The Solar Panel Tax Credit: Unlocking Solar Benefits
In today’s rapidly evolving world, pursuing low-carbon and more sustainable energy sources has become crucial. Solar energy has emerged as a leading contender in the realm of renewable resources, offering a promising path toward a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future. Through the harnessing of the sun’s energy, solar panels have become a symbol of our commitment to environmental responsibility and energy autonomy.
This article will explore the significant role of solar panel tax credits in this landscape. Our aim is to shed light on the importance of these tax incentives and explain how they can help individuals and businesses adopt solar energy, ultimately contributing to the global shift of decarbonisation.
Solar Panel Tax Credits: The Basics
The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a critical incentive designed to encourage the adoption of solar energy in the United States. Established as part of the Energy Policy Act of 2005, the ITC has a rich history of promoting renewable energy growth. Its primary function is to provide financial relief to individuals and businesses who invest in solar power systems.
The ITC has been instrumental in making solar energy more accessible and affordable for homeowners and companies nationwide. It offers a substantial tax credit, allowing qualified taxpayers to offset a significant portion of their solar system’s installation cost. This financial incentive is a powerful driver in the transition to clean energy, reducing the barriers to entry for those considering solar energy adoption.
At its inception, the ITC offered a 30% tax credit, with a cap of $2,000 for residential projects. However, the cap was lifted in 2008, opening the door to more significant financial benefits for homeowners. Over the last decade, the ITC has experienced multiple revisions, extensions, and rate adjustments. In 2022, the tax credit was reduced to 26% and was set to decrease to 22% in 2023, with eventual phasing out in 2024.
The ‘Residential Clean Energy’ Credit: A Lifeline For Residential Solar PV
The landscape for the solar panel tax credit markedly improved when US Congress passed the Inflation Reduction Act, which was then signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 16, 2022. As part of the Inflation Reduction Act, the government extended the availability of federal tax credits for solar until 2034. Officially known as the ‘Residential Clean Energy Credit’, this program covers various expenses, including equipment and installation costs for a number of different renewable energy types (read on to find out more of the details!).
Crucially for solar power, the incentives remain accessible to consumers who have installed a qualifying system into service anytime between 2017 and 2034, thanks to the extension. For the tax year 2023 (to be filed in 2024), the solar panel tax credit remains at a consistent rate of 30% of eligible expenses. This 30% credit will persist from the tax year 2023 through 2032.

Solar Panel Tax Credits: Fuelling US Solar Growth
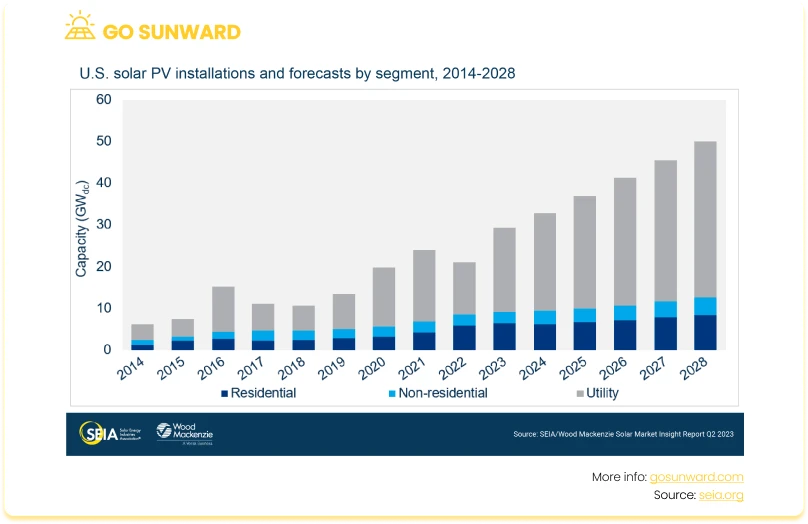
The adoption of solar photovoltaic (PV) power in the US has witnessed a remarkable surge in recent years, transforming it into a key component of the country’s energy landscape. A key part of this has been the favourable tax credits introduced by the government. Therefore, the recent extension to the credit is undeniably positive for the country’s expanding residential solar sector and signals the government’s commitment to decarbonization.
According to a report by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie, over the coming five years, the US solar industry is predicted to almost triple in size. From 2023 to 2028, it will grow from 142GW to 378GW, making solar the primary technology driving the clean energy transition.
Solar Panel Tax Credits: Unlocking Solar Benefits
So, what are the primary benefits of solar panel tax credits, and how do they open the door to solar energy advantages for both households and businesses?
1. Financial Savings
One of the most compelling advantages of solar panel tax credits is their ability to substantially reduce the overall cost of solar installations. Solar energy systems, while environmentally friendly and energy-efficient, often require a significant upfront investment. However, solar panel tax credits, such as the ITC help mitigate this financial barrier.
The way these tax credits work is by allowing eligible individuals and businesses to deduct a portion of their solar installation expenses from their federal or state income taxes (more on how exactly they work later!). This deduction can translate into substantial savings, making solar power more financially accessible.
