Is There A Downside To Having Solar?
Solar energy has undoubtedly become a major player in the renewable energy landscape, with homes and businesses across the US embracing the sun’s power to reduce their environmental footprint and utility bills. But, like any energy source, solar power is not without its downsides.
In this article, we’ll take a practical look at the disadvantages of solar energy, and help answer the question: is there a downside to having solar? From initial costs to intermittent energy generation, we’ll shed light on the real-world challenges associated with solar energy adoption. We will also highlight some of the key solutions that can be sought to mitigate some of the issues with solar energy, such as batteries and tax incentives. If you want to know – are solar panels worth it? – you should be able to establish that ofter knowing BOTH the downsides, and the upsides.
The Power Of Solar
Solar energy has the potential to reshape the global energy sector. Solar energy harnesses the sun’s radiant light, creating a renewable energy source. One of the most compelling advantages of solar power is its environmental sustainability. Unlike fossil fuels, which release harmful greenhouse gases and contribute to climate change, solar energy emits no pollutants during electricity generation. By reducing our dependence on non-renewable resources, solar power plays a pivotal role in mitigating the effects of climate change. It also helps curb air pollution, conserves water resources, and promotes biodiversity, creating a more sustainable and habitable planet for future generations.
Solar energy is also incredibly versatile and accessible. It can be harnessed virtually anywhere the sun shines, from remote villages far from the grid to urban rooftops and vast solar farms. This accessibility democratizes energy production, empowering individuals, communities, and nations to generate their electricity and reduce their reliance on centralized, often fossil fuel-based, power sources. Solar panels are modular and scalable, allowing systems to be tailored to meet specific energy needs, whether for residential homes, commercial businesses, or large-scale utilities.
Moreover, solar power offers economic benefits that extend to both individuals and society at large. Through the installation of solar panels, homeowners can significantly reduce their electricity bills or even generate income by selling surplus energy back to the grid. On a broader scale, the solar industry generates jobs and stimulates economic growth. As technology advances and economies of scale come into play, solar energy becomes increasingly affordable, making it an attractive investment for governments, businesses, and individuals alike.
But Is There A Downside To Having Solar?
While solar energy offers numerous benefits, there are also some downsides to having solar installed in your home. These are outlined below, as well as the potential solutions to help mitigate these challenges!
Upfront Costs
One significant challenge relates to the upfront cost of solar panel installation and the accompanying infrastructure. The technology’s expensive nature can present a significant obstacle, especially for smaller businesses or developing nations with limited financial resources. Overall, the cost of a solar panel system can vary from a few thousand dollars for a small residential system to tens of thousands of dollars for a larger, high-efficiency system with energy storage. On average, in the United States, a typical residential solar panel installation might cost between $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives and rebates.
However, governmental entities and local authorities frequently provide financial incentives like tax incentives, rebates, feed-in tariffs, and grants to promote the adoption of solar energy, thus alleviating some of the financial burden. Furthermore, the costs associated with renewable energy technologies, particularly solar power, have experienced substantial declines in recent decades, rendering them an increasingly cost-effective choice for generating electricity. Our research indicates that this trend will persist over the next decade, reducing the barrier posed by prohibitive costs. For instance, by 2030, the global average levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for solar photovoltaic (PV) is projected to decrease by 58% from its 2018 levels.
Intermittency and Storage Needs
Intermittency stands as a substantial obstacle within the world of renewable energy sources. In contrast to the consistent and predictable electricity supply offered by fossil fuel-based power generation, many renewable sources, such as solar and wind, rely on variables like weather patterns and sunlight. As a result, energy availability from these sources fluctuates, making them an intermittent energy source. These fluctuations can also disrupt the stability of the electricity grid, leading to challenges in maintaining a steady power supply to consumers and businesses. Sudden changes in renewable energy output, brought about by factors such as cloud cover, night time or abrupt decreases in wind speed, can result in imbalances between electricity generation and demand. This scenario, known as grid instability, carries the risk of power outages and voltage fluctuations.
