Will Solar Panels Get Cheaper?
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, where sustainability, climate change and energy savings are central concerns, the pricing of solar panels has become paramount. Many people ask: why is solar so expensive?
This article aims to take a deep dive into the multifaceted world of solar panel pricing, shedding light on the various factors that influence costs and providing insight into the future outlook for pricing. We aim to answer the question: will solar panels get cheaper? and in doing so, empower individuals, businesses, and policymakers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the transitioning solar industry. Another way to make your solar panels ‘cheaper’ is to think about the rebates you can get back on your taxes under the Biden solar panel tax credit scheme.
The Present Landscape Of Solar Panel Pricing
Over the past decade, there has been a significant decrease in the cost of solar panels, making solar energy more accessible to a wider range of consumers. On average, the cost of solar panels is measured in dollars per watt or kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Our research shows that the average cost of solar panels in the United States ranges from $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. This pricing includes both the cost of the solar panels themselves and the installation expenses. Looking in terms of a residential system, a typical residential solar panel installation might cost between $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives and rebates.
These figures have gradually declined due to technological advancements, increased manufacturing efficiency, and a growing competitive market – more on this later! Furthermore, economies of scale and government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, have significantly driven down the cost of solar installations for residential, commercial, and utility-scale projects. What des this mean? Well, solar panels are getting cheaper.
Regional variations in solar panel prices are important to consider. Factors such as sunlight intensity, local market conditions, and government policies can lead to substantial differences in pricing. For instance, regions with abundant sunlight and strong solar incentives, such as the southwestern United States, tend to have lower solar panel prices compared to less sunny or less supportive regions.
Globally, solar panel prices also exhibit variations due to factors like trade tariffs, import/export regulations, and economies of scale in manufacturing. China, as one of the largest solar panel manufacturers in the world, has historically offered competitive pricing due to its manufacturing capabilities, resulting in a global impact on solar panel costs.
A Note On Pricing
In this article, we discuss solar panel pricing in terms of the gross cost, which is the cost before factoring in any solar rebates and federal incentives that could potentially lower the initial expense of going solar or provide gradual financial benefits. This is because solar rebates and incentives may not be universally accessible, and are instead dependant on a range of factors including where you live in the country and your general income status.
When discussing average pricing, we typically refer to residential solar systems, not utility-scale ones. Utility-scale solar installations are much larger in size and capacity compared to residential installations. This difference in scale significantly impacts the overall cost structure. Utility-scale projects benefit from economies of scale, which means that, on a per-unit basis, they can often secure lower costs for equipment, labour, and materials. Understanding this distinction helps in accurately assessing the cost-effectiveness and competitiveness of solar energy in different contexts.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Costs
Many factors influence the cost of solar panels, each playing a crucial role in determining the overall price of solar energy systems.
- Raw Materials: The availability and cost of raw materials used in solar panel production are primary drivers of solar panel prices. Silicon, for instance, is a key component in most solar modules, and fluctuations in silicon prices can significantly impact solar panel costs. The supply and demand dynamics of materials such as glass, aluminum, and conductive materials also contribute to pricing variations.
- Economies of Scale: The scale of production matters. Large-scale manufacturing facilities benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to produce solar panels more efficiently and cost-effectively. As production volumes increase, per-unit manufacturing costs decrease, often leading to lower consumer prices.
- Supply Chain Factors: The global supply chain for solar panels can introduce pricing variations. Factors such as shipping costs, import/export tariffs, and trade regulations can impact the final cost of solar panels in different regions. The resilience and efficiency of the supply chain also influence the overall cost structure.
- Labor Costs: Labor is a significant component of solar panel installation costs. Local labor costs and the complexity of the installation process can vary widely, impacting the overall price of solar energy systems.
- Quality and Performance: High-quality solar panels with better performance characteristics often come at a premium price. Solar panel manufacturers invest in research and development to enhance their products’ efficiency, durability, and reliability. While these advancements can contribute to higher upfront costs, they may result in a greater long-term rate of return (ROI) and energy production.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Government incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs, can significantly reduce the upfront cost of solar panel installations. These incentives can vary by region and greatly affect solar energy adoption’s overall cost-effectiveness.
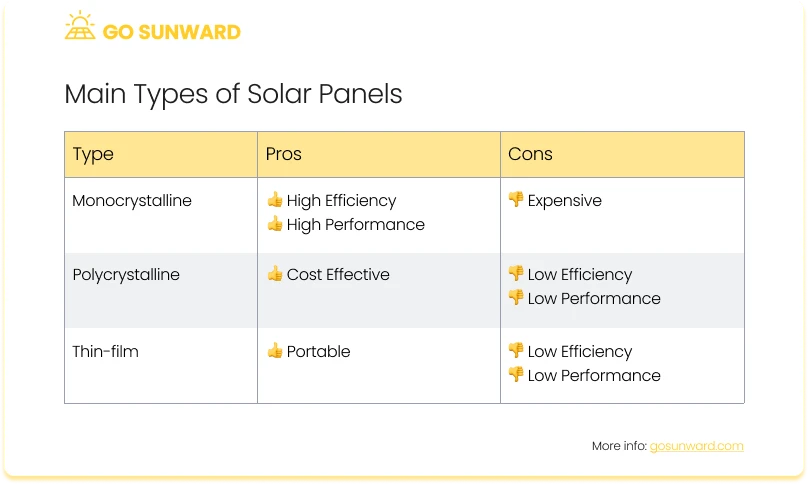
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing technological advancements in solar cell materials and designs continue to influence solar panel costs. Breakthroughs in photovoltaic technologies, such as perovskite solar cells or bifacial solar panels, can potentially improve efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs over time. For more information on the various types of panels on the market, click here.
