How Much Money Do You Need To Live Off The Grid?
In an increasingly interconnected and technology-driven world, there is a growing interest in a lifestyle that offers a stark departure from the norm – living off the grid. This concept entails relying on one’s resources, generating power independently, and disconnecting from conventional utilities and services. It’s a lifestyle characterized by self-sufficiency, environmental consciousness, and a desire for a simpler way of living.
As we witness a surge in the desire for off-grid living, one pressing question often arises: How much money do you need to live off the grid? This question is not only about quantifying the financial investment required but also about understanding the broader implications and considerations that come with embracing a lifestyle that prioritizes independence from traditional systems.
In this article we will delve into the various facets of living off the grid, dissecting the costs involved, and shedding light on the motivations driving individuals towards this way of life. If you’re already done with your financial research and instead you want to know the exact costs and risks of installing solar, then read our guide on what it costs to install solar.
Understanding Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid is a lifestyle choice that involves disconnecting from centralized infrastructure and services, such as electricity, water supply, and sewage systems, to become self-reliant in meeting one’s basic needs. It’s about living independently, often in remote or rural areas, and generating the necessary resources on-site.
There are a few driving forces behind living off-grid:
Many individuals are drawn to off-grid living due to concerns about environmental sustainability. By reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing their carbon footprint, they aim to contribute positively to the planet’s health.
The desire for self-sufficiency is a driving force for those who choose to live off the grid. This lifestyle empowers individuals to take control of their essential resources, reducing their dependence on external sources and the vulnerability that comes with it.
Off-grid living often embraces a simpler, more minimalist approach to life. By cutting ties with the complexities of modern urban living, individuals can prioritize a more intentional, less consumer-oriented lifestyle. See these insane off the grid homes for more inspiration.

The Essential Elements Of Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid encompasses several fundamental aspects, each of which plays a crucial role in achieving self-sufficiency:
- Energy: Off-grid residents typically rely on renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, or hydropower to generate electricity and for some heating. Energy efficiency and conservation practices are key to managing power effectively.
- Water: Off-grid living necessitates independent water systems, utilising sources such as wells, rainwater collection, or natural springs. Water purification and conservation are essential considerations to ensure a sustainable supply.
- Food: Many off-grid individuals grow their own food through gardening, raising livestock, or practising hunting and foraging. This self-sustaining approach to food production reduces dependence on grocery stores.
- Housing: Off-grid homes are designed to be energy-efficient and often incorporate sustainable building materials. These structures are tailored to the specific needs and environmental conditions of the location. They could be anything from a basic shelter, van, log cabin or tiny home.
Costings
While a modest off-grid dwelling on an affordable plot of land can be established for as little as $10,000 to $20,000, particularly if you undertake much of the construction work independently, it’s important to note that the reality often differs. For most individuals venturing into off-grid living, the total expenditure typically exceeds the $100,000 mark when determining land and property costs.
Should your goal be complete self-sufficiency or generating income from your land, the financial commitment escalates considerably. High-quality land, larger acreage, and implementing more intricate systems necessitate a budget of at least $200,000.
Let’s break down how much money you need to to live off the grid:
How Much Money Do You Need To Live Off-Grid? The Initial Investment
When embarking on the journey of off-grid living, the initial investment is a crucial consideration. This phase involves substantial upfront costs that lay the foundation for self-sufficiency and sustainability. So, how much money do you really need to live off the grid?
Securing a suitable parcel of land is often the first and most significant expense. The cost of land varies greatly depending on location, accessibility, size, and terrain. Remote, off-grid properties in pristine natural settings may come at a premium, while more accessible plots in rural areas could be more affordable.
Building a self-sustaining, off-grid lifestyle necessitates investing in key infrastructure. This includes the installation of solar panels to harness solar power, establishing water sources such as wells or rainwater collection systems, and implementing septic systems for waste disposal. The costs associated with these infrastructure components can vary significantly depending on the scale and complexity of the setup.
The choice of shelter is another significant upfront expense. Off-grid enthusiasts may opt to build their own eco-friendly homes or purchase existing off-grid properties. Building materials, construction labor, and the integration of energy-efficient features, like a solar system, can all contribute to the cost of shelter.
Location is pivotal in determining the overall cost of transitioning to an off-grid lifestyle. Properties in regions with abundant natural resources, favorable climates, and proximity to essential amenities may come with a higher price tag but offer greater convenience. Conversely, more remote or challenging locations might demand lower initial investments but come with increased self-reliance requirements.
