Solar Loans: What To Know Before Getting A Loan For Solar
With the rising awareness of environmental concerns and the desire for energy independence, the demand for solar panel installations has surged. However, the upfront cost of solar systems can be a barrier for many. This is where solar loans come into play, offering a financial lifeline to those eager to harness the sun’s power.
As we delve into the world of solar loans, it becomes clear that they play a pivotal role in democratizing solar energy. They provide an accessible avenue for individuals and organizations to join the renewable energy revolution, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a greener planet.
Yet, before embarking on this exciting journey, it’s essential to navigate the nuances of solar loans and understand the key considerations that accompany them. In this article, we’ll illuminate the path towards solar financing success, ensuring that you make informed decisions about your solar future.
Understanding Solar Panel Costs: A Crucial Factor for Solar Loans
When exploring the expenses associated with solar panels, it becomes evident that cost considerations are fundamental, especially when contemplating solar loans. These costs are traditionally quantified in dollars per watt or kilowatt-hour (kWh). In the context of the United States, our research reveals that the average cost of solar panels typically falls within the range of $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. This pricing not only encompasses the direct costs linked to the solar panels themselves but also extends to cover the expenses associated with their installation.
However, the relevance of comprehending these costs extends further. For those considering the financial aspect of solar panel adoption, understanding the pricing dynamics is essential in making informed decisions about pursuing a solar loan. Before factoring in any incentives, rebates, or net metering schemes, a residential solar panel system’s typical cost hovers in the range of approximately $15,000 to $25,000.
Therefore, recognizing the costs involved in solar panel installations is not only relevant but crucial when contemplating the financial aspects of solar loans. It allows potential borrowers to assess their budget, understand their financing needs, and explore the most suitable loan options to embark on their solar energy journey.

A Recap On Solar Financing Options
The financial benefits of solar panels are substantial, given their lifespan of 25 years or more. They can offset a significant portion, if not the entirety, of your monthly electricity costs. To put this into perspective, if your current monthly electricity bill amounts to $150, you could potentially spend over $65,000 on electricity over the next 25 years.
There are three primary solar financing solutions: cash purchases, solar loans, and solar leases/Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). While this article will focus on solar loans, click here for a more detailed guide on the other options for solar financing.
Solar Loans 101
Solar loans are financial tools designed to facilitate the adoption of solar energy systems. They enable borrowers to secure the necessary funds for the purchase and installation of solar panels, allowing them to harness the benefits of renewable energy. These loans are structured to provide individuals with the financial means to invest in solar technology, even if they lack the upfront capital required for an outright purchase.
The significance of solar loans lies in their ability to democratize solar energy. They break down financial barriers, granting homeowners and businesses the opportunity to reduce their reliance on traditional fossil fuels and transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy source. By offering accessible financing options, solar loans empower a broader demographic to participate in the renewable energy revolution.
Banks offer various types of loans to support solar projects, each with its characteristics:
- Personal Secured Loan: These loans require collateral, like an asset, offering lower interest rates but risking loss of collateral if you can’t repay.
- Personal Unsecured Loan: No collateral is needed, but interest rates are often higher due to the increased lender risk.
- EEM (Energy Efficient Mortgage): Designed for energy-efficient home improvements, it lets you include solar costs in your mortgage, beneficial for new home purchases or refinancing.
- PACE (Property Assessed Clean Energy) Loan: Allows financing of solar and energy-efficient improvements through property tax assessments. Repaid via property tax bills, tied to property rather than credit score, available in specific regions.
- Home Equity Loan (HELOC – Home Equity Line of Credit): Uses home equity as collateral, offering lump sums or revolving credit lines with lower interest rates but risking home loss if you default.
The Pros & Cons Of Solar Loans
Like all financing mechanisms, there are some distinct advantages and disadvantages when it comes to solar loans. We outline them below:
Advantages:
- Ownership: With a solar loan, you own the solar panel system from day one, allowing you to benefit from both the energy savings and potential increase in property value.
- Interest Rates and Terms: Solar loans come with various interest rates and loan terms. Some offer low-interest rates, making them an attractive option for those who wish to minimize interest expenses.
- Tax Benefits: Depending on your location, the interest paid on solar loans may be tax-deductible, further reducing the overall cost of the system.