An effective solution for addressing the challenges of intermittency associated with renewable energy lies in energy storage technologies, such as Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). Systems like batteries and pumped hydro storage have the capacity to store surplus energy generated during periods of strong renewable output, subsequently releasing it during times when renewable sources produce less or no energy. By balancing the supply and demand of energy, these storage solutions play a crucial role in stabilizing the electrical grid and ensuring an uninterrupted and reliable power flow, effectively mitigating the variable nature of renewable energy sources.

Technical Proficiency and Maintenance Challenges
Becoming skilled in technical matters and keeping solar systems well-maintained are extra hurdles when adopting solar power. Using solar energy means understanding how to design, install, and take care of the systems properly. These tasks can be complicated and may require specific knowledge, which might slow down organizations looking to switch to solar.
To overcome this obstacle, businesses or homeowners can consider collaborating with experienced solar companies, leveraging their knowledge to ensure accurate installation and optimized system performance. Effectively navigating these aspects is essential for maximizing the benefits derived from solar energy systems.
Space Constraints and Aesthetic Impact
Solar panels require a significant amount of roof or ground space. If you have a small roof or limited yard space, installing a solar system that can meet your energy needs may not be possible. Furthermore, some people find solar panels unattractive and believe they detract from the visual appeal of their home. While solar panel designs have improved over the years, not everyone considers them aesthetically pleasing.
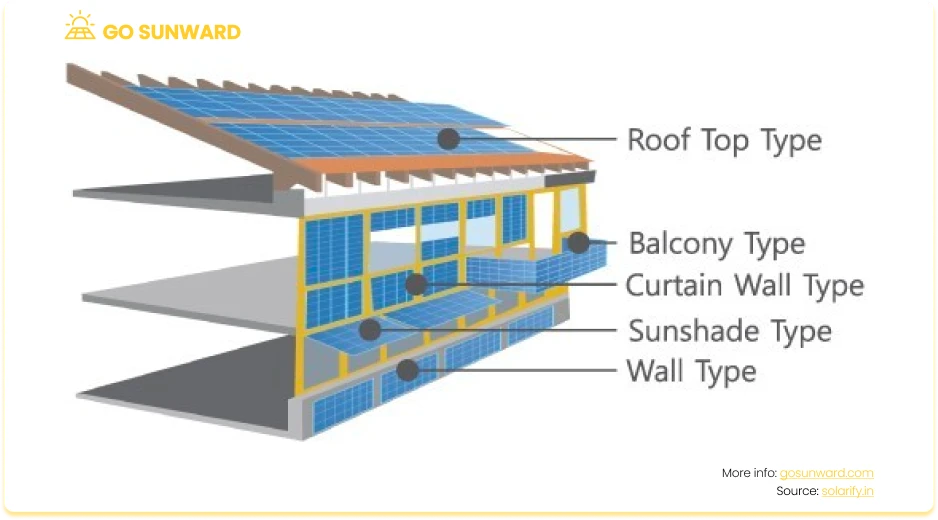
Thanks to technology. the downside of having solar is mitigated by the many different types of panels on the market that it’s becoming increasingly feasible to find panels that suit your tastes and space. For example, Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) refers to solar panels that are integrated directly into building materials such as roofing, windows, or facades. This approach combines solar power generation with architectural design, offering a seamless and aesthetically pleasing way to harness solar energy.
Weather Dependency
One notable drawback of solar energy systems is their susceptibility to weather conditions. Solar panels rely on the availability of sunlight to generate electricity, and various weather-related factors can impact their efficiency. During snowy winters, solar panels may become covered in snow, inhibiting their ability to capture sunlight. Likewise, the accumulation of dirt, leaves, or other debris on the panel’s surface can obstruct sunlight and diminish energy production. Furthermore, shading caused by nearby trees, buildings, or structures can create localized reductions in power output.