- Solar Tax Rebates: You can also reduce your costs by claiming incentives from the US government after installing solar. How Does The Federal Tax Credit Work For Solar?
Manufacturing Processes: The efficiency and sophistication of manufacturing processes play a critical role in solar panel pricing. Improvements in manufacturing technologies can reduce production costs, resulting in more affordable solar panels. Innovations in techniques like thin-film and multi-junction solar cell manufacturing have the potential to drive down costs and boost the efficiency of solar panels.
So, Will Solar Panels Get Cheaper?
The future of solar panel pricing is a subject of keen interest, as it carries profound implications for adopting renewable energy and its role in addressing global energy challenges. Predicting future prices involves considering a range of factors, including market dynamics, policies, and technological advancements. While the specifics may vary, several trends that we have unearthed in our research offer insights into what we can expect in the coming years and it appears as though solar panels are getting cheaper.
- Continued Cost Reduction
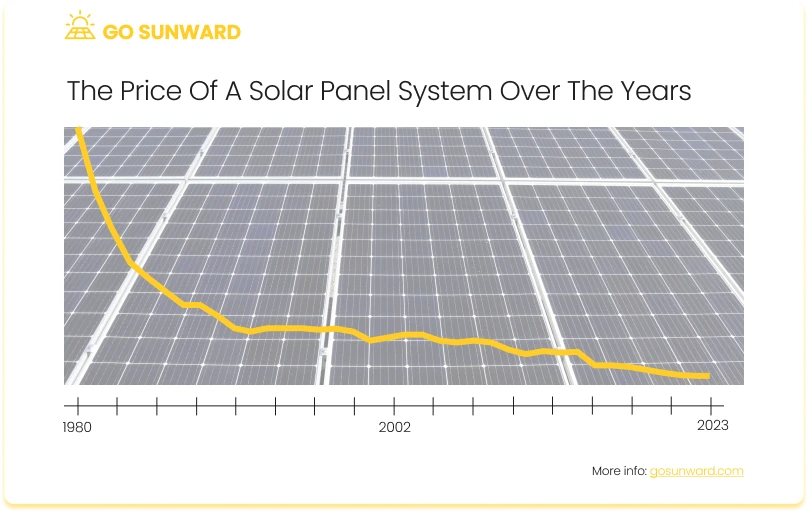
Experts and industry analysts generally predict that solar panel costs will continue to decline in the future. This trend is largely driven by ongoing technological advancements and economies of scale in production. As solar cell efficiency improves and manufacturing processes become more efficient, the cost per watt will decrease. This trajectory aligns with the historical trend of falling solar panel prices over the past decade. According to industry experts, in the last decade, residential solar panel system costs have seen a remarkable 70% reduction. Over the past four years, these costs have continued to decrease, albeit at a slightly slower rate of approximately 3%.
- Technological Advancements
The development of new solar technologies, such as perovskite solar cells and tandem solar cells, holds the potential to increase the efficiency and reduce the manufacturing costs of solar panels. These advancements are likely to play a pivotal role in driving down prices while improving the overall performance of solar energy systems.
- Market Dynamics
Market dynamics, including supply and demand, can influence solar panel prices. As the demand for solar energy continues to grow, especially in regions with strong policy support and environmental considerations, the scale of production is likely to increase. This growth in demand and production could further contribute to lower costs through economies of scale.
- Policy and Incentives
Government policies and incentives will remain influential in shaping the future of solar panel pricing. Extending and enhancing incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and net metering can make solar energy more financially attractive for consumers and businesses. Conversely, policy changes, such as tariffs on imported solar panels, can impact pricing by affecting the supply chain and market competition.
- Global and Regional Variations
Solar panel prices may vary by region due to trade policies, local market conditions, and availability of solar resources. In some regions, where solar energy adoption is still emerging, prices may decrease more slowly. In contrast, mature markets with robust solar industries may experience faster price declines.
- Integration Costs
It’s essential to consider not just the cost of solar panels themselves but also the overall cost of solar energy systems, which includes installation, inverters, and other components. As installation processes become more streamlined and standardized, installation costs may decrease, making solar energy even more affordable.
Conclusion
In a rapidly changing energy landscape, monitoring solar panel pricing is crucial for potential investors and individuals contemplating solar installations. As we have explored the myriad factors influencing solar panel costs and researched the future outlook, it becomes clear that the affordability of solar energy is on an encouraging path and that solar panels are continuing to get cheaper.