Disadvantages:
- Interest Costs: Borrowing money through a solar loan means you’ll incur interest charges over the loan term, which can make it a more expensive option compared to paying for the system outright.
- Credit Influence: The interest rates available to you depend on your creditworthiness. Those with better credit typically secure more favorable rates, reducing the overall loan cost.
- Collateral Risks: Secured loans require collateral, often your home. If you’re unable to meet your loan obligations, your lender can potentially foreclose on your property.
Solar Loan FAQs
What is considered a favorable interest rate for a solar loan?
Interest rates on solar loans exhibit a wide range, spanning from approximately 4% to potentially as high as 36%. Therefore, a good interest rate for a solar loan typically falls on the lower end of this spectrum, ideally between 4% and 8%. It’s crucial to note that the specific interest rate you secure depends on several factors, including your loan amount, geographical location, credit history, and overall financial situation. Furthermore, various companies and lenders offer solar loans with varying interest rates, underscoring the importance of shopping around for the best deal.
What’s the usual duration of a solar loan?
Typically, a solar loan is repaid over a period of 6 to 20 years. However, it’s worth noting that you have the option to accelerate your payments and pay off the loan ahead of schedule. Be mindful of potential prepayment fees that may apply in such cases.
How do solar loans compare with other solar financing options?
Solar loans stand as a distinct financing option amidst other solar energy financing solutions such as leases and power purchase agreements (PPAs). Unlike leases and PPAs, which involve third-party ownership of solar systems, solar loans grant the borrower full ownership and control over their solar panel system from day one. This autonomy allows borrowers to reap the full financial rewards of solar energy, including reduced electricity bills and potential income from excess energy production.
How are solar loans structured? Solar loans resemble home improvement loans and other financial products in many ways. Primarily, your solar loan comes with an interest rate and a defined repayment period. Some solar loans may also entail collateral requirements and origination fees. Importantly, borrowers with higher credit scores typically secure more favorable loan terms.
What Costs Are Included in Solar Financing?
Solar financing encompasses the system’s cost, installation expenses, and related upgrades, such as pole or ground mounts and batteries. It’s important to note that maintenance and ongoing energy purchase costs are not covered by the loan.
Key Considerations Before Getting A Solar Loan
Before embarking on the path of obtaining a solar loan, it’s essential to navigate a series of key considerations that can significantly impact your financial journey. In this section, we’ll explore these vital factors, ensuring that you embark on your solar financing adventure well-prepared and informed.

Financial Readiness Assessment: Evaluating your financial readiness is the first step in the solar loan journey. It involves a comprehensive review of your financial situation, including your current income, expenses, savings, and outstanding debts. This assessment helps you gauge your capacity to take on a solar loan without straining your finances.
Creditworthiness and Credit Scores: Creditworthiness plays a pivotal role in determining your eligibility for a solar loan and the interest rates you qualify for. Lenders rely on credit scores to assess the risk associated with lending, with higher credit scores typically resulting in more favorable loan terms. Understanding your credit score and addressing any issues is crucial in securing competitive loan offers.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: One of the most critical considerations before obtaining a solar loan is conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis. This analysis involves weighing the upfront costs of a solar panel installation, the loan’s interest rates and terms, and the potential long-term savings from reduced electricity bills. It helps you determine whether the financial benefits of solar energy outweigh the costs of the loan.
Long-Term Financial Impact: Solar loans are more than just a financial transaction; they can have a lasting impact on your overall financial picture and long-term goals. Consider how the monthly loan payments will fit into your budget and how the loan’s duration aligns with your financial plans. Balancing your short-term solar goals with your broader financial objectives is crucial for a sustainable financial future.
Documentation and Information Gathering: To streamline your solar loan application, gather the required documentation and information in advance. This may include proof of income, tax returns, credit history, and details about your solar panel installation project. Having these documents readily available can expedite the application process and enhance your loan eligibility.Shopping Around for Solar Loans: Before committing to a solar loan, it’s wise to shop around and compare offers from various lenders. This practice allows you to assess different interest rates, loan terms, and repayment options. By doing so, you can make an informed decision that not only suits your budget but also maximizes the value of your solar investment. Additionally, reading the fine print and checking customer reviews can help you uncover hidden costs, prepayment penalties, and lender reputations, ensuring a smooth financing experience.