This weather-dependent aspect of solar power can be a downside to having solar. However, it also highlights the need for careful site selection, routine upkeep, and careful choice of panel. For example, bifacial panels can capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides, making them more efficient by reflecting sunlight off surrounding surfaces. They are often used in installations where light can bounce off reflective surfaces, such as white roofs or snowy environments. Furthermore, it is possible to thoroughly assess your local area’s renewable energy potential, including sunlight availability with online tools, before installation. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) offers comprehensive access to a wealth of renewable energy resource information via a range of tools, maps, reports, and data collections.
Installation Time
Installing solar panels to power a house is not quick; it requires careful planning and execution. Installation timing hinges on factors like house size, electricity requirements, solar panel efficiency, and installation complexity. The installation process typically involves several stages. The duration of each stage can vary based on factors such as local regulations and availability of equipment and personnel. On average, the entire process may take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months.
One solution to expedite the process of installing solar panels for residential use is to engage with experienced solar installation companies. These companies specialize in the planning and execution of solar panel installations, streamlining the process and ensuring that it is carried out efficiently. Their expertise can help navigate local regulations and optimize equipment and personnel scheduling, potentially reducing the overall installation timeline. Additionally, homeowners can proactively prepare their homes for solar panel installation by conducting necessary assessments and addressing any structural or electrical requirements in advance. This collaborative approach between homeowners and professional installers can speed up the transition to solar power.
Depreciation of Equipment
Solar panels and inverters, valuable assets in the renewable energy landscape, typically have a finite lifespan, ranging from 25 to 30 years. As these components age, their efficiency may gradually decline, resulting in reduced energy output compared to their initial years of operation. This decrease in efficiency can impact the return on investment and the overall cost-effectiveness of the solar energy system, potentially necessitating equipment replacement or upgrades to maintain optimal energy generation.
Proactively monitoring and maintenance remain crucial to mitigate the effects of equipment depreciation. By continuously tracking the performance of solar panels and inverters, any decline in efficiency can be detected early, allowing for timely interventions such as equipment upgrades or replacements. Moreover, as technology advances, newer and more efficient solar equipment becomes available, which can potentially counteract the depreciation effects and maintain or even improve overall energy generation.
Environmental Impact
The production of solar panels involves the use of raw materials, energy, and transportation, which can have environmental impacts. Additionally, the disposal of old solar panels at the end of their life can be an issue if proper recycling and disposal methods are not followed.
While solar panels do have lifecycle emissions, generated during production, transportation, installation, and disposal, these emissions are lower compared to fossil fuel-based electricity generation over the panel’s 25 to 30-year lifespan. Solar power also offsets CO2 emissions from fossil fuels, significantly reducing net emissions. The “carbon payback period,” the time to offset manufacturing and installation emissions, has shortened due to cleaner manufacturing and energy grids. This payback period is often just a few years, after which the panel provides emissions-free electricity for decades.

Conclusion
While solar power undeniably offers numerous benefits in the pursuit of clean, renewable energy, it is essential to acknowledge and address its downsides to make informed decisions about its adoption. The challenges associated with solar energy, such as intermittency, high upfront costs, land use concerns, and environmental impacts of manufacturing, cannot be ignored.
However, it’s crucial to recognize that many of these downsides are not insurmountable obstacles. Ongoing technological advancements, coupled with innovative solutions like energy storage, are progressively mitigating the issue of intermittency. Government incentives and policy changes are helping to make solar more financially accessible for a broader range of individuals and organizations.
As the solar industry matures and evolves, it will continue to address and alleviate its drawbacks, ultimately offering a more sustainable and reliable source of power. Moreover, when weighed against the numerous environmental, economic, and societal benefits it provides, the downsides of solar power serve as challenges to be overcome rather than reasons to dismiss this transformative energy source.
As we collectively transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy system, acknowledging and proactively addressing these downsides is a necessary step. By doing so, we can harness the full potential of solar energy while minimizing its drawbacks.




