Solar Panel Calculator: See How Many Solar Panels You Need
Solar energy has emerged as a compelling solution for those who want to reduce their environmental footprint whilst at the same time cutting down on electricity expenses. With the increasing awareness of climate change and the rising cost of traditional grid electricity, more people are turning to solar power as a sustainable and cost-effective alternative.
As solar energy systems become more accessible, homeowners are keen to harness the sun’s power to generate clean, renewable electricity. However, determining the right number of solar panels needed for their specific energy requirements can be a complex task. This is where a solar panel calculator becomes an invaluable tool.
This article aims to demystify the process of sizing a solar panel system by guiding readers on how to use solar panel calculators effectively. Whether you’re considering solar energy for your home or business, understanding the factors involved in calculating your solar panel requirements is essential.
Understanding Solar Panel Systems
Solar panels operate on the principle of harnessing sunlight and converting it into electricity through a process called photovoltaics. These panels consist of photovoltaic cells that capture sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
A complete solar panel system comprises several components, with solar panels being the primary component responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. In addition to panels, the system includes inverters, which convert DC electricity into the alternating current (AC) used in homes and businesses. Mounting hardware is essential for securing the panels in the optimal position to capture sunlight effectively.
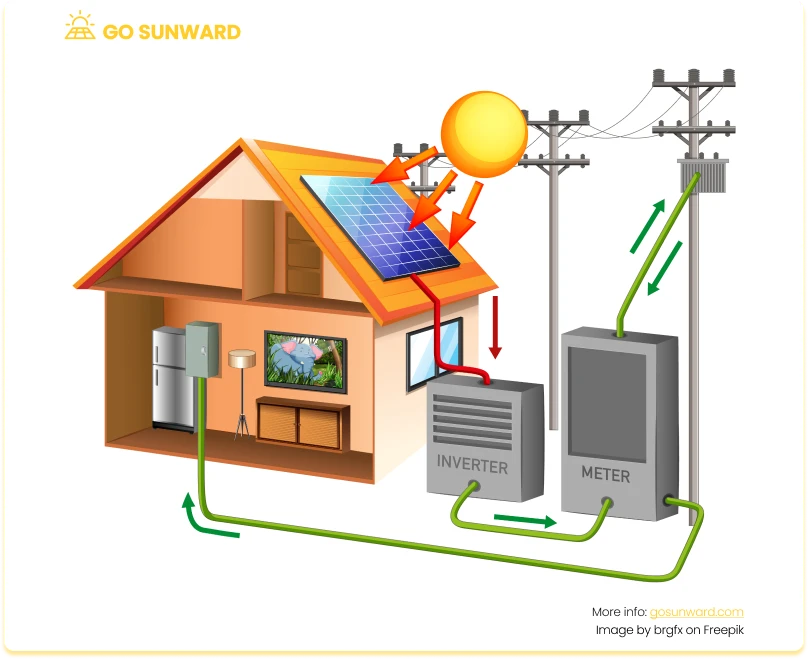
Properly sizing a solar panel array is crucial to meet your energy needs. An accurately sized system maximizes energy production and can significantly reduce or eliminate your reliance on conventional grid electricity, leading to greater cost savings and environmental benefits. A solar panel calculator aims to help you determine the ideal size for your specific requirements, making the transition to solar power seamless and efficient.
Solar Panel Calculators: The What & The Why
Solar panel calculators are valuable tools that help homeowners estimate the number of solar panels required to meet their energy needs based on factors like location, energy consumption, and panel efficiency.

5 Reasons Why You Should Use A Solar Panel Calculator
#1: Precision in Planning – Solar calculators estimate how many solar panels are needed for your specific energy consumption, helping you avoid over or under-sizing your solar system.
#2: Cost Estimation –They help you calculate the initial costs of a solar panel installation, allowing for better financial planning and budgeting.
#3: Enhanced Savings – By accurately determining your solar panel requirements, you can maximize energy production and savings, ensuring you get the most out of your investment.
