Which Solar Panels Are The Most Efficient?
Solar energy has gained immense popularity as a renewable energy source, which is sustainable and increasingly affordable. Solar has emerged as a practical step towards reducing our carbon footprint and lessening our reliance on fossil fuels.
However, not all solar panels are created equal, and that’s where efficiency comes into play. Solar panel efficiency is crucial because it determines how effectively a panel can convert sunlight into usable electricity. In simple terms, the more efficient a solar panel is, the more electricity it can produce from the same amount of sunlight.
So, the main question we’ll explore in this article is, “Which solar panels are the most efficient?” We’ll delve into the world of solar panel efficiency, break down what it means, and examine why it’s essential. We’ll also discuss the various types of solar panels and their respective efficiencies, helping you make an informed choice if you’re considering solar energy for your home or business.
The Basics of Solar Panels
First, we need to cover the basics of solar power and how panels generate solar electricity.
Solar radiation, an electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun, bathes the Earth in its radiant glow. Although every corner of our planet experiences sunlight year-round, the quantity of solar radiation arriving at any given location varies. Innovative solar technologies harness and convert this radiation into practical forms of energy.
Solar power, being both renewable and environmentally friendly, faces limitations only in terms of our ability to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness in its conversion to electricity. Fortunately, two primary solar energy technologies efficiently translate solar energy into electrical power: photovoltaics (PV) and concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP).

The primary distinction between solar PV and solar CSP lies in their methods of converting solar energy into electricity. Solar PV systems directly convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells, while solar CSP systems concentrate sunlight to generate thermal energy used to produce electricity via steam-driven turbines.
For the purpose of this article, we will focus on solar PV, as it is used more commonly in the US and for the application of residential solar systems.
Solar PV 101
Solar PV technology harnesses the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon where photons, the basic units of light, strike the surface of a semiconductor material, such as silicon. This interaction imparts energy to electrons within the material, causing them to detach from their atomic bonds.
As these electrons, each bearing a negative charge, migrate toward the solar cell’s front surface, an electrical imbalance emerges between the cell’s front and rear surfaces. This discrepancy generates a voltage potential, akin to a battery’s positive and negative terminals. Electrical conductors on the cell capture these electrons. Electric current flows through the circuit when these conductors connect to an external load, such as a battery. This flow of electric current is recognized as direct current (DC), as electrons move in a continuous, unidirectional manner. Later, this DC is transformed into alternating current (AC) using inverters.
Solar PV technology finds common application in various settings, including rooftop installations, solar farms and arrays, as well as small-scale setups.
Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency
So which solar panels are the most efficient?To answer this, let’s first recap the term solar panel efficiency. In essence, it’s a measure of how well a solar panel can convert sunlight into electricity. The higher the efficiency, the more energy it can produce, which is vital for maximizing the benefits of solar power.
Efficiency isn’t just about generating more electricity; it’s also about cost savings. More efficient panels mean you get more bang for your buck, as you’ll need fewer panels to achieve the same energy output. This can significantly impact your investment in solar energy.
To gauge solar panel efficiency, we rely on something called an efficiency rating. This rating gives us a standardized way to compare different panels’ performance. In the upcoming sections, we’ll delve deeper into the efficiency rating and how it’s measured, giving you a clear understanding of what to look for when shopping for solar panels.
The average efficiency rating of a standard monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panel typically falls in the range of 16% to 20%. This means that these panels can convert about 16% to 20% of the sunlight they receive into electricity. High-efficiency panels, such as those produced by companies like SunPower or LG Solar, can have efficiency ratings exceeding 20%, often reaching 23% or higher. On the other hand, lower-cost panels may have efficiency ratings closer to the lower end of the range.
