How Much Solar Do I Need To Be Completely Off-Grid?
‘Off grid living’ has transcended its niche status and become increasingly popular. This lifestyle shift is driven by a growing awareness of environmental issues and a stronger desire for self-sufficiency and sustainability. Off-grid living represents a departure from the traditional reliance on centralized utilities, where individuals and communities take charge of their energy needs, resource management, and ecological impact. At the heart of this transformation lies the crucial role of solar power, as it empowers off-grid enthusiasts to harness renewable energy, reduce their carbon footprint, and forge a path toward complete self-sufficiency. Amidst this shift towards off-grid living, a pivotal question arises: “How much solar do I need to be completely off-grid? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of off-grid living, explore the energy needs of a self-sustaining lifestyle, and provide insights into the solar solutions that can pave the way to total off-grid freedom.
Off-Grid Living 101
communities disconnect from centralized utilities and services to rely on their resources fully. This lifestyle choice is driven by several compelling factors, including environmental consciousness, the pursuit of self-sufficiency, and a desire for sustainable simplicity.
At its core, off-grid living involves several key components, each contributing to the overall goal of autonomy and sustainability:
1. Energy: Energy self-sufficiency is paramount in off-grid living. It means generating electricity and heating independently, often through renewable sources like solar power. Solar panels play a central role, capturing the sun’s energy and converting it into electricity. This energy powers essential appliances, lighting, heating, and cooling systems, allowing off-grid individuals to maintain a comfortable and functional living environment while reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and conventional power grids.
2. Water: Off-grid residents must manage their water supply carefully. This includes the acquisition and purification of water from natural sources, such as wells or rainwater harvesting systems. Solar-powered water pumps and filtration systems are commonly used to ensure a clean and reliable water source for drinking, irrigation, and household needs.
3. Food: Growing one’s food is a hallmark of self-sufficiency in off-grid living. Solar power can support food production through efficient irrigation systems, greenhouse heating, and powering equipment for gardening and food preservation. It plays a crucial role in enabling off-gridders to sustain themselves through homegrown crops and livestock.
4. Waste Management: Responsible waste management is vital in off-grid living to minimize environmental impact and maintain a clean and healthy environment. Solar-powered composting toilets and waste management systems are commonly used to process waste efficiently while adhering to sustainable principles.
All Eyes On Solar
Solar power is at the forefront of off-grid living. Understanding the fundamental principles of solar energy and the various types of solar systems is essential for those seeking off-grid independence.
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, harness the sun’s energy through the photovoltaic effect. Each solar cell within a panel contains semiconductor materials that absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and appliances. Solar panels are typically installed on rooftops or in open areas to capture maximum sunlight throughout the day.
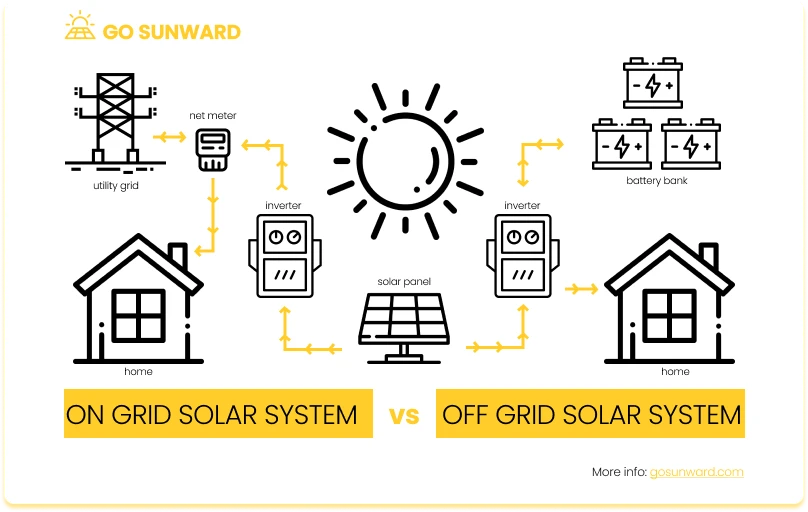
Off-grid solar setups operate independently of the utility grid. They rely on solar panels, charge controllers, inverters, and battery storage to generate, store, and distribute electricity. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations or those seeking complete self-sufficiency.
