What Is The 2023 Federal Solar Tax Credit?
The federal solar tax credit, officially known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), has emerged as a crucial driver in the push towards renewable energy adoption in the United States. As the world grapples with the urgent need to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the ITC plays a pivotal role in making solar power an economically attractive choice for both homeowners and businesses. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the intricacies of the federal solar tax credit environment in 2023. We will delve into the tax credit percentage, the risks of potential changes, explore updated eligibility criteria, and provide insights into maximizing your solar photovoltaics (PV) savings.
Federal Tax Credit: The Basics
Before we can get into what the solar panel tax credit environment for 2023, it is important to first understand the basics of the ITC.
The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) serves as a pivotal incentive aimed at fostering the widespread adoption of solar energy throughout the United States. Enacted as a part of the Energy Policy Act of 2005, the ITC boasts a storied history of propelling the growth of renewable energy. Its core mission revolves around extending financial support to both individuals and businesses who choose to invest in solar power systems.
The ITC has played a transformative role in democratizing solar energy, rendering it more accessible and economically viable for homeowners and corporations across the nation. This incentive offers a substantial tax credit, enabling eligible taxpayers to alleviate a significant portion of the expenses associated with installing solar systems. This financial boost acts as a potent catalyst for the transition to clean energy, substantially lowering the financial hurdles for those contemplating the adoption of solar power.
At its inception, the ITC provided a 30% tax credit, coupled with a 2,000 dollar cap for residential projects. Nevertheless, the year 2008 marked a pivotal moment when the cap was eliminated, ushering in enhanced financial benefits for residential solar installations with increased capacity.
Since its inception, the ITC has undergone a series of revisions, extensions, and adjustments in its rates, reflecting its dynamic role in shaping the landscape of solar energy incentives. Understanding this history and the recent developments surrounding the ITC is vital for those considering solar installations, as it sheds light on the tax credit’s evolution and the current favourable conditions for solar investment.
What Is The 2023 Federal Solar Tax Credit?
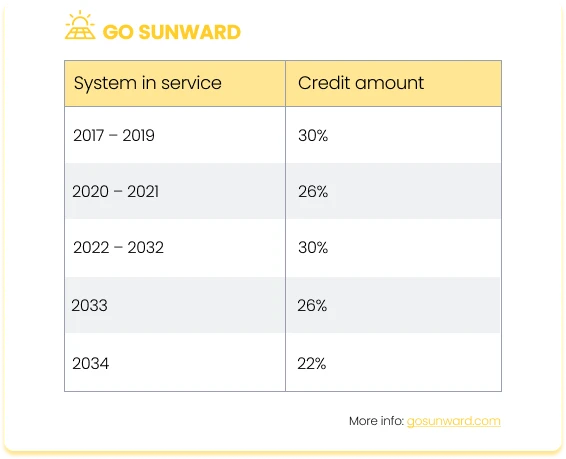
In August 2022, President Joe Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act, extending the availability of solar tax credits until 2034. Officially named the ‘Residential Clean Energy Credit’, this program encompasses various expenses, including equipment and installation costs, while excluding structural alterations solely intended for panel support. Furthermore, the solar tax credit can, in certain cases, be combined with state incentives and utility-backed initiatives that promote clean energy adoption.
The actual amount accessible as solar tax credits may fluctuate, contingent upon your project expenditures and completion date. Nevertheless, these solar incentives remain accessible to homeowners who put a qualifying system into service anytime between 2017 and 2034, thanks to the recent extension.
For the tax year 2023 (to be filed in 2024), the solar panel tax credit stands at a consistent rate of 30% of eligible expenses. This 30% credit will persist from the tax year 2023 all the way through 2032.
How Does The Federal Tax Credit For Solar Actually Work?
The federal tax credit for solar represents a significant financial incentive, amounting to 30% of the total gross system cost of your installed solar project. To put it into perspective, if your solar project’s overall expense is $20,000, you would be eligible for a tax credit of $6,000 ($20,000 x 30% = $6,000).
It’s essential to grasp that the solar tax credit operates as a reduction in your federal income tax liability rather than a direct payment. This reduction can have two beneficial outcomes: it can either increase your tax refund or decrease the amount you owe in taxes.
For example, if your solar system is certified as operational by a city inspector in 2023, you can claim a tax credit of $6,000 when filing your 2023 federal income tax return, which is due in 2024. If your tax liability exceeds $6,000, you can fully utilize the credit within a single tax year. Conversely, if your tax liability falls below $6,000, you have the flexibility to carry forward the remaining credit to offset taxes in subsequent years.
You might also want to read: How Much Can I Claim On My Taxes For Solar Panels?
Eligibility Criteria
In 2023, the federal solar tax credit continues to offer substantial benefits, provided you meet the updated eligibility criteria. Here’s an overview of who can benefit from the tax credit and the types of solar installations that qualify:
Eligible Beneficiaries:
The federal solar tax credit remains accessible to a diverse range of beneficiaries, including both residential and commercial property owners. This can include various types of homes, such as houses, houseboats, mobile homes, cooperative apartments, condominiums, and manufactured homes conforming to Federal Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards. This inclusivity ensures that homeowners and businesses alike can harness the advantages of solar energy adoption.
Qualifying Solar Installations:
Qualifying solar installations encompass various components, as stipulated by Energy.gov, all of which contribute to the gross system cost:
- Solar panels
- Inverters
- Balance-of-system equipment, which includes racks and conduit
- Installation labor
- Permitting fees
- Inspection costs
- Other soft costs
- Sales tax
- Energy storage devices, commonly known as batteries, whether they are physically integrated into the solar system or not (as of January 1, 2023).
