On Grid Vs Off Grid Solar: What’s The Difference?
Solar energy is a sustainable and renewable power source that has gained widespread recognition for its environmental benefits, accessibility and increasing affordability. Solar power systems harness the sun’s energy to generate electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. In recent years, the adoption of solar power has surged, finding its way into an increasing number of homes and businesses. This growing popularity is a testament to the desire for cleaner and more sustainable energy, and as consumers seek to make savings on their electricity bills. This article will explore the fundamental distinctions between on-grid vs off-grid solar systems.
On-grid systems are connected to the conventional utility grid, allowing users to both consume and potentially sell excess energy back to the grid. In contrast, off-grid systems operate independent of the grid, often utilizing energy storage solutions like batteries. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of these two approaches is crucial for individuals and businesses considering solar energy as a viable option for their energy needs.
On-Grid Solar
On-grid solar systems, often referred to as grid-tied solar systems, are solar energy setups that are seamlessly integrated with the conventional utility grid. These systems harness sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels, converting it into electricity using solar inverters, and feeding the generated power directly into the utility grid. The key distinguishing feature of on-grid solar is their connection to the grid, which allows for a dynamic exchange of energy.
The connection to the utility grid offers a significant advantage: net metering. Net metering is a billing arrangement that allows solar system owners to send excess electricity they generate back into the grid when their solar panels produce more power than is consumed. This surplus energy is essentially credited to their account, and they can draw from these credits during periods when their solar panels are not generating sufficient electricity, such as at night.
On-grid solar systems thus enable homeowners and businesses to reduce their electricity bills and even earn income by selling surplus energy to the grid, making them a financially attractive option for those connected to the grid.

Off-Grid Solar
Off-grid solar systems, in contrast to on-grid systems, operate independently of the utility grid. These self-sufficient systems are designed to meet all the energy needs of a home, business, or remote location without any reliance on external power sources. The hallmark of off-grid solar systems is their use of energy storage solutions, typically in the form of batteries, to store excess energy generated during the day for use during periods when sunlight is scarce, such as at night or during cloudy days.
One of the primary advantages of off-grid solar is the freedom it offers from the utility grid. This independence is particularly valuable in remote or rural areas where grid access may be limited or unavailable. Off-grid systems provide reliable and continuous power, ensuring that critical loads, such as lights and essential appliances, remain operational even without grid electricity.
This reliability and autonomy make off-grid solar an ideal choice for those embracing off-grid living, where self-sufficiency and resilience are key priorities. For more information on ‘off-grid living’, click here.
On-Grid vs Off-Grid
When comparing on-grid vs off-grid solar systems, several fundamental distinctions come to the forefront. These differences have implications for energy storage, cost considerations, and the level of grid dependence.
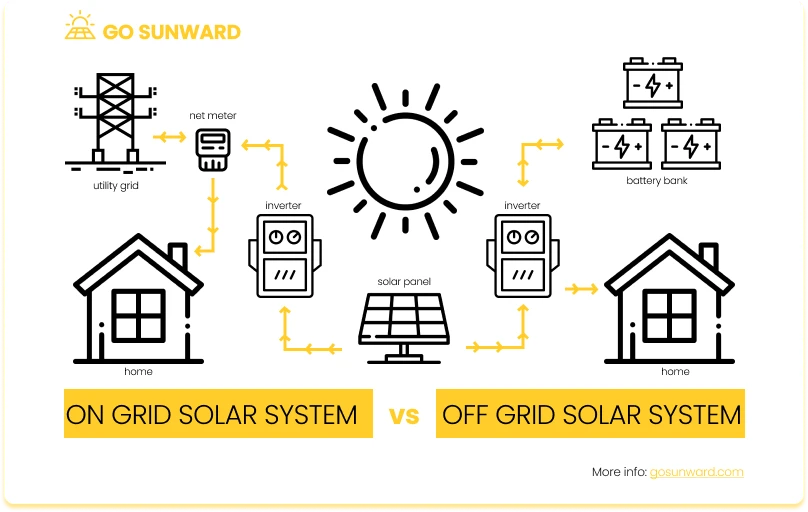
Firstly, the primary difference lies in energy storage. On-grid solar systems typically do not require extensive energy storage solutions because they feed excess energy directly into the utility grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when needed. In contrast, off-grid solar systems heavily rely on energy storage, typically using batteries to store surplus energy generated during the day for use during periods with limited or no sunlight.
Secondly, cost considerations vary significantly between the two systems. On-grid solar systems are generally more cost-effective to install since they do not require expensive battery storage. Off-grid solar systems tend to have higher upfront costs due to the need for batteries and additional components for energy storage and management.
