Living Off The Grid: Important Things You Need To Know
Living off the grid, once considered an unconventional choice, has gained significant traction in recent years as a lifestyle that offers an alternative to the mainstream. This intriguing way of life revolves around the conscious decision to disconnect from traditional utility services, such as electricity, water supply, and sewage systems, in favor of self-sufficiency and a reduced environmental footprint. It represents a growing movement of individuals and communities seeking a simpler, more sustainable existence.
In an era marked by environmental awareness and a desire for greater autonomy, the allure of off-grid living has never been stronger. People are increasingly drawn to the prospect of generating their energy, cultivating their food, and minimizing their environmental impact. Yet, embarking on this journey requires careful consideration and preparation.
This article will delve into the crucial factors and important considerations that anyone contemplating an off-grid lifestyle should be aware of, offering valuable insights into what it means to live off the grid and the essentials required to thrive in this unique way of life.
What Does ‘Living Off The Grid’ Mean?
The phrase “off the grid” encapsulates a lifestyle characterized by disconnection from traditional public utility services, such as electricity, water supply, and sewage systems. Those who choose to live off the grid intentionally opt for self-sufficiency, relying on alternative sources for their basic needs. While the concept shares a common thread of independence from centralized services, it can manifest in various interpretations and degrees of self-reliance.
One of the primary motivations for embracing an off-grid lifestyle is the pursuit of self-sufficiency. Off-grid individuals and communities seek to produce their energy, obtain water from natural sources, and grow their food. This self-reliance empowers them to reduce their dependency on external resources, fostering a sense of autonomy and resilience.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in the decision to go off the grid. Many off-grid enthusiasts are driven by a desire to minimize their ecological footprint. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and adopting sustainable practices, they can decrease their environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Furthermore, the appeal of a simpler, less hectic life is a compelling factor. Living off the grid often involves a closer connection to nature, a slower pace of life, and a focus on the essentials. This simplicity can lead to a greater sense of contentment and well-being, drawing individuals away from the hustle and bustle of urban living.
Living Off The Grid: 6 Things You Need To Consider

So, you’re intrigued by the idea of living off the grid. It might seem as simple as escape to the wilderness, set up a self-sustaining cabin with solar panels, wind turbines, and a vegetable garden, and bask in the serenity of nature. However, the reality of off-grid living is a bit more nuanced. It’s a journey that demands meticulous planning, careful preparation, and ongoing dedication to sustain a self-reliant lifestyle.
From choosing the right location to mastering utilities management, along with the joys and challenges of sustainable food production, let’s explore the essential things you need to know before embarking on this unique path.
Location & Land
The importance of choosing the right location cannot be overstated. The climate and environmental conditions of your chosen area will play a fundamental role in determining the success of your off-grid venture. Consider the climate’s temperature extremes, precipitation patterns, and seasonal variations, as these factors will influence your energy needs, heating and cooling strategies, and food production capabilities. Additionally, assess the environmental conditions, such as the presence of natural hazards like floods, wildfires, or hurricanes, which can pose challenges to your off-grid setup, the resilience of your shelter and your overall safety.
Access to resources is another vital consideration. Ensure that your chosen location provides access to essential resources, primarily focusing on clean water sources. Access to rivers, lakes, or dependable wells is crucial, as water is a fundamental requirement for off-grid living. Moreover, evaluate the availability of renewable energy sources like sunlight and wind, as they are the backbone of energy generation in off-grid systems.
Navigating legal regulations is equally essential. Familiarize yourself with local, regional, and national regulations governing land use and off-grid living. Zoning laws, building codes, and environmental restrictions can vary significantly by location and may significantly impact your off-grid plans. Engage with local authorities and regulatory agencies to gain a thorough understanding of the legal requirements for constructing and living in an off-grid home or property.
Land acquisition and property ownership require careful consideration. Understand the process of acquiring land for off-grid living, including property ownership rules and land-use restrictions. Ensure you thoroughly review property deeds and land titles to secure clear ownership rights, free from encumbrances that could hinder your off-grid lifestyle.
