Are LED Lights Energy-Saving?
In recent years, LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the lighting industry, presenting a promising solution to the rapidly increasing demand for energy-efficient lighting options. LED lights have gained widespread popularity for their longevity, versatility, and potential to reduce energy consumption. This article will examine the following question in depth: Are LED lights energy-saving? It will explore the technology and mechanisms behind LED lighting, compare them with traditional lighting technologies, and discuss both their environmental and economic benefits.
LEDs 101
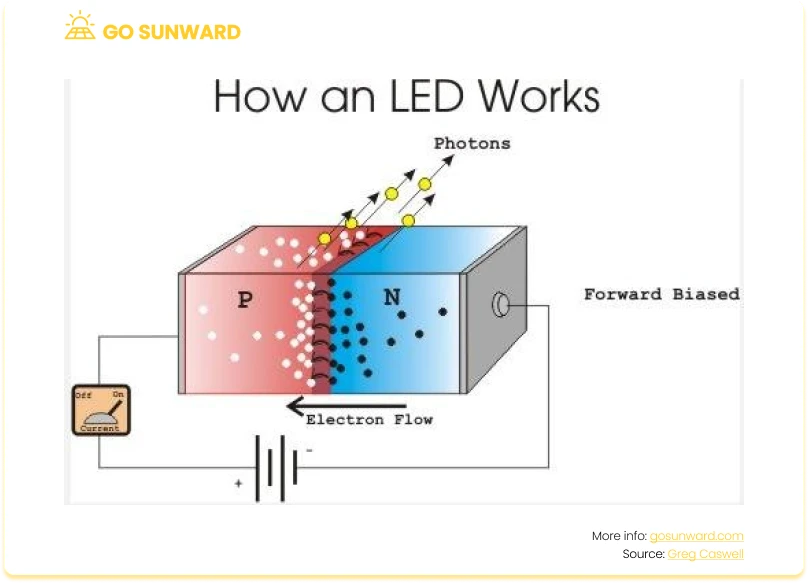
LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Unlike traditional incandescent or fluorescent bulbs, which produce light by heating a filament or exciting a gas, LEDs convert electrical energy directly into light through a process known as electroluminescence.
At the heart of an LED lies a semiconductor material, typically made from compounds like gallium, arsenic, and phosphorus. This semiconductor material contains both positively charged “holes” and negatively charged electrons. When an electric current is applied to the LED, electrons are injected into the semiconductor from the negative terminal, while the positively charged holes are injected from the positive terminal.
As these charged particles traverse the semiconductor material, they encounter each other in the region known as the “p-n junction.” This junction represents the boundary between the positively and negatively doped portions of the semiconductor. As electrons fall into the holes, they release energy through photons, which are packets of light. This process is the very essence of electroluminescence – the conversion of electrical energy into radiant light.
Deep Dive Into LED Applications & Devices
Formerly recognized primarily for applications like indicator lights and traffic signals, modern LEDs have evolved into a high quality, durable and energy-efficient lighting technology for general lighting potential and application. These devices consume as much as 90% less energy and boast a lifespan up to 25 times greater than conventional incandescent bulbs – read on for more information on the economic and environmental benefits of LEDs.
The versatility of LED technology is evident across a wide spectrum of lighting products. These encompass replacements for traditional 40W, 60W, 75W, and 100W incandescent bulbs, as well as reflector bulbs utilized in recessed fixtures, track lights, doors, task lighting, and undercabinet illumination. Outdoor applications, such as outdoor area lights, pathway lights, step lights, and porch lights, benefit from LEDs’ capacity to perform well in various environments. Their resilience and performance even extend to cold conditions, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor settings. Furthermore, certain LEDs are dimmable and include practical features like daylight and motion sensors, while others offer the convenience of adjusting colors or shades of white light.
While there are many types of LED lights, here are some of the more common technologies that will be familiar to you:
- Standard LED Bulbs: These are the most common and widely used LED lights. They are highly energy-efficient, using up to 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs. Standard LED bulbs are available in various shapes and sizes, making them suitable for various applications.
- LED Lamps: LED lamps are designed to replace traditional fluorescent lamps. They are highly efficient and provide excellent lighting with low energy consumption. LED lamps are commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, as well as in homes.
