction in federal income tax liability, making it an appealing prospect for individuals and businesses alike.
The ITC is characterized by its percentage-based benefit. Eligible solar system owners can claim a tax credit equal to a percentage of their solar system’s cost. The exact percentage can vary depending on the implementation timeline, with a significant focus on driving solar adoption.
The Residential Clean Energy Credit
Since its inception, the ITC has undergone a series of revisions, extensions, and adjustments in its rates. Most recently, in 2022, President Joe Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act, extending the availability of solar tax credits until 2034. Officially named the ‘Residential Clean Energy Credit’, this program encompasses various expenses, including equipment and installation costs, while excluding structural alterations solely intended for panel support.
The actual amount accessible as solar tax credits may fluctuate, contingent upon your project expenditures and completion date. Nevertheless, these solar incentives remain accessible to homeowners who put a qualifying system into service anytime between 2017 and 2034, thanks to the recent extension.
For the tax year 2023 (to be filed in 2024), the solar panel tax credit stands at a consistent rate of 30% of eligible expenses. This 30% credit will persist from the tax year 2023 all the way through 2032.

Let’s use an example to illustrate how the Residential Clean Energy Credit can lead to tax savings:
The federal tax credit for solar offers a substantial financial incentive, equivalent to 30% of your installed solar project’s total cost. For instance, if your solar project costs $20,000, you can claim a tax credit of $6,000 ($20,000 x 30%). It’s important to note that this tax credit reduces your federal income tax liability rather than providing a direct payment. This reduction can either increase your tax refund or lower the taxes you owe.
For example, if your solar system becomes operational in 2023 and you file your 2023 federal income tax return in 2024, you can claim the $6,000 tax credit. If your tax liability is higher than $6,000, you can use the full credit in a single tax year. Conversely, if your tax liability is less than $6,000, you can carry forward the unused credit to offset taxes in future years.
For more information on the federal tax credit and a guide to eligibility and how to get involved, click here.
State & Local Solar Incentives
As we’ve explored the realm of federal solar incentives, it’s essential to recognize that the support for solar energy adoption extends beyond the national level. State and local governments are also pivotal in promoting and incentivizing solar installations, often tailoring their programs to meet regional needs.
In this section, we’ll delve into the significance of state and local incentives, showcase examples of state-specific solar incentives and rebates, and underscore the importance of researching these programs to maximize your solar savings.
The Importance of State and Local Incentives
While federal incentives provide a robust foundation for solar adoption, state and local incentives serve as valuable complements. They take into account specific regional circumstances, energy goals, and environmental concerns, resulting in programs that can significantly enhance the financial appeal of going solar.
State-specific solar incentives and rebates can vary widely, so it’s crucial to be aware of what’s available in your area. Here are a few examples of the types of incentives you may encounter:
- State Solar Tax Credits: Some states offer their own tax credits in addition to the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC). These credits can further reduce your tax liability, making solar installations even more cost-effective.
- Cash Rebates: Many states provide cash rebates to homeowners and businesses based on the size of their solar installations. These rebates directly lower the upfront cost of your solar system.
- Performance-Based Incentives: Certain states offer incentives based on the actual energy production of your solar panels. You can receive payments for the clean energy your system generates over time.
- Property Tax Exemptions: Some states grant property tax exemptions for the added value of solar panels, ensuring that your property taxes do not increase due to your solar investment.
Sales Tax Exemptions: Several states exempt solar equipment purchases from sales tax, reducing the overall cost of your solar installation.To harness the full potential of state and local incentives, it’s essential for readers to conduct thorough research specific to their location. This can involve visiting official state and local government websites, contacting local energy agencies, or consulting with solar installation professionals well-versed in regional programs.
Stacking Your Solar Incentives
To illustrate the substantial potential for cost savings, let’s take the example of a solar project with a total gross system cost of $20,000. Initially, you would be eligible for a federal tax credit of $6,000, equivalent to 30% of the project’s cost.
Now, let’s consider that you’re in California, a state known for its robust support of solar energy. In this scenario, California offers a generous state rebate of $2,000 for your solar installation. By applying this rebate, your total project expenses are effectively reduced to $18,000.
But the story doesn’t end there. Many local municipalities in California have their own solar incentive programs in place. Let’s say your local municipality provides an additional $1,000 in savings to support your solar project.
If your utility company supports net metering, you have the opportunity to further maximize your long-term savings. Net metering allows you to sell any excess solar-generated power back to the grid, effectively earning credits on your utility bill. These cumulative incentives, including federal, state, and local incentives, along with the potential for ongoing savings through net metering, can significantly enhance the affordability and financing options of your solar investment.
Taking the Next Steps Toward Savings: Navigating Federal, State, and Local Solar Incentives
Whether you’re aiming to claim federal, state, or local incentives for your solar installation, understanding the process is crucial to make the most of these savings opportunities.
Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to assist you in navigating the intricate landscape of solar incentives at different levels:
Step 1: Eligibility Check (Federal, State, and Local) Before initiating the claiming process, verify that you meet all eligibility criteria for the relevant solar tax incentives. This includes having a qualifying solar installation and meeting the required conditions for federal, state, or local programs.
Step 2: IRS Form 5695 (Federal) For federal incentives like the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), the cornerstone of claiming solar tax credits is IRS Form 5695, officially titled “Residential Energy Credits.” You must complete this form to calculate the precise credit amount for which you qualify. The form includes sections for various residential energy credits, including the federal solar tax credit.
Step 3: State and Local Forms (State and Local) In addition to federal forms, some states and localities may require their own specific forms to claim solar incentives. Be sure to identify and complete any state or local forms that apply to your location and incentive programs.