According to our research, the states offering the most affordable land, with an average cost of less than $2,000 per acre for farmland, are Nebraska, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Wyoming, New Mexico, Nevada and Montana.
It’s also important to note that you can claim various solar tax incentives from the US government, this will help you to save more on solar and ultimately lower your cost investment.
How Much Money Do You Need To Live Off-Grid? Ongoing Expenses
Beyond the initial investment, off-grid living entails a spectrum of ongoing expenses necessary to maintain self-sufficiency and ensure a comfortable, sustainable lifestyle.
Energy Production & Storage
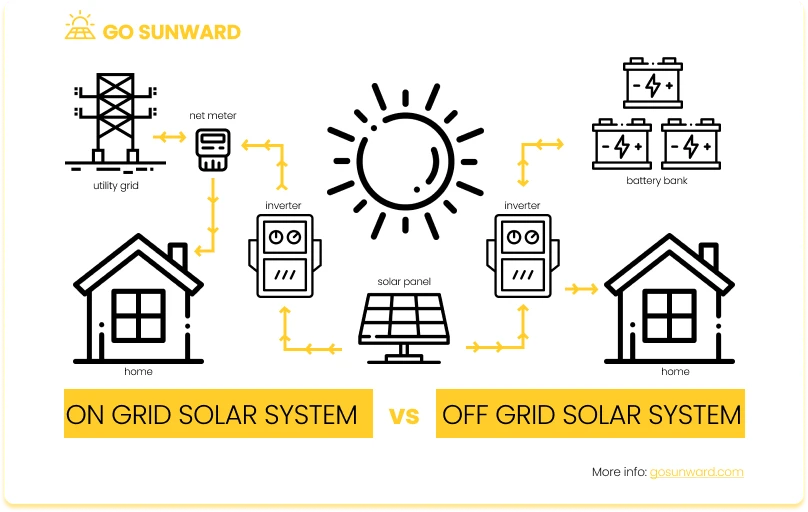
Off-grid energy production typically relies on renewable sources such as solar panels. Ongoing expenses encompass the maintenance of solar panels, inverters, and charge controllers, as well as backup batteries. Ensuring a reliable energy supply is critical for powering essential appliances and systems.
As a rough estimate, the initial investment for a basic off-grid solar system, including solar panels, inverters, charge controllers, and batteries, can range from $5,000 to $15,000.
Heating
Heating is a significant component of off-grid energy usage, and its cost can vary depending on the type of heating system used (e.g., wood stove, propane, electric heating) and the climate in the off-grid location.
As a rough estimate, heating costs for an off-grid household can range from $500 to $2,500 or more per year, depending on the heating method and energy efficiency of the home.
Water Management
Off-grid residents must manage their water supply carefully. Costs include water filtration and purification systems to ensure water quality, regular well maintenance, and occasional pump replacements. Effective water management is essential for drinking, irrigation, and daily household needs.
A rough estimate for the total cost to set up a comprehensive water system over a 10-year period might range from $10,000 to $30,000 or more. Remember that this estimate can be higher or lower based on specific circumstances, water quality, and individual preferences for water treatment and storage systems.
Food Production
Many off-grid individuals cultivate their own food through gardens and livestock. Recurring expenses encompass seeds, livestock care, fencing, and irrigation systems. Investing in sustainable farming practices and preserving food for the long term is essential for self-sufficiency.
As a rough estimate, over a 10-year period, the total cost for food production for an off-grid household can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more.
Waste Disposal
Responsible waste disposal is vital in off-grid living. Costs include the maintenance and periodic emptying of septic systems or composting toilets. Proper waste management not only ensures a clean and hygienic environment but also aligns with environmental principles.
As a rough estimate, over a 10-year period, the total cost for waste disposal in an off-grid setting can range from $2,000 to $10,000 or more.

How Much Money Do You Need To Live Off-Grid? Reducing The Costs
There are various strategies you could try to help reduce costs of living off-grid, mainly centred on boosting self-sufficiency.
Top Tip #1: Growing Your Own Food
One of the most effective ways to cut costs in off-grid living is by growing your own food. Establishing gardens and orchards allows you to produce fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs, reducing the need for costly trips to the grocery store. Additionally, raising livestock for meat, dairy, and eggs can further enhance your self-sufficiency in terms of sustenance.