Finally, take into account the potential challenges associated with remote or isolated locations. While such areas offer solitude and tranquillity, they may also present unique challenges. Consider factors like access to medical facilities, emergency services, and the logistics of obtaining supplies and provisions. Be prepared to address the logistical aspects of living off-grid in remote areas, such as transportation, waste disposal, and communication options.
Energy Independence
Energy independence stands as a cornerstone of off-grid living, embodying the essence of self-sufficiency and sustainability. It represents the ability to generate and manage one’s electricity needs independently, without reliance on centralized utility grids. The significance of energy independence in off-grid living is multi-faceted. It not only reduces the environmental footprint by minimizing dependence on fossil fuels but also ensures a consistent power supply in remote or off-grid locations.
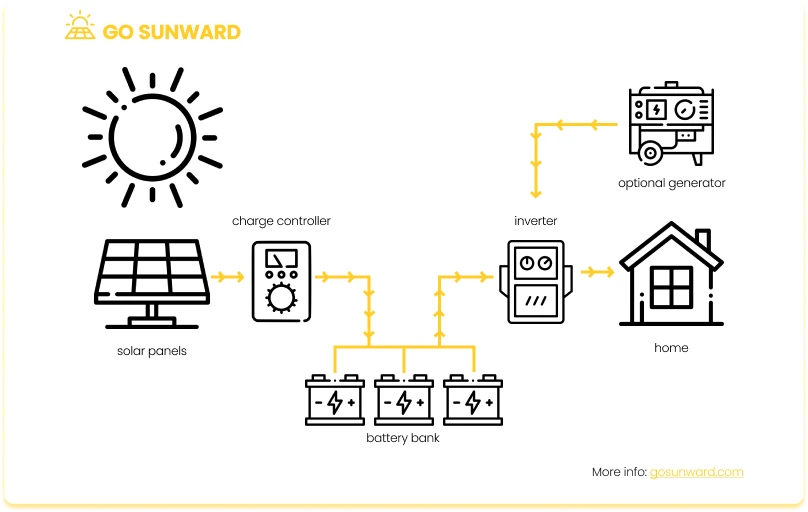
Off-grid energy solutions harness the potential of renewable energy sources, transforming them into reliable power generation. Solar panels, which capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, are a key component of off-grid energy setups. Wind turbines and micro-hydro systems harness the kinetic energy of the wind and flowing water, respectively, further diversifying the renewable energy sources available. These systems provide a consistent source of electricity, even in off-grid environments.
Efficient energy management and storage are crucial elements of off-grid living. Energy storage solutions, often in the form of batteries, store excess energy generated during the day for use during periods when sunlight or wind is scarce, such as at night or during cloudy days. Additionally, considering backup generators can provide an extra layer of assurance. These generators can serve as a reliable source of power during extended periods of low energy production or emergencies, ensuring that essential systems continue to operate smoothly. Efficient energy management, combined with backup solutions, ensures that power is consistently available when needed, contributing to the overall sustainability and resilience of off-grid energy systems.
Heating & Cooling
Heating and cooling are crucial aspects of off-grid living and are closely connected to your energy independence strategy. Your specific heating and cooling requirements will be influenced by both your climate and the size of your off-grid home.
For off-grid heating, one popular choice is a wood stove, which not only provides warmth but can also be utilized for cooking and heating water. Wood stoves are particularly advantageous as they do not rely on a power source, ensuring efficient and reliable heating in various circumstances.
In hot climates, it’s equally essential to have a cooling strategy in place. Solar-powered fans, small air conditioning units, or swamp coolers can effectively cool your off-grid home. These options are energy-efficient and well-suited for off-grid living.
Additionally, implementing passive heating and cooling techniques can help regulate the temperature within your off-grid dwelling without overburdening your power supply. Strategies such as shading, proper insulation, ventilation, and strategic window placement can significantly reduce your dependence on energy-intensive heating and cooling systems.
Water Management
Responsible water management lies at the heart of off-grid living, reflecting a commitment to sustainable practices and self-sufficiency. Off-grid individuals and communities prioritize water conservation and responsible usage as essential components of their lifestyle.