Types of Solar Panels
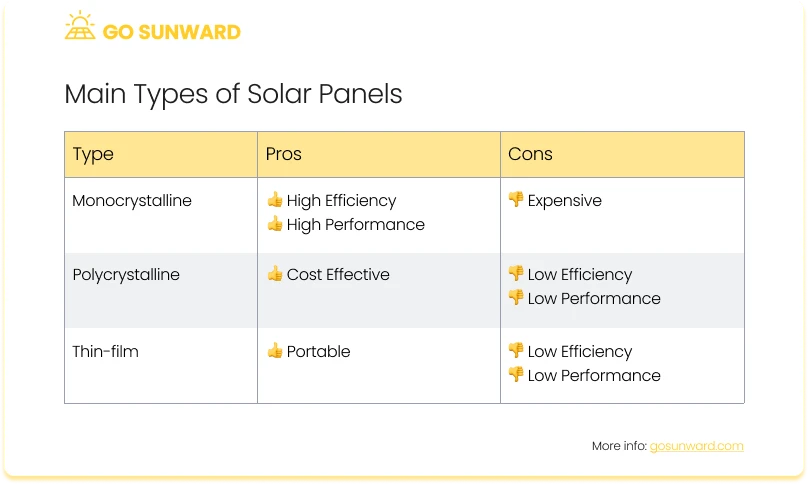
Solar panels come in various types, each with unique characteristics and efficiencies. At present, photovoltaics is one of the most recognizable methods for capturing solar energy and mainly utilizes three technology panel types: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline and Thin-Film Solar Panels. For more detailed information on the different types of panels, click here.

Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from single-crystal silicon, producing an exceptionally efficient and uniform structure. The production process involves slicing cylindrical silicon ingots into thin wafers, which are the foundation for individual solar PV cells. Thanks to the high purity of monocrystalline silicon, these panels outperform other types in terms of converting sunlight into electricity.
Their distinctive dark black hue and rounded edges set monocrystalline solar panels apart. Their superior efficiency means they occupy less space to achieve the same power output, making them ideal for installations with limited rooftop or ground area. However, it’s worth noting that their higher manufacturing costs can result in slightly elevated prices.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels feature multiple crystal structures of silicon, giving them a distinctive bluish tint. The production process entails melting raw silicon and casting it into molds to form square-shaped wafers. Polycrystalline panels are known for their cost-effectiveness, as they are easier and more economical to manufacture compared to monocrystalline panels.
Although slightly less efficient than monocrystalline counterparts, ongoing technological advancements have narrowed the efficiency gap between the two types. Polycrystalline panels now offer good performance while remaining a popular choice for both residential and commercial installations due to their cost-effectiveness and durability.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made from thin layers of semiconductor materials, such as amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). This technology yields solar panels that are lightweight, flexible, and adaptable, capable of integration into various surfaces, including those with curves or irregular shapes.
While thin-film panels exhibit lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, they offer distinct advantages in specific scenarios. They excel in low-light conditions and demonstrate resilience to high temperatures. Their ease of integration makes them well-suited for applications like building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), solar shingles, and other innovative solar designs.
New Panel Technologies To Keep An Eye On
Here are some promising technologies and trends that are worth exploring to enhance the efficiency of solar panels.
Perovskite Solar Cells: Perovskite solar cells have gained significant attention due to their potential for high efficiency and low production costs. These cells use a different material structure than traditional silicon cells, allowing them to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight. Researchers continue to work on improving their stability and longevity.
Bifacial Solar Panels: Bifacial solar panels can capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides of the panel, reflecting sunlight off surfaces like rooftops or the ground. By utilizing this reflected light, bifacial panels can achieve higher energy yields, especially in environments with high albedo (reflectivity) surfaces.
Tandem Solar Cells: Tandem or multi-junction solar cells combine different materials with varying bandgaps in a single panel. This allows them to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, increasing efficiency. Tandem solar cells have shown promise in laboratory settings and are gradually making their way into commercial production.
Solar Tracking Systems: Solar tracking systems adjust the orientation of solar panels to follow the sun’s path throughout the day. By directly facing the sun, panels can maintain optimal angles for sunlight absorption, resulting in increased energy production. Single-axis and dual-axis tracking systems are becoming more common.
Advanced Materials: Ongoing research into advanced materials for solar panels aims to enhance their efficiency. This includes improving the conductivity of materials, reducing optical losses, and increasing panels’ durability under harsh environmental conditions.
Thin-Film Technologies: Thin-film solar panels, such as CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide) and CdTe (cadmium telluride), continue to evolve. These panels have the advantage of flexibility and can be integrated into various surfaces. Researchers are working on improving their efficiency and reducing production costs.
Anti-reflective Coatings: Anti-reflective coatings are designed to reduce the amount of sunlight that bounces off the surface of solar panels. By minimizing reflection, more light can be absorbed by the panel’s photovoltaic cells, increasing overall efficiency.