By significantly lowering the financial burden associated with going solar, these tax incentives encourage more people to invest in solar energy systems. This, in turn, fosters greater adoption of clean energy solutions, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Environmental Benefits
Beyond the economic advantages, solar panel tax credits have a profound positive impact on the environment. Increased solar energy use contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, making it a pivotal tool in the fight against climate change.
Solar panels generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants or carbon dioxide, which are associated with conventional fossil fuel-based power generation. By harnessing the sun’s energy, we reduce our reliance on non-renewable energy sources, thereby decreasing air pollution and minimizing our carbon footprint.
Furthermore, solar energy systems are often installed on existing structures like rooftops, utilizing otherwise unused space and minimizing the need for land-intensive power plants. This land conservation helps protect natural habitats and ecosystems, fostering biodiversity and preserving the environment. For more information on the environmental benefits of solar energy, click here.
3. Job Creation & Economic Growth
Another notable advantage of solar panel tax credits is their role in job creation and the stimulation of local economies. The solar industry has experienced exponential growth in recent years, driven in part by these incentives. As more individuals and businesses opt for solar installations, demand for solar-related products and services increases.
This surge in demand has a ripple effect on employment opportunities. The solar industry requires a skilled workforce for various tasks, from manufacturing solar panels to installation, maintenance, and research and development. Consequently, tax credits for solar installations help create job opportunities in a range of sectors, including manufacturing, construction, engineering, and sales.
Moreover, the economic benefits extend beyond job creation. Solar energy investments often result in increased property values for homeowners, and businesses can benefit from reduced energy bills, freeing up capital for other investments. Additionally, by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels, local economies become more resilient to energy price fluctuations, contributing to long-term economic stability.
Solar Panel Tax Credits: FAQs
Now, let’s take a closer look at the intricate aspects of these tax credits. In doing so, we will address essential questions such as their functioning, the eligible technologies, and the individuals or entities that can reap their benefits.
How Does The Federal Tax Credit Work For Solar?
The solar tax credit is a valuable nonrefundable credit equivalent to 30% of your solar project’s gross system cost. To illustrate, if your solar project’s total cost is $20,000, the tax credit would amount to $6,000 ($20,000 x 30% = $6,000).
It’s crucial to understand that the solar tax credit is not a direct payment but rather a credit that can reduce your federal income tax liability. This reduction can either increase your tax refund or lower the amount you owe in taxes.
For instance, if your solar system is deemed operational by a city inspector in 2023, you can claim a $6,000 tax credit when filing your 2023 federal income tax return, due in 2024. If your tax liability surpasses $6,000, you can claim the entire credit in a single year. However, if your tax liability is less than $6,000, you have the option to carry forward the remaining credit to offset taxes in future years.
What Is Covered Under The Solar Tax Credit?
As outlined by Energy.gov, the solar tax credit encompasses the following components within the gross system cost:
- Solar panels
- Inverters
- Balance-of-system equipment, which includes racks and conduit
- Installation labor
- Permitting fees
- Inspection costs
- Other soft costs
- Sales tax
- Energy storage devices (commonly known as batteries), whether they are physically integrated into the solar system or not (as of January 1, 2023).
It’s important to note that while the solar tax credit covers a broad range of expenses associated with solar installations, it does not extend to cover roofing expenses unless the roof itself is an integral part of the solar equipment. Additionally, electrical panel or wiring upgrades are not included in the solar tax credit; however, separate incentives for these upgrades are available.
Who Are The Eligible Beneficiaries?
The federal solar tax credit remains accessible to a diverse range of beneficiaries, including both residential and commercial property owners. This can include various types of homes, such as houses, houseboats, mobile homes, cooperative apartments, condominiums, and manufactured homes conforming to Federal Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards.
This inclusivity ensures that homeowners and businesses alike can harness the advantages of solar energy adoption.
What About Other Renewable Energy Projects?
The residential clean energy credit extends its coverage to various other types of renewable energy projects embarked upon by homeowners, including:
- Solar electric installations.
- Solar water heaters.
- Small wind energy projects.
- Biomass fuel systems.
- Fuel cell projects.
- Geothermal heat pumps
How Do I Claim The Tax Credits?
To claim the solar tax credit, you’ll need to complete IRS Form 5695, titled “Residential Energy Credits.” This form allows you to determine the precise credit amount based on the expenses related to your solar project. After completing Form 5695, attach it to your federal income tax return, such as Form 1040 or Form 1040NR.
Maximizing Solar Panel Tax Credits: Taking Advantage Of Additional Incentives
Besides the federal tax credit, there are other ways to claim tax benefits for solar energy systems. These can vary depending on your location and specific circumstances.
- Many states and local governments offer their own solar incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, or performance-based incentives. These can significantly reduce the cost of your solar installation.
- Some states also have Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs), that are programs that allow you to earn and sell SRECs based on the amount of solar energy your system generates. This can provide additional income or savings.
- In addition, certain areas offer property tax exemptions or reductions for properties with solar installations. This can help you save on your property taxes.
- Meanwhile, net metering and feed-in tariff programs allow you to earn credits or revenue for excess electricity your solar panels generate and feed back into the grid. It effectively reduces your electricity bill or provides an income stream.