A Note On Government Incentives & Tax Credits
Government incentives and tax credits can indeed influence your decision regarding solar loans. Researching and understanding these incentives at various government levels, including the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), is crucial. These incentives can effectively lower the total cost of your solar panel installation, enhancing the attractiveness of solar loans as a financing option.
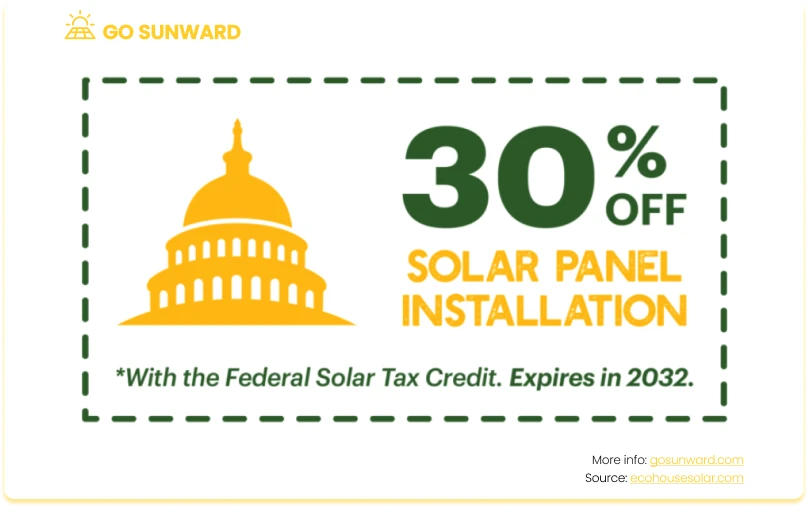
Federal Solar Tax Credit (Investment Tax Credit – ITC): One of the most valuable incentives for solar panel installations is the federal solar tax credit, officially known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This credit allows you to receive a substantial financial benefit by crediting you 30% of the total cost of your solar panel system directly from your federal income tax. The ITC has proven to be a powerful incentive for homeowners and businesses to embrace solar energy. Importantly, the ITC is set to remain at 30% through end-2032, providing an extended period of opportunity for those considering solar adoption. Moreover, there is no cap on the eligible system’s value, meaning you can deduct 30% of the total system cost, regardless of your initial investment.
State and Local Incentives: In addition to the federal ITC, many states and local governments offer incentives and rebates for solar panel installations. The availability and generosity of these incentives can vary significantly depending on your location. Some states, like New York, California, Iowa, Connecticut, and Maryland, are particularly known for offering favorable solar tax incentives, making solar adoption even more appealing in these regions. These state and local programs can further reduce the upfront costs of going solar and enhance the overall return on investment.
Next Steps In Your Solar Loan Journey
With loan approval in hand, your solar panel installation project kicks off, marking a new phase in your solar journey. This phase involves a coordinated effort between your chosen solar installer and the lender to ensure a seamless installation process, bringing your solar panel system to life.
As the installation progresses, you’ll encounter the disbursement of your solar loan funds, typically released in stages to coincide with project milestones. This financial support facilitates the construction of your solar system, allowing you to move closer to harnessing the power of the sun.
Following installation, it’s vital to monitor your solar panel system’s performance and track the resulting energy savings closely. Keep a keen eye on your electricity bills and system output to ensure everything aligns with your expectations. Over time, the financial benefits of solar energy will materialize as you reduce or eliminate your reliance on traditional grid electricity.
Life circumstances can change, potentially impacting your financial situation. If you find opportunities to improve your loan terms or consider early repayment of your solar loan, discuss these options with your lender. Exploring options like refinancing or early repayment can help optimize your financial strategy to better align with evolving needs and goals.
Conclusion
In your solar financing decision-making process, it’s vital to approach it thoughtfully, considering your unique financial situation and goals. Solar energy offers substantial benefits, from reducing your utility bills to contributing to a low-carbon energy future.
Making an informed choice regarding a solar loan is not just wise; it’s a significant step toward embracing renewable energy. We urge you to assess your financial readiness, explore your loan options, and collaborate with lenders who share your vision. This approach will help you secure a solar loan that suits your needs and aligns with a greener, more sustainable future.




