Solar Financing Options: How To Pay For Solar Panels
The significance of solar energy lies in its dual promise: it can considerably reduce energy costs for households and businesses while concurrently lessening the environmental impact associated with conventional energy sources. This dual benefit has transformed solar panels into a transformative force in the global energy landscape. However, embracing solar power often starts with a practical question: “How can I afford solar panels?” This is where understanding various solar financing options becomes imperative. Accessibility to solar panels should not be reserved solely for the few but extended to a broader audience eager to embrace a sustainable energy future. In this article, we delve into the world of solar financing options, demystifying the pathways to make solar panels not just a possibility but a tangible reality for homeowners and businesses alike.
Understanding the Costs of Solar Panels
The costs associated with solar panels are typically measured in terms of dollars per watt or kilowatt-hour (kWh). As per our research findings within the United States, the average cost of solar panels currently falls within the range of $2.50 to $3.50 per watt. This pricing encompasses not only the expenses directly tied to the solar panels themselves but also the costs associated with their installation.
When considering an entire residential solar panel system, it’s essential to note that a typical system may range in cost from approximately $15,000 to $25,000, prior to accounting for any incentives, rebates, or net metering schemes that may be applicable.

Factors Influencing Solar Panel Costs
Beyond the technology type itself, several other factors influence the overall cost of solar panels, each playing a pivotal role in determining the final price tag of solar energy systems.
- System Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of the solar panel system you opt for have a substantial impact on the overall cost. Larger systems with higher capacity can generate more electricity but typically entail a greater upfront investment.
- Location and Solar Resource: The geographical location of your solar panel installation is a key determinant of its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Areas blessed with abundant sunlight and favorable solar resources can maximize energy production, potentially reducing costs over time.
- Installation and Labor Costs: The cost associated with installation and labor constitutes a significant portion of the overall expense. Professional installation is essential to ensure proper setup and performance, but it does contribute to the total cost of your solar panel system.
- Incentives and Rebates: Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates can serve as valuable financial incentives to offset the cost of your solar panel system. These incentives vary by location and can significantly reduce the initial expense of transitioning to solar energy.
- Warranty and Maintenance Expenses: Solar panel systems come equipped with warranties that cover equipment for a specified period. It’s crucial to consider the warranty terms and potential maintenance costs when calculating the overall cost of ownership. High-quality panels often come with longer and more comprehensive warranties, which may influence your decision-making process.
Exploring the Variety of Solar Financing Solutions
Solar panel installations represent a significant investment, but the good news is that numerous financing options are available to make solar energy accessible to a broader audience. In this section, we’ll delve into various solar financing options, each tailored to meet different financial needs and preferences. We will focus on the three primary options: cash purchase, solar load and solar lease/power purchase agreement (PPA).
Solar panel systems typically have a lifespan of 25 years or more, effectively offsetting a substantial portion, if not the entirety, of your monthly electricity expenses. These cumulative savings can accumulate rapidly. For instance, if your current monthly electricity bill stands at $150, you could potentially spend over $65,000 on electricity over the course of the next 25 years. You can use an online solar calculator to estimate the potential solar energy generation, cost savings, and financial returns of a solar panel installation for a specific location.
However, by making an investment in solar energy, you have the opportunity to circumvent the majority, if not all, of these anticipated electricity expenditures. Much like any home improvement or upgrade project, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess the range of financing options at your disposal and identify the one that best aligns with your individual needs and circumstances.
Solar Financing Option 1: Buy It Outright
Purchasing a solar panel system outright is one of the most straightforward and financially rewarding ways to go solar. With this financing option, you make an upfront payment for the solar panels and their installation, having the perks of full ownership of the system from day one.
Under this financing model, you pay for the entire solar panel system upfront, covering the cost of the solar panels themselves, inverters, installation, and any associated equipment.
Advantages:
- Ownership: Buying the system outright means you own it outright, which entitles you to all the benefits and savings generated by the solar panels.
- Maximum Savings: As the owner, you reap the full financial benefits of the solar panel system, including reduced or eliminated electricity bills and potential income from excess energy production if you feed it back into the grid.