Quantum Dot Solar Cells: Quantum dots are nanoscale semiconductor materials that can be incorporated into solar cells. They have unique optical properties that can improve the absorption of light and the conversion of photons into electricity.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
Efficiency is not just about the design and quality of the panels; external factors also significantly determine their efficiency.
Here are some key factors to consider:
Temperature: Solar panels operate most efficiently when they are cooler. High temperatures can reduce their efficiency, causing a drop in electricity production. This phenomenon is known as the temperature coefficient. To mitigate this, solar panels are often installed with a slight tilt to allow air to flow underneath and cool them down.
Shading: Shade, even a small amount, can substantially negatively impact a solar panel’s efficiency. When any part of a panel is shaded, it disrupts the entire panel’s performance. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure solar panels are placed in locations with minimal shading throughout the day.
Orientation: The orientation of solar panels plays a crucial role in their efficiency. Panels should ideally face the sun to maximize energy production. This typically means facing south in the Northern Hemisphere, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it’s north. Proper placement and orientation are essential considerations during installation
Dust and Debris: The accumulation of dirt, dust, or debris on the surface of solar panels can reduce their efficiency. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Technological advancements have been instrumental in improving solar panel efficiency over time. Engineers and scientists have continually refined solar panel designs, materials, and manufacturing processes to increase their ability to convert sunlight into electricity efficiently. These advancements have led to higher efficiency ratings, more durable panels, and increased energy production, making solar power a more viable and attractive option for consumers and businesses alike.
What Can You Do To Boost Efficiency?
While the efficiency of your solar panels largely depends on their design and quality, there are several steps you can take to maximize their performance and make the most of your solar energy system.
Here are some practical strategies to boost solar panel efficiency:
Proper Installation and Orientation: Ensuring that your solar panels are correctly installed and oriented is crucial. Panels should be positioned to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the day. This typically means facing them south in the Northern Hemisphere and north in the Southern Hemisphere. Additionally, the tilt angle should be optimized for your geographical location.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Over time, dust, dirt, leaves, and other debris can accumulate on the surface of your solar panels, reducing their efficiency. Regular cleaning, typically with water and a soft brush, can help maintain optimal performance. Also, inspect the panels for any physical damage or shading issues that may have developed. For more information on panel maintenance, read this article.
Shading Management: Shading, even from a single tree or rooftop obstacle, can significantly impact solar panel efficiency. Trim or remove any nearby obstructions that cast shadows on your panels, especially during peak sunlight hours. Shade can disrupt the entire panel’s performance.
Monitoring System Performance: Invest in a monitoring system for your solar panels. This technology allows you to track the real-time performance of your system, including individual panel efficiency. Monitoring can help you identify issues promptly and ensure that your system is operating at its best.
Energy-Efficient Appliances: Pair your solar panels with energy-efficient appliances and lighting. By reducing your overall energy consumption, you can make the most of the clean energy generated by your panels and potentially decrease the size of your solar installation.
Battery Storage: Consider adding battery storage to your solar energy system. Batteries store excess energy generated during the day for use during nighttime or cloudy periods. This can increase the self-sufficiency of your solar power system and reduce dependence on the grid.
Regular Professional Inspections: Schedule periodic inspections by a qualified solar technician. They can identify and address any issues with your system that may be affecting efficiency, such as wiring problems or inverter malfunctions.
Stay Informed: Keep up with advancements in solar technology and best practices for maintaining efficiency. As the solar industry continues to evolve, new technologies and techniques may become available to enhance your system’s performance.
Top 5 Brands To Look Out For
In today’s market, several top-performing solar panels stand out for their exceptional efficiency and energy production. These panels not only generate more clean energy but also offer long-term benefits in terms of cost savings and sustainability.
- SunPower: SunPower has consistently been a leader in solar panel efficiency. Their Maxeon solar panels are known for their high conversion rates, often exceeding 23% efficiency. SunPower’s panels are renowned for their durability and performance, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial installations.
- Panasonic: Panasonic is a reputable brand that offers highly efficient solar panels. Some of their panels boast efficiency ratings above 20%. Panasonic’s panels are recognized for their reliability and performance in various environmental conditions
- REC Group: REC Group is a Norwegian solar panel manufacturer that produces panels with competitive efficiency ratings. Their Alpha series panels have achieved efficiency levels of around 21%. REC Group’s panels are known for their robust design and innovative technology.