Rainwater harvesting and water collection is a key practice in off-grid water management. Collecting rainwater allows off-grid residents to obtain a consistent water supply without relying on centralized water distribution systems. Water filtration techniques further ensure that collected rainwater is safe and potable for various needs, from drinking to irrigation.
Efficient water use practices are paramount in sustaining off-grid lifestyles. Off-grid individuals implement strategies to minimize water waste, such as low-flow fixtures, drip irrigation systems, and water recycling. These practices not only conserve a precious resource but also contribute to long-term self-sufficiency.
Sustainable Food Production
Food security assumes a critical role in off-grid living. Off-grid individuals and communities prioritize sustainable food production as a means of reducing reliance on external food suppliers and fostering self-sufficiency. This emphasis on food security is rooted in recognising the importance of access to fresh, healthy, and locally sourced food.
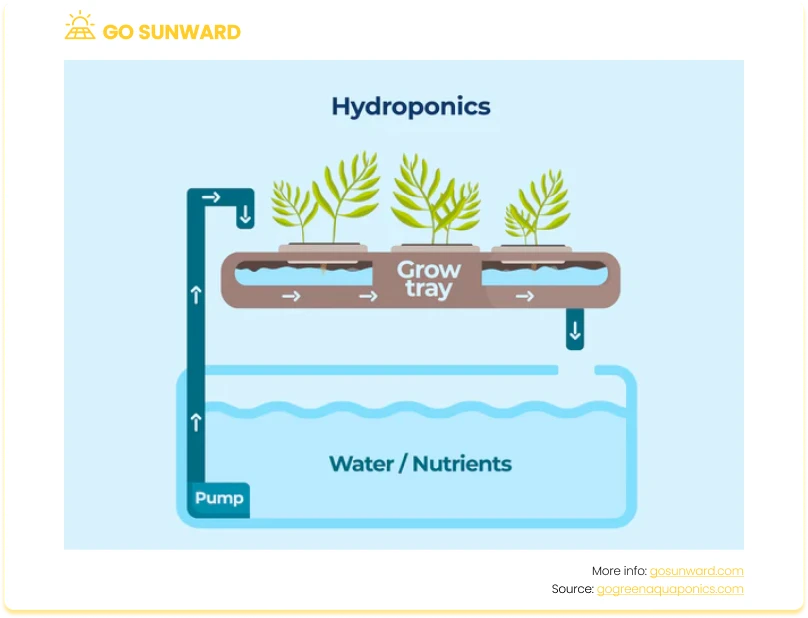
Various methods are employed for sustainable food production in off-grid settings. Gardening allows off-grid residents to cultivate their fruits and vegetables, while raising livestock and fishing provides a source of meat, fish, dairy, and eggs. Innovative techniques like aquaponics and hydroponics expand food production possibilities, particularly in areas with limited arable land.
Reducing reliance on external food suppliers not only enhances self-sufficiency but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with long-distance food transportation. It fosters a deeper connection with the land and the food production process, aligning with the principles of sustainability that underpin off-grid living.
Waste Management & Environmental Impact
Minimizing waste and environmental impact is a fundamental commitment to off-grid living. Responsible waste management practices are implemented to ensure the sustainability and health of the land.
Composting techniques are employed to convert organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments. Greywater usage, where wastewater from sinks and showers is treated and reused for irrigation, reduces water waste and contributes to sustainable agriculture practices.
Responsible waste disposal practices, including recycling and proper disposal of non-recyclable materials, help minimize the environmental footprint of off-grid communities. These efforts support the long-term health and fertility of the land, aligning with the holistic sustainability goals of off-grid living.
Common Challenges & Solutions When Living Off The Grid
Living off the grid, while rewarding, comes with its fair share of challenges. Individuals and communities pursuing this lifestyle often encounter obstacles that require creative solutions and a resilient mindset.
One of the foremost challenges is coping with extreme weather conditions. Remote off-grid locations can be susceptible to harsh winters, scorching summers, or inclement weather patterns. To mitigate these challenges, off-grid residents invest in robust insulation, energy-efficient heating and cooling systems, and backup power sources to ensure comfort and safety during extreme weather events.