- Long-Term Investment: While the initial upfront cost may seem substantial, it’s important to view this as a long-term investment that can provide substantial returns over the system’s life, typically 25 years or more.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Cost: The most prominent drawback of this financing option is the significant upfront cost. For many individuals and businesses, paying the entire amount upfront may pose a financial challenge.
- Delayed ROI: Although buying outright offers substantial long-term savings, it may take several years to achieve a complete return on your investment. The exact payback period varies based on factors like local electricity rates and your energy consumption.
- Limited Budget Flexibility: Making a substantial upfront payment for a solar panel system can limit your budget flexibility for other expenses or investments. This may not be an ideal choice if you have other financial priorities.
Solar Financing Option 2: Solar Loans
Solar loans offer a flexible financing solution for those eager to embrace solar energy but unable to make an upfront payment. They empower you to transition to solar power without needing a substantial down payment. Solar loans, or personal loans, enable you to install a solar panel system without paying the full cost upfront. Instead, you borrow the necessary funds and repay the loan over a predetermined period. These loans can be obtained from banks, credit unions, or solar financing companies.
Regarding solar loans, there are two primary types to consider. Unsecured loans don’t require collateral but tend to come with higher interest rates. In contrast, secured loans offer more competitive interest rates but necessitate using your home as collateral. It’s important to be aware that opting for a secured loan entails some risk, as failure to meet loan obligations could potentially result in the foreclosure of your home. Carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each loan type is crucial when determining the best fit for your financial situation and goals.
Advantages:
- Ownership: With a solar loan, you own the solar panel system from day one, allowing you to benefit from both the energy savings and potential increase in property value.
- Interest Rates and Terms: Solar loans come with various interest rates and loan terms. Some offer low-interest rates, making them an attractive option for those who wish to minimize interest expenses.
- Tax Benefits: Depending on your location, the interest paid on solar loans may be tax-deductible, further reducing the overall cost of the system.
Disadvantages:
- Interest Costs: Borrowing money through a solar loan means you’ll incur interest charges over the loan term, which can make it a more expensive option compared to paying for the system outright.
- Credit Influence: The interest rates available to you depend on your creditworthiness. Those with better credit typically secure more favorable rates, reducing the overall loan cost.
- Collateral Risks: Secured loans require collateral, often your home. If you’re unable to meet your loan obligations, your lender can potentially foreclose on your property.
Solar Financing Option 3: Solar Leases/PPAs
Solar leases and power purchase agreements (PPAs) have played a significant role in the solar industry’s growth, although their popularity has waned in recent years due to evolving financial dynamics. Often grouped together, these financing options fall under the category of third-party ownership (TPO), involving a company installing solar panels on your property and selling you the electricity generated at a predetermined rate.
In a lease or PPA arrangement, you typically secure a fixed electricity rate. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, this rate should be approximately 10% to 30% lower than your current electricity rate. Notably, these agreements often incorporate an annual rate increase, known as an escalator, meaning that each year, your solar energy cost rises compared to the previous year. However, there has been a shift in recent years towards locking in a specific rate for the full contract term. Furthermore, with a lease or PPA, the third-party owner assumes responsibility for system monitoring and maintenance, which can be an advantage or disadvantage, depending on the reliability of the leasing company.
Advantages:
- Lower Initial Costs: Solar leases and PPAs typically require little to no upfront payment, making solar energy accessible to those with budget constraints.
- Predictable Energy Costs: With a fixed electricity rate, you can anticipate your solar energy expenses, providing stability in your monthly budget.
- Maintenance Responsibility: The third-party owner is responsible for system maintenance, sparing you from the burden of upkeep and repairs.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Ownership Benefits: Since you don’t own the solar panel system, you aren’t eligible for financial incentives and rebates associated with solar energy; instead, these benefits go to the system’s owner.
- Potential Impact on Home Resale: Homes with solar typically have a higher resale value, but this may not hold true for leased or PPA systems. New homeowners might be hesitant to take over additional monthly payments.