Lastly, the level of grid dependence is a crucial difference. On-grid solar systems remain connected to the utility grid, providing a continuous power supply even when solar energy generation is insufficient. Off-grid systems, as the name suggests, operate independently and do not rely on the grid. This makes off-grid solar an attractive option for individuals and communities seeking complete energy self-sufficiency.
Considerations For Choosing On Grid vs Off Grid Solar
Choosing between on-grid vs off-grid solar systems requires careful consideration of individual needs and circumstances.
Here, we offer guidance on making an informed decision based on various factors, including location, budget, energy goals, and environmental priorities.
- Location: Assess the accessibility of the utility grid. If you are in a remote area with limited or no grid access, off-grid solar may be the practical choice. Conversely, if you reside in an urban or suburban location with reliable grid access, on-grid solar may suffice.
- Budget: Consider your budget constraints. On-grid solar systems typically have lower upfront costs, making them more budget-friendly. Off-grid systems require investment in energy storage solutions, which can increase the initial expenditure.
- Energy Goals: Define your energy goals. If reducing your carbon footprint and achieving energy self-sufficiency are top priorities, off-grid solar aligns better with these objectives. On-grid solar is more suitable for those looking to save on electricity bills without complete energy independence.
- Environmental Priorities: Examine your commitment to environmental sustainability. Both systems contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but off-grid solar allows for a more direct and immediate impact by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels.
What About Hybrid Solar Systems?
As we look ahead to the future of solar energy, there are exciting emerging trends that warrant attention. One notable development is the rise of hybrid solar systems.
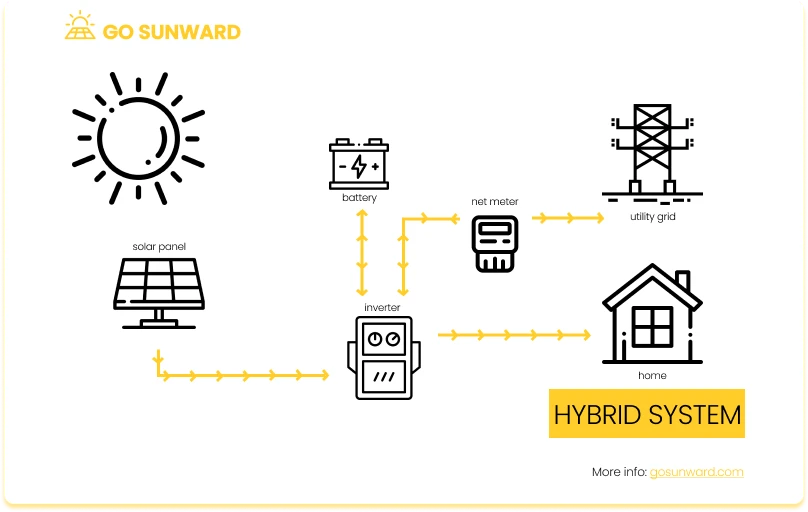
A hybrid solar system offers a blend of the advantages associated with both on-grid and off-grid solar setups. This hybrid configuration incorporates battery storage akin to off-grid systems while retaining the capability to connect to the utility grid. This dual functionality brings about several benefits, including the ability to rely on the grid as a backup power source when your battery reserves are depleted, and the potential to leverage net metering.
One key advantage of hybrid systems is their capacity to deliver a consistent electricity supply, especially in situations where the grid experiences disruptions or when solar panel output is insufficient. During daylight hours, excess solar energy is stored in the system’s batteries, ensuring a surplus of power for nighttime use or periods of low solar generation. Moreover, should the batteries reach low levels, the hybrid system can seamlessly tap into the grid to maintain a continuous electricity supply.
Overall, hybrid solar systems cater to homeowners aiming for a high degree of self-sufficiency while retaining the security of a grid connection. However, it’s worth noting that the installation of hybrid solar systems is more intricate and costly compared to their purely on-grid or off-grid counterparts.
Conclusion
This article has delved into the fundamental differences between on-grid and off-grid solar systems, shedding light on their unique characteristics, benefits, and considerations. Whether you prioritize reduced electricity bills, energy self-sufficiency, or environmental sustainability, understanding these distinctions is essential in making informed decisions about adopting solar energy solutions.
The adoption of solar power, whether on-grid or off-grid, plays a pivotal role in our collective efforts to transition towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly energy landscape. The choice between these systems ultimately depends on your specific needs and circumstances.