- In some cases, you may be eligible for grants or low-interest loans to help finance your solar project, which can indirectly reduce your tax burden by lowering the overall cost.
- If you install solar panels for a business, you may be eligible for various tax incentives and deductions specific to commercial solar installations. Businesses can also often depreciate the cost of solar equipment over time, reducing their taxable income
Stacking Incentives
To demonstrate the potential for significant cost savings, let’s consider a solar project with a total gross system cost of $20,000. Initially, you would qualify for a federal tax credit of $6,000, which is equivalent to 30% of the project’s cost.
Now, let’s envision that California offers a state rebate of $2,000 for your solar installation. By applying this rebate, your total expenses are reduced to $18,000.
Furthermore, your local municipality has a solar incentive program in place, providing an additional $1,000 in savings to support your project.
If your utility company supports net metering, you have the opportunity to maximize long-term savings by selling any excess solar-generated power back to the grid. These cumulative incentives can significantly enhance the affordability and financial benefits of your solar investment.
Solar Panel Tax Credit Challenges and Criticisms
In examining the landscape of solar energy incentives, it is important to address the challenges and criticisms associated with solar panel tax credits.
Phase-Out Concerns
While solar panel tax credits have played a pivotal role in promoting solar energy adoption, one significant challenge lies in their gradual phase-out. Federal tax credits, such as the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC), have historically offered substantial benefits to early adopters of solar technology. However, these incentives are designed to decrease over time, which can raise concerns for prospective solar investors.
The phase-out process reduces the percentage of the tax credit available, potentially leading to decreased financial incentives for those who delay their solar installations. This phase-out structure can create a sense of urgency for individuals and businesses considering solar, as waiting too long may result in reduced financial savings.
Equity & Accessibility
An ongoing concern within the realm of solar panel tax credits revolves around equity and accessibility. Critics argue that these incentives primarily benefit higher-income individuals and businesses, as they are more likely to have the financial resources required to invest in solar installations. This disparity in access to tax credits can exacerbate existing socioeconomic inequalities.
Efforts are being made to address these equity concerns through initiatives like community solar programs, which aim to make solar energy accessible to low- and moderate-income households. Furthermore, President Biden’s US$7 billion fund for the “Solar for All” initiative aims to enhance access to affordable and clean solar energy for low-income households throughout the country. Nevertheless, there is still work to be done to ensure that solar incentives reach a broader demographic, ultimately democratizing access to clean energy.

Policy Uncertainty
Political landscapes and government policies highly influence the solar industry. Changes in leadership and shifting political priorities can create uncertainty for individuals and businesses interested in solar investments. The unpredictability of solar policies at the federal, state, and local levels can make planning for long-term solar projects challenging.
Policy uncertainty can hinder the growth of the solar industry and discourage potential investors, as they may fear that their financial incentives will be reduced or eliminated altogether in the future. This instability can have a dampening effect on the pace of solar adoption and the overall growth of the renewable energy sector.
Next Steps & Top Tips
If you’re intrigued by the advantages of solar panels for your home and eager to leverage the solar tax credit, what should be your next steps, and are there any valuable tips to keep in mind along the way?
#1: Consult with solar professionals
When considering a solar panel installation and the associated tax credits, it’s highly advisable to consult with seasoned solar professionals. These experts possess the knowledge and experience to help you make informed decisions regarding the type of solar system that suits your needs and financial situation. They can also provide insights into maximizing the benefits of available tax credits and incentives, ensuring your solar investment is as cost-effective as possible.
#2: Stay informed
Tax credit policies and incentives can evolve over time, influenced by changes in legislation and government priorities. To stay ahead and make the most of these opportunities, it’s crucial to stay informed about any modifications or updates to solar tax credit policies. Regularly check with relevant government agencies, industry associations, or trusted sources to ensure you’re aware of the latest developments. Being well-informed empowers you to make timely decisions that optimize your solar investment.
#3: Explore financing options
Solar panel installations can be a substantial upfront investment, but there are various financing options available to make them more accessible and affordable. Consider exploring financing avenues like solar loans or leases, both of which can help spread the cost of installation over manageable terms. Here is an article that will help you assess your financing options.
Solar loans allow you to finance your system while retaining ownership, while leases offer the option to pay for the solar installation over time with a fixed monthly fee. These financing solutions can make the transition to solar energy more budget-friendly, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of clean, renewable energy without significant upfront expenses.
Conclusion
Solar panel tax credits are a practical tool for advancing solar energy adoption and fostering a sustainable energy future. These incentives offer tangible benefits such as cost savings, environmental improvements, and job opportunities, contributing to a cleaner and more prosperous world.
It is essential to recognize the immense potential that solar panel tax credits hold. By reducing the financial barriers associated with solar installations, they make solar energy accessible to a broader spectrum of individuals and businesses, ensuring a more equitable transition to renewable power sources.
As you consider the possibilities of solar energy and the advantages of tax credits, remember that taking the initiative to explore solar options, consult professionals, and stay informed about evolving policies is key. Embracing solar energy not only benefits you but also plays a crucial role in our collective efforts to transition to a low-carbon economy and decarbonized energy sector.