Isolation is another challenge, particularly for those living in remote areas. The sense of seclusion, while appealing to some, can lead to feelings of loneliness and limited social interaction. To combat isolation, off-grid individuals often build a sense of community with like-minded neighbors, engage in local activities, and leverage digital connectivity to stay in touch with friends and family.
Maintenance of off-grid systems and infrastructure presents an ongoing challenge. Solar panels, wind turbines, and water systems require regular upkeep to ensure their optimal performance. Off-grid residents become adept at DIY maintenance and often maintain a stock of essential spare parts to address issues promptly.
How Much Money Will I Need For Living Off The Grid?
While it’s possible to set up a modest off-grid dwelling on an affordable plot of land for as little as $10,000 to $20,000, especially if you take on much of the construction work independently, it’s essential to acknowledge that the reality often differs. For most individuals embarking on the journey of off-grid living, the total expenditure typically surpasses the $100,000 mark when factoring in land and property costs.
If your goal is complete self-sufficiency or generating income from your land, the financial commitment escalates significantly. Investing in high-quality land, larger acreage, and implementing more intricate systems may necessitate a budget of at least $200,000 or more.
For more information on the breakdown costs involved with off-grid living, read this article.
The Balance Between Comfort & Simplicity
In the pursuit of off-grid living, the balance between comfort and simplicity is a defining aspect of one’s unique journey. It’s a path that grants individuals the liberty to tailor their lifestyle according to their values and priorities.
For some dedicated off-grid enthusiasts, the appeal lies in embracing a minimalist approach to life. They find joy in modest living spaces and voluntarily restrict their energy and resource consumption. This choice reflects a commitment to a simplified existence in harmony with nature.
Others, however, seek to strike a balance that allows them to enjoy modern comforts and conveniences while still minimizing their environmental impact. These individuals find innovative ways to incorporate high-efficiency appliances, internet connectivity, and entertainment systems into their off-grid lifestyle.
Ultimately, the harmony between comfort and simplicity in off-grid living is a profoundly personal decision. It empowers individuals and communities to define their own path towards a meaningful and fulfilling life within the context of self-sufficiency and sustainability. This dynamic spectrum of choices is a testament to the adaptability and versatility of the off-grid lifestyle.
Some Inspiration For Living Off The Grid
Sometimes, all it takes is a bit of inspiration!
Here, we’re sharing our top three favorite homes that have embraced off-grid living. These dwellings were built with their own power and waste management systems, and many of them even produce their own food. For more off-grid living inspiration, click here.
#1 ZeroHouse
ZeroHouse embodies off-grid living principles. Designed by Specht Architects, this home strives for complete self-sufficiency with renewable energy sources, solar panels, and advanced battery storage, reducing grid reliance. Energy-efficient materials and systems promote conservation. The rainwater harvesting system and advanced filtration provide water self-sufficiency for drinking, bathing, and irrigation.

#2 Gawthorne’s Hut
Gawthorne’s Hut, a creation of Cameron Anderson Architects, epitomizes off-grid living in the remote Australian wilderness. This contemporary take on a shepherd’s hut relies on solar panels and battery storage for electricity, ensuring autonomy from conventional grids. Its compact, eco-conscious design prioritizes energy efficiency while promoting the core principles of off-grid living.

#3 La Cabin
La Cabin, nestled in Quebec, Canada, serves as a striking embodiment of off-grid living. This compact cabin design prioritizes energy efficiency and environmental responsibility, fully operating off the grid. Solar panels generate electricity, reducing the carbon footprint while ensuring a modern lifestyle. Propane powers its cooling, and a wood stove provides heating. In addition, La Cabin boasts water self-sufficiency through rainwater harvesting systems and advanced filtration, delivering purified water for various needs.

Conclusion
Off-grid living isn’t just a lifestyle; it’s a holistic approach to sustainability. It allows individuals and communities to minimize their environmental footprint, promote self-sufficiency, and rediscover the beauty of the natural world.
Off-grid living offers a path to a more connected, intentional, and sustainable life for those ready to embrace its challenges and benefits. It proves that a simpler, self-sufficient way of life can harmonize with modern comforts and conveniences.