- Canadian Solar: Canadian Solar is a global player in the solar industry and offers a range of solar panels, including high-efficiency options. Their most recently released panel series have efficiency ratings between 19% and 21%. Canadian Solar is known for providing cost-effective, high-quality panels.
- Trina Solar: Trina Solar is one of the world’s leading solar panel manufacturers, based in China, and known for producing a wide range of high-quality solar panels for residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar installation. Trina Solar panels are known for their competitive efficiency ratings. Their monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels often have efficiency levels ranging from 16% to 22%, depending on the specific model and technology used.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of solar panels can vary depending on the specific model and series within each brand. When considering solar panels for your project, it’s essential to research the latest models, consult with local solar installers, and consider factors such as budget, available space, and local climate conditions.
High Efficiency Panels: Advantages vs Disadvantages
Using the most efficient solar panels has both advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully considered when deciding on a solar panel system.
Advantages:
One significant advantage of opting for highly efficient solar panels is their ability to generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. This translates into increased clean energy production, potentially allowing you to cover a larger portion of your electricity needs, ultimately fostering greater energy independence.
High-efficiency panels also offer space efficiency. They can produce the same amount of electricity as their lower-efficiency counterparts while occupying less physical space. This feature is especially beneficial for properties with limited roof or ground space for solar installations.
Moreover, high-efficiency panels may lead to reduced installation costs. Since they generate more electricity per panel, you may require fewer panels to meet your energy goals. This not only minimizes the physical footprint of the installation but can also result in cost savings related to racking, mounting, and installation labor.
Aesthetically, high-efficiency panels often boast sleeker designs and a more uniform appearance. This aesthetic appeal can be particularly advantageous for residential installations where visual harmony with the property is a priority.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of high-efficiency panels are noteworthy. Generating more electricity from fewer panels reduces the overall environmental impact, including lower carbon emissions associated with the production and transportation of solar panels.
Disadvantages:
It is also crucial to consider the potential drawbacks of high-efficiency solar panels:
One notable disadvantage is the higher initial cost. High-efficiency panels typically come with a premium price tag compared to standard-efficiency alternatives. This upfront cost can be a significant hurdle for some homeowners or businesses, despite the long-term savings they may offer.
There is also a concept of diminishing returns. As you move up the efficiency scale, the additional cost per percentage point of efficiency improvement tends to rise. This means that the economic benefit of transitioning from standard-efficiency to high-efficiency panels might be more favorable than the leap to ultra-high-efficiency panels.
For installations with ample space, the reduced space requirements of high-efficiency panels may not be a significant advantage. In such cases, the added cost of high-efficiency panels might not be justified.
Manufacturing high-efficiency panels can sometimes involve the use of rare materials, which may have environmental implications. However, advancements in sustainable production practices are working to mitigate these concerns.
Lastly, high-efficiency panels may exhibit increased sensitivity to shading issues compared to standard panels. Even a small amount of shade on a high-efficiency panel can result in a notable loss of energy production.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the critical role of solar panel efficiency in our journey towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. We’ve looked into the definition of efficiency, how it affects energy production and cost savings, and the various factors that can influence it, successfully answering ‘which solar panels are the most efficient’. We’ve also examined the common types of solar panels, their differences in efficiency, and the pros and cons of each.
The significance of solar panel efficiency cannot be overstated. It directly translates to harnessing more clean energy from the sun’s abundant rays, reducing our carbon footprint, and advancing our transition to a greener planet. High-efficiency solar panels not only help protect the environment but also provide tangible cost savings over the long term, making them a wise investment for homeowners and businesses alike.
As we’ve seen, the solar industry is continually evolving, with new technologies and innovations on the horizon. Perovskite cells, bifacial panels, tandem solar cells, and advanced materials are just a few of the exciting developments that hold promise for further enhancing solar panel efficiency.
If you’re considering harnessing the power of the sun through solar panels, we encourage you to take action and explore your options. Consult with local solar professionals to assess your unique needs, evaluate the latest advancements in solar technology, and determine the most suitable solar panel solution for your location and budget.
By making informed choices and embracing solar panel efficiency, we can collectively contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.