- LED Tube Lights: LED tube lights are an energy-efficient alternative to traditional fluorescent tube lights. They offer similar brightness levels while consuming significantly less energy. LED tube lights are commonly used in offices, schools, and other commercial spaces.
- LED Spotlights: LED spotlights are highly energy-efficient and provide focused illumination. They are commonly used in track lighting, accent lighting, and landscape lighting. LED spotlights highlight specific areas or objects while minimizing energy consumption.
LED Downlights: These are recessed ceiling lights that provide uniform and efficient lighting. They are commonly used in residential and commercial spaces. They are designed to create an unblemished and streamlined ceiling appearance.

Widespread Benefits: Cost & Sustainability
LED lights have become increasingly popular due to their energy-efficient properties. Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, LED lights consume significantly less energy, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced carbon emissions.
Economic Benefits:
There has been a steady decline in the cost of LED light bulbs since their inception, and this trend is expected to continue with the expanding availability of LED products. Although LEDs carry a higher upfront expense than traditional incandescent bulbs, their cost-effectiveness is evident in their extended lifespan and minimal energy consumption.
As a result, users ultimately experience significant savings over time. According to our research, LED bulbs can last up to 25,000 to 50,000 hours or more, compared to the typical 1,000-hour lifespan of incandescent bulbs.
Environmental Benefits:
The benefits of LED lights extend far beyond mere energy savings. Their reduced energy consumption is pivotal in curbing greenhouse gas emissions, a significant step in combatting climate change. For a detailed look at the link between energy consumption and climate change, click here. This eco-friendly attribute aligns with global efforts to create a more sustainable, low-carbon future. Moreover, the extended lifespan of LED lights not only lessens the frequency of replacements but also mitigates the environmental impact associated with manufacturing, transportation, and disposal of traditional bulbs. This remarkable durability directly reflects a commitment to sustainable practices and responsible resource management.
Furthermore, the absence of mercury and other hazardous substances in LED lights has profound implications for human well-being and the environment. Mercury, a hazardous element, poses severe risks to both health and ecosystems when improperly discarded. By opting for LED lights, you eliminate the potential hazards associated with mercury exposure, thus safeguarding both human health and the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
LEDs vs. Traditional Lighting
Comparing LED lights to traditional lighting technologies, such as incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, highlights their energy-saving potential. On average and according to the Department of Energy, LED lighting uses about 75-80% less energy than traditional lighting options. Incandescent bulbs emit light by heating a filament, which results in a significant amount of energy wasted as heat. Fluorescent lights use a gas discharge and phosphor coating process, which is less efficient than direct electroluminescence in LEDs. Overall, LEDs convert a higher percentage of electricity into light, minimizing wastage and resulting in reduced energy consumption.
Additionally, LED lights provide better directional lighting, meaning they emit light in a specific direction without the need for reflectors or diffusers. This focused lighting minimizes light wastage and ensures the intended areas are properly illuminated. In contrast, traditional lighting sources emit light in all directions, requiring additional equipment or fixtures to direct the light where it is needed.
To put the energy savings into perspective, let’s look at an example. If you were to replace a traditional incandescent bulb with an LED bulb of the same brightness, the LED bulb would use about 75-80% less energy to produce the same amount of light. This means that for every 100 watts of electricity consumed by the incandescent bulb, the LED bulb would only consume around 20 watts.
While the initial investment may be higher, the energy efficiency and lifespan of LED lights make them a more cost-effective choice in the long run when compared to traditional lighting. Additionally, the decreasing cost of LED technology has made them more affordable in recent years. As technology advances and becomes more widespread, the price of LED lights will continue to decline, making them a more accessible option for consumers.
What else can you you do to save on electricity?
Besides lighting, there are many other areas you can save. Learn what costs a lot of electricity and then devise a plan to reduce it. Lighting is only one say to save, solar panels are another!
Conclusion
So, are LED lights energy-saving? LED lights are undeniably energy-saving due to their inherent efficiency, reduced energy consumption, extended lifespan, and environmental benefits. Their ability to produce bright, high-quality light, for longer, while using significantly less electricity positions them as a key player in the transition towards a more energy-efficient and sustainable lighting landscape. As individuals, businesses, and governments increasingly recognize the economic and environmental advantages of LED technology, the adoption of these energy-saving lights is positioned to become a cornerstone of modern lighting solutions.