Roofing Expenses & Electrical Upgrades:
It’s essential to note that while the solar tax credit encompasses a wide array of expenses associated with solar installations, it does not extend to cover roofing expenses unless the roof itself is an integral part of the solar equipment.
Furthermore, electrical panel or wiring upgrades are not included in the solar tax credit. However, separate incentives are available for these specific upgrades, providing additional avenues for optimizing your solar system.
Are Other Renewable Energy Projects Eligible?
The residential clean energy credit extends its coverage to various other types of renewable energy projects embarked upon by homeowners, including:
- Solar electric installations.
- Solar water heaters.
- Small wind energy projects.
- Biomass fuel systems.
- Fuel cell projects.
- Geothermal heat pumps.
Combining the Federal Tax Credit with Other Incentives: A Guide to Maximizing Solar Savings In 2023
As the drive towards solar energy adoption continues to gain momentum, understanding how the federal solar tax credit can be strategically combined with various state, local, and utility incentives becomes increasingly pertinent. This synergy of incentives can result in substantial cost reductions for your solar installation.

State-Level Incentives: Many states offer a spectrum of incentives to promote solar energy adoption. These state-level incentives may include cash rebates, performance-based incentives, or other financial rewards designed to further lower the initial cost of your solar system.
Local Municipality Programs: Local governments within a state often run incentive programs tailored to their communities. These programs can encompass additional rebates or incentives, and their availability can vary based on your specific location.
Utility-Funded Initiatives: Utility-funded initiatives can encompass incentives, rebates, or innovative net metering arrangements that allow you to not only reduce your energy bills but also potentially sell surplus solar-generated electricity back to the grid. As per IRS guidelines, when calculating your tax credit, the total cost considered must account for any assistance received from a public utility, unless you have previously reported that incentive as income for federal tax purposes.
Examples of Stacking Incentives:
- To illustrate the potential cost savings, consider a solar project with a total gross system cost of $20,000. Initially, you would qualify for a $6,000 federal tax credit (30% of $20,000).
- Now, imagine California provides a state rebate of $2,000 for your solar installation. By applying this rebate, your expenses reduce to $18,000.
- Additionally, your local municipality offers a solar incentive program, adding another $1,000 in savings.
- If your utility company supports net metering, you can further capitalize on long-term savings by selling excess solar-generated power back to the grid.
Next Steps: Pursuing Solar Savings
Navigating the process of claiming the federal tax credit for solar is essential to maximize savings and ensure a seamless experience.
Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to assist you:
Step 1: Eligibility Check – Before initiating the claiming process, verify that you meet all eligibility criteria for the federal solar tax credit. This includes having a qualifying solar installation and sufficient tax liability.
Step 2: IRS Form 5695 – The cornerstone of claiming the solar tax credit is IRS Form 5695, officially titled “Residential Energy Credits.” You must complete this form to calculate the precise credit amount for which you qualify. The form includes sections for various residential energy credits, including the solar tax credit.
Step 3: Gather Documentation – Compile all necessary documentation to substantiate your claim. This may encompass invoices, receipts, and proof of payment related to your solar system installation. Proper documentation is crucial to validate your expenses and ensure a successful claim.
Step 4: Complete IRS Form 5695 – Thoroughly fill out IRS Form 5695, ensuring accuracy in calculations and entries. Adhere to the provided instructions and include specific details regarding your solar project.
Step 5: File Your Tax Return – When filing your federal income tax return (e.g., Form 1040 or Form 1040NR), attach the completed IRS Form 5695. Ensure that you meet the annual tax filing deadline, typically April 15th, unless an extension applies.
Step 6: Reduce Tax Liability – The solar tax credit directly reduces your federal income tax liability. If the credit amount exceeds your tax liability, it can result in a tax refund or offset future tax obligations.
Top Tip: Consult With Tax Professionals – While the process of claiming the solar tax credit is straightforward, seeking guidance from a tax professional or accountant is advisable to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax regulations. Tax professionals can offer expert advice to help you maximize your eligible credit while avoiding potential errors.
Beyond 2023: Policy Risks & Legislative Changes
In the realm of renewable energy incentives, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), government policies and tax laws wield substantial influence. These policies, ever-evolving, shape the availability and scope of incentives.
Government Policy Impact: Government policies and tax laws shape the accessibility of incentives such as the ITC. Political shifts can lead to changes in energy and environmental priorities, potentially affecting solar incentives.
Potential Revisions, Extensions, or Expirations: Tax incentives, including the ITC, are subject to change. They can be revised, extended, or allowed to expire based on legislative decisions. The ITC has seen multiple extensions, significantly impacting solar adoption.
Informed Decision-Making: Staying updated on legislative changes is crucial for solar investors. Awareness of potential tax incentive shifts can influence project timing and scale. Engaging with industry groups and advocates can help track developments.
Conclusion
The federal solar tax credit is a pivotal catalyst in promoting the widespread adoption of renewable energy, particularly solar power, in the US. As we have explored throughout this article, understanding how the federal tax credit works for solar in 2023 and beyond is paramount for those seeking sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions.
We strongly encourage our readers to explore solar energy options and make informed decisions to harness the benefits of renewable energy incentives. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and businesses can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future while maximizing the advantages of solar power.