#4: Informed Decision-Making – Solar calculators provide valuable insights into the potential benefits of solar energy, aiding you in making informed choices.
#5: Comparative Analysis – You can use solar calculators to compare different scenarios, such as panel efficiency, location, and shading, to find the optimal solar setup for your needs.
Online Solar Panels Calculators vs The DIY Calculator Approach
In the quest to determine the right number of solar panels for your home, two primary approaches stand out: the convenience of online solar panel calculators and the hands-on DIY method through step-by-step guides.
Online solar panel calculators are user-friendly digital tools designed to estimate your solar panel needs swiftly. They cater to individuals seeking a streamlined solution without requiring extensive technical analysis. These calculators guide users to input essential information like location, monthly energy consumption, and roof characteristics. Subsequently, they generate a quick result, often specifying the required number of solar panels to meet energy demands.
These calculators are ideal for those desiring a rapid assessment without delving deep into the intricacies of solar panel sizing. However, their customization options can be limited, and they may lack detailed explanations of the calculations, making them more suitable for users seeking a quick answer rather than an in-depth understanding.
On the contrary, opting for a DIY approach through a step-by-step guide offers a more comprehensive understanding of the solar panel sizing process. These educate readers on various factors impacting solar panel requirements, such as energy consumption, location specifics and panel efficiency.
While articles demand more time and engagement than online calculators, they empower readers with knowledge and flexibility. Readers can adapt calculations to their unique situations, account for seasonal variations, and explore diverse scenarios.
DIY Solar Calculator: Follow These Steps
Step 1: Calculate Your Energy Usage
To determine your average energy needs, determine your household’s typical electricity consumption over a set period, like a month or a year. You’ll find this information on your utility bills, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). If you don’t have a daily average, you can derive it by dividing your monthly or yearly usage by 30 or 365 days, respectively. Then, divide that result by 24 to get your hourly average electricity use
For reference, the average US home uses around 900 kWh per month, which is roughly 30 kWh per day or 1.25 kWh per hour. However, energy use varies depending on factors like house size, location, appliance efficiency, and local utility rates.
Your daily energy target serves as a baseline for calculating your solar needs, representing the kilowatt-hours your solar system should generate to cover a significant portion, if not all, of your electricity needs.
Remember that energy use can fluctuate due to seasonal changes and lifestyle adjustments. To make a more accurate estimate, calculate separate averages for different seasons and consider future changes like home upgrades or energy-efficient appliances. Solar panels also have varying efficiency, so it’s wise to include a 25% buffer in your daily energy target to ensure consistent solar energy production to meet your needs.

Step 2: Assessing Sunlight Availability
The amount of sunlight your location receives directly impacts your residential solar system’s energy generation potential. Typically, the average American roof receives about four hours of “usable” sunlight each day. However, this duration varies significantly based on your geographical location, ranging from sun-drenched deserts to misty mountain regions. To assess your area’s sunlight availability, you can utilize the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) resources, such as tools, maps, reports, and data.
Next, convert your hourly energy consumption (as determined in step 1) into watts by multiplying it by 1,000. Then, divide this average hourly wattage requirement by the daily peak sunlight hours specific to your location. This calculation yields your panels’ hourly energy production target. For instance, a typical U.S. home (consuming 900 kWh/month) in an area with five daily peak sunlight hours would require a 6,000-watt solar system.
Step 3: Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency and Wattage
Determining the right solar panel system for your property involves grasping the relationship between panel efficiency and wattage. Here’s a clear breakdown:
Solar Panel Efficiency:
- Efficiency gauges how effectively a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity, expressed as a percentage.
- Higher efficiency means a panel captures more sunlight as electricity. For instance, a 20% efficient panel turns 20% of sunlight into power, with the rest lost as heat or other forms.
- Average solar panel efficiency ranges from 18% to 20%, but it can vary.
Solar Panel Wattage:
- Wattage measures the actual electrical power a solar panel generates under specific conditions, usually in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
- Panels come with labels indicating their kilowatt-hour output per hour under ideal conditions, called Standard Test Condition (STC) rating. For example, a panel with a 300W STC rating can produce 300 watts under perfect conditions.