Top Tip #2: Choose Solar Power!
Off-grid living often relies on renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, and hydropower. While the initial investment in these systems can be substantial, they pay dividends in the long run by significantly reducing or eliminating energy bills. This not only lowers your expenses but also aligns with eco-friendly principles.
Solar power is particularly well-suited to off-grid living, due to its accessibility, sustainability, and ability to provide energy independence. Off-grid locations often lack access to conventional power grids, making solar energy an ideal solution as it can be harnessed virtually anywhere the sun shines. Moreover, solar power generates electricity without emitting pollutants, aligning with off-grid living’s environmental and sustainability goals. Its scalability allows for customization to meet specific energy demands, and when paired with battery storage, it provides reliable power during periods of low sunlight or at night.
Top Tip #3: Resource Conservation
Practicing resource conservation is another key aspect of reducing costs. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, utilizing water-saving fixtures, and adopting sustainable waste management practices all contribute to lower ongoing expenses. Being mindful of resource consumption not only saves money but also minimizes your environmental impact.
Top Tip #4: DIY Solutions
Off-grid individuals often find creative, do-it-yourself (DIY) solutions to various challenges. This can involve building and repairing infrastructure, crafting homemade cleaning products, or constructing energy-efficient appliances. DIY projects not only save money but also foster a sense of self-reliance and empowerment.
Top Tip #5: Bartering & Trading
Living in a close-knit off-grid community offers the potential for bartering or trading with neighbors. This practice can help you access resources or services you may not have on your own property while minimizing cash expenditures. Bartering fosters a sense of community and mutual support, making it a valuable aspect of off-grid living.
Challenges and Unforeseen Costs
Living off the grid offers a unique and rewarding lifestyle, but it has its challenges and unforeseen expenses. We’ve detailed the challenges you. need to consider when budgeting how much money you need to live off the grid.
Extreme weather events: Off-grid locations are often in remote or rural areas, which can be susceptible to extreme weather events such as hurricanes, wildfires, heavy snowfalls, or droughts. These conditions can disrupt energy production, damage infrastructure, and pose safety risks. It’s crucial to invest in resilient systems and have contingency plans in place to mitigate the impact of such events.
Equipment breakdowns: Off-grid living relies heavily on various equipment, including solar panels, batteries, water pumps, etc. Like any machinery, these components can break down or require maintenance over time. Budgeting for repairs, replacements, and routine maintenance is essential to ensure a continuous and reliable off-grid lifestyle.
Regulatory compliance: Depending on the region, off-grid living may be subject to various regulatory requirements, such as zoning laws, building codes, and environmental permits. Ensuring compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a consideration to prevent unexpected costs related to fines or adjustments to your off-grid setup.
Budgeting for emergencies: Off-grid living can present unexpected challenges, from sudden equipment failures to unexpected medical expenses or urgent repairs. Having an emergency fund specifically earmarked for such situations is crucial for maintaining a secure and stable off-grid lifestyle. This preparation fund can cover unexpected costs that might otherwise jeopardize your self-sufficiency.
Routine maintenance: Off-grid systems require regular maintenance to operate efficiently. This includes cleaning solar panels, servicing generators, and monitoring water and waste systems. Budgeting time and resources for routine maintenance helps prevent larger problems down the road, ensures the long-term sustainability of your off-grid setup and helps boost savings over the longer-term.
Conclusion
This article has delved into the multifaceted world of off-grid living, exploring the financial considerations and aspects that shape this unconventional lifestyle. We’ve examined the initial investment required, ongoing expenses, and strategies for reducing costs through self-sufficiency. We’ve also highlighted the challenges and unforeseen costs that off-grid individuals may encounter, emphasizing the importance of emergency budgeting and routine maintenance.
It’s essential to recognize that the cost of living off the grid can vary significantly from one person to another and from one location to the next. Factors such as your choice of land, the extent of infrastructure needed, and the level of self-sufficiency you aim to achieve all play a role in determining the financial requirements.
As you contemplate the prospect of off-grid living, we encourage you to embark on a journey of thorough research and careful planning. Assess your unique needs, resources, and objectives. Consult with experts and seek guidance from those who have embraced this lifestyle. By understanding the costs and commitments involved and tailoring your off-grid approach to your individual circumstances, you can embark on a path that aligns with your vision of self-sufficiency and sustainability.