Step 4: Gather Documentation (Federal, State, and Local) Compile all necessary documentation to substantiate your claim, whether it’s for federal, state, or local incentives. This may include invoices, receipts, and proof of payment related to your solar system installation. Proper documentation is crucial to validate your expenses and ensure a successful claim.
Step 5: Complete the Forms (Federal, State, and Local) Thoroughly fill out the required forms, ensuring accuracy in calculations and entries. Adhere to the provided instructions and include specific details regarding your solar project. This step applies to federal, state, and local incentive programs.
Step 6: File Your Tax Returns (Federal, State, and Local) When filing your federal income tax return (e.g., Form 1040), state tax return, or local tax return, attach the completed forms relevant to your incentives. Ensure that you meet the annual tax filing deadline, which may vary by jurisdiction and program.
Step 7: Reduce Tax Liability (Federal, State, and Local) The solar tax credits, whether federal, state, or local, directly reduce your tax liability. If the credit amount exceeds your tax liability, it can result in a tax refund or offset future tax obligations. Enjoy the financial benefits of your solar investment across all levels of government incentives.
Top Tip: Consult With Tax Professionals (Federal, State, and Local) While the process of claiming solar tax incentives is generally straightforward, seeking guidance from a tax professional or accountant is advisable to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Tax professionals can offer expert advice to help you maximize your eligible credits while avoiding potential errors.
By following these steps and staying informed about the specific requirements for federal, state, and local incentives, you can make the most of the various savings opportunities available to you and enjoy the rewards of your solar investment.
Whether you’re aiming to claim federal, state, or local incentives for your solar installation, understanding the process is crucial to make the most of these savings opportunities.
Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to assist you in navigating the intricate landscape of solar incentives at different levels:
Step 1: Eligibility Check (Federal, State, and Local) Before initiating the claiming process, verify that you meet all eligibility criteria for the relevant solar tax incentives. This includes having a qualifying solar installation and meeting the required conditions for federal, state, or local programs.
Step 2: IRS Form 5695 (Federal) For federal incentives like the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), the cornerstone of claiming solar tax credits is IRS Form 5695, officially titled “Residential Energy Credits.” You must complete this form to calculate the precise credit amount for which you qualify. The form includes sections for various residential energy credits, including the federal solar tax credit.
Step 3: State and Local Forms (State and Local) In addition to federal forms, some states and localities may require their own specific forms to claim solar incentives. Be sure to identify and complete any state or local forms that apply to your location and incentive programs.
Step 4: Gather Documentation (Federal, State, and Local) Compile all necessary documentation to substantiate your claim, whether it’s for federal, state, or local incentives. This may include invoices, receipts, and proof of payment related to your solar system installation. Proper documentation is crucial to validate your expenses and ensure a successful claim.
Step 5: Complete the Forms (Federal, State, and Local) Thoroughly fill out the required forms, ensuring accuracy in calculations and entries. Adhere to the provided instructions and include specific details regarding your solar project. This step applies to federal, state, and local incentive programs.
Step 6: File Your Tax Returns (Federal, State, and Local) When filing your federal income tax return (e.g., Form 1040), state tax return, or local tax return, attach the completed forms relevant to your incentives. Ensure that you meet the annual tax filing deadline, which may vary by jurisdiction and program.
Step 7: Reduce Tax Liability (Federal, State, and Local) The solar tax credits, whether federal, state, or local, directly reduce your tax liability. If the credit amount exceeds your tax liability, it can result in a tax refund or offset future tax obligations. Enjoy the financial benefits of your solar investment across all levels of government incentives.
Top Tip: Consult With Tax Professionals (Federal, State, and Local) While the process of claiming solar tax incentives is generally straightforward, seeking guidance from a tax professional or accountant is advisable to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Tax professionals can offer expert advice to help you maximize your eligible credits while avoiding potential errors.
By following these steps and staying informed about the specific requirements for federal, state, and local incentives, you can make the most of the various savings opportunities available to you and enjoy the rewards of your solar investment.

Future Outlook For Solar Tax Incentives
As we journey into the future, it’s essential to consider the potential changes and developments in solar tax incentives. Government policies are dynamic, and updates can significantly impact the landscape of solar incentives at federal, state, and local levels.
The world of solar incentives is subject to policy changes, including updates to tax credits, rebates, and other support mechanisms. Federal solar tax credits, for instance, have historically been extended and modified through legislative acts. It’s crucial to keep an eye on potential revisions that may impact the availability and benefit levels of these incentives.
Staying informed about legislative developments is paramount for homeowners and businesses looking to invest in solar energy. Regularly checking for updates from federal, state, and local authorities, as well as industry news sources, can help you make informed decisions about the timing and scope of your solar projects.
Amid potential changes, one fact remains constant: solar energy’s vital role in the fight against climate change. Solar power is a clean and renewable energy source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigates environmental impacts, and contributes to a sustainable energy future. As governments worldwide commit to carbon reduction goals, solar energy will continue to play a central role in achieving these objectives.
Conclusion
This article has illuminated the world of solar tax incentives, showcasing their significance in making solar energy accessible and cost-effective for homeowners and businesses alike. Let’s recap the key takeaways:
- Solar tax incentives, spanning federal, state, and local levels, offer substantial financial benefits to those who choose to embrace solar energy.
- By understanding and leveraging these incentives, you can reduce the upfront costs of solar installations and enjoy long-term savings on your energy bills.
- It’s essential to follow a step-by-step process when claiming these incentives, ensuring that you meet eligibility criteria and gather the necessary documentation.
- Staying informed about legislative developments is crucial, as policy updates can influence the availability and terms of solar incentives.
- Solar energy remains a cornerstone of the global effort to combat climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and transition towards a sustainable energy future.
As you consider adopting solar energy, remember to explore the potential savings and environmental benefits it offers. This choice can help reduce your energy costs and have a positive impact on the environment.