- Wattage relies on panel size, solar cell efficiency, and sunlight intensity.
Solar panels vary widely in performance and characteristics. Common in residential setups, photovoltaic (PV) solar panels range from 150W to 370W per panel, based on factors like size, efficiency, and cell technology. Panels with higher efficiency produce more wattage, potentially reducing the quantity needed for the same energy output. On average, typical solar panels generate around 250 watts, but this can vary. Choose panels that align with your location, energy needs, and budget.
Step 4: Determining Your Solar Panel Size
When working with a small or uniquely shaped roof, the size and quantity of solar panels become critical considerations. If you have ample roof space, you might want to explore larger panels, even with slightly lower efficiency, as they often come at a more cost-effective price per panel. This approach can help you achieve your desired energy production levels.
Conversely, if your available roof area is limited or experiences partial shading, opting for smaller, high-efficiency panels can be more advantageous. This strategy maximizes the long-term power generation potential, resulting in greater cost savings over time.
Regarding solar panel dimensions, most residential panels today measure approximately 65 inches by 39 inches, equivalent to 5.4 feet by 3.25 feet, with slight variations depending on the manufacturer.
Step 5: Final Calculations
You can calculate how many solar panels you need by multiplying your household’s hourly energy requirement (in watts) by the peak sunlight hours for your area and dividing that by a panel’s wattage. In other words:
Number of Panels = (Hourly Energy Requirement in watts x Peak Sunlight Hours) / Solar Panel Wattage
Companies often consider a 20% buffer when planning a solar installation to consider system inefficiencies.
Common Mistakes To Avoid With Solar Panel Calculators
While solar panel calculators are useful tools, they are subject to errors if not used correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using solar panel calculators and how to prevent them:
Inaccurate Energy Consumption Data: One of the most significant mistakes is providing incorrect or outdated data about your energy consumption. This can lead to an overestimation or underestimation of your solar panel requirements. To prevent this, gather recent utility bills to ensure accurate kWh data.
Neglecting Location Details: Location plays a vital role in solar panel calculations. Failing to enter precise location information can result in inaccurate estimations of sunlight availability and climate conditions. Always double-check the location details to get reliable results.
Ignoring Panel Efficiency: Solar panel calculators often use default efficiency values, which may not reflect the actual performance of your chosen panels. If you have specific efficiency data for your panels, be sure to enter it accurately to receive more precise results.
Overlooking Shading and Obstructions: Some calculators may not account for shading from nearby trees, buildings, or other obstructions. Failing to consider shading can lead to an overestimation of solar panel output. Ensure you provide shading information for accurate calculations.
Unrealistic Energy Goals: Setting unrealistic energy independence goals or expecting too much from your solar panel system can result in oversized or undersized installations. Be realistic about your energy needs and goals to ensure your solar panel system is appropriately sized.
Disregarding Local Regulations: Local regulations, incentives, and permits can impact your solar panel project. Neglecting these factors can lead to complications and delays. Research and understand the local requirements and regulations to avoid potential issues.
Relying Solely on Online Calculators: While solar panel calculators are valuable tools, they should not be the sole basis for your solar panel decisions. It’s essential to consult with a local solar professional or installer to validate your calculations and ensure they align with your specific circumstances.
Not Considering Future Changes: Failing to account for future changes in your energy consumption or household size can result in an inadequate solar panel system. Anticipate future needs and factor them into your calculations for a long-term solution.
By avoiding these common mistakes and using solar panel calculators as a starting point rather than a final decision-maker, you can make more informed choices about your solar panel installation.
Conclusion
Using a solar panel calculator is a vital step in your journey towards harnessing the benefits of solar energy. By leveraging these tools, you can tailor a solar system to your specific energy needs and location.
We encourage all readers to take the next proactive step in their solar journey. Don’t rely on guesswork when it comes to your solar panel requirements; instead, use our calculators to obtain precise and actionable insights.