- Escalating Costs: Many lease and PPA agreements include annual rate increases, which means your solar energy costs could rise over time, offsetting some of the initial savings.
Tax Benefits and Rebates for Solar Panels: Maximizing Savings
When considering the financial aspects of installing solar panels, it’s essential to explore the various rebates and incentives available to help offset costs. These financial incentives can significantly enhance the affordability and attractiveness of adopting solar energy solutions.
In the US, federal tax credits and state/local incentives play a pivotal role in rendering solar panel installations financially feasible and appealing. Leveraging these programs can significantly reduce the initial cost of transitioning to solar energy.
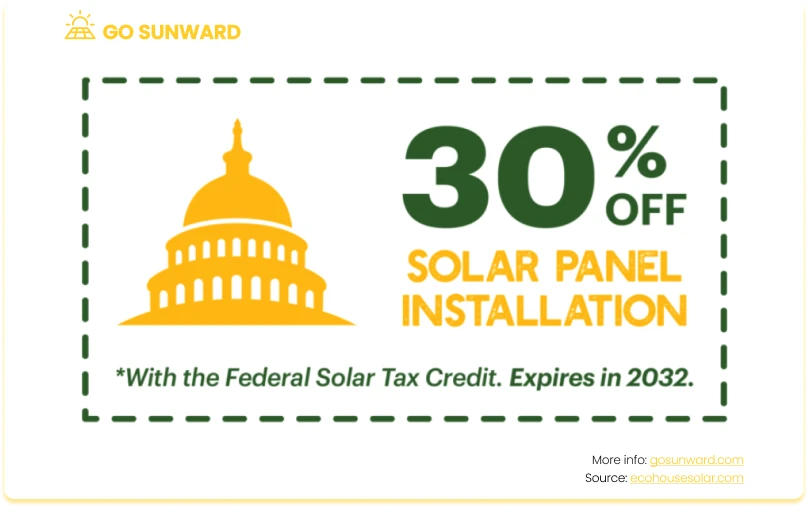
Federal Solar Tax Credit (Investment Tax Credit – ITC): One of the most valuable incentives for solar panel installations is the federal solar tax credit, officially known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This credit allows you to receive a substantial financial benefit by crediting you 30% of the total cost of your solar panel system directly from your federal income tax. The ITC has proven to be a powerful incentive for homeowners and businesses to embrace solar energy. Importantly, the ITC is set to remain at 30% through end-2032, providing an extended period of opportunity for those considering solar adoption. Moreover, there is no cap on the eligible system’s value, meaning you can deduct 30% of the total system cost, regardless of your initial investment.
State and Local Incentives: In addition to the federal ITC, many states and local governments offer incentives and rebates for solar panel installations. The availability and generosity of these incentives can vary significantly depending on your location. Some states, like New York, California, Iowa, Connecticut, and Maryland, are particularly known for offering favorable solar tax incentives, making solar adoption even more appealing in these regions. These state and local programs can further reduce the upfront costs of going solar and enhance the overall return on investment.
It’s crucial to research and stay informed about the specific incentives and rebates available in your area, as they can substantially impact the financial feasibility of your solar panel project. To ensure you have the most accurate and up-to-date information, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional or visit the government energy department website for the latest details on federal tax credits for solar panel installations.
By leveraging these tax benefits and incentives, you can not only lower your initial investment but also accelerate the payback period, making solar energy an increasingly attractive and financially prudent choice for both homeowners and businesses alike.
Conclusion
In our exploration of solar financing options, we’ve uncovered the diverse pathways available for individuals and businesses to harness the abundant benefits of solar energy. From outright ownership to leasing arrangements and power purchase agreements, each option comes with its unique advantages and considerations.
It’s essential to recognize that the solar revolution is not merely an eco-conscious endeavor; it’s a financially savvy one too. By investing in solar panels, you embark on a journey towards greater energy independence and long-term savings on your utility bills. The positive impact resonates on both personal finances and the broader environment, reducing carbon footprints while enhancing financial sustainability.