Components Of An Off-Grid Solar System
To create a comprehensive off-grid solar system, it’s essential to understand its key components and how they work together seamlessly. These components include solar panels, charge controllers, inverters, batteries, and, if needed, backup generators.
Solar Panels: Solar panels are the heart of the system, capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity. They generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Charge Controllers: Charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries. They prevent overcharging and ensure the batteries receive the right amount of charge, extending their lifespan.
Inverters: Inverters convert the DC electricity produced by the solar panels and stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is what most household appliances and electronics use.
Batteries: Batteries store excess electricity generated during sunny days for use during cloudy or nighttime periods. They are a vital component for maintaining a continuous power supply in off-grid systems.
Backup Generators (if applicable): Backup generators serve as a secondary power source in case of extended periods of low sunlight or when battery capacity is depleted. They provide added security for uninterrupted power.
How Much Solar Do I Need To Be Completely Off-Grid?
Now, let’s address the pivotal question: How much solar power is necessary for achieving complete off-grid independence? Below we will delve into the steps and factors involved in determining this crucial information.
Step 1: Assessing Your Energy Needs
Living off the grid requires a thoughtful assessment of your energy needs to ensure a sustainable and self-sufficient lifestyle.
When determining your energy requirements for off-grid living, start by compiling a detailed list of all electrical devices and appliances in your home. Record their power consumption in watts and estimate the number of hours each device is used daily. To find your daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh), multiply the power consumption by the daily usage for each device and add these values together. It’s essential to consider seasonal variations in energy requirements, particularly for heating or cooling.
Several factors influence energy consumption in off-grid living:
- Household Size: Larger households typically have higher energy demands due to increased appliance usage and more significant lighting needs.
- Appliance Efficiency: The type, efficiency, wattage and voltage of appliances play a significant role. Opt for energy-efficient models and consider LED lighting to reduce overall electricity usage.
- Climate: Climate conditions impact energy needs, with colder regions requiring more energy for heating and warmer areas needing additional power for cooling.
Conducting an energy audit is a practical way to gain insights into your energy usage patterns and identify areas for improvement. Understanding your energy consumption patterns through an energy audit is a valuable foundation for accurately sizing your off-grid solar system. It empowers you to make informed decisions about the size and capacity of your solar setup.
Step 2: Sizing your off-grid solar system
Sizing your off-grid solar system appropriately is a crucial step to ensure a reliable and sustainable energy source for your off-grid lifestyle.
Here are the key considerations for sizing your system:
- Daily Energy Consumption: Begin by calculating your daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) as discussed in the section aboce. This figure represents the baseline energy requirement you need to meet with your solar system.
- Sunlight Hours: Assess the average daily sunlight hours in your location throughout the year. This information helps estimate your daily solar energy generation potential. It’s essential to consider seasonal variations in sunlight availability.
- Battery Capacity: Determine the battery bank capacity needed to store excess solar energy for use during non-sunny periods. This capacity should cover days with reduced sunlight, ensuring a continuous power supply.
- Roof Size: The size of your roof determines how many solar panels can fit on it. A larger roof can accommodate more panels, which means you can generate more electricity. Additionally, the orientation and angle of your roof can affect the efficiency of solar panels. Ideally, you want your solar array to face south or southwest at an angle that maximizes sunlight exposure.
- Type Of Solar Panel: Different types of panels have varying levels of efficiency and energy output. Monocrystalline panels, for example, are known for their high efficiency but may come at a higher cost. Polycrystalline panels are more cost-effective but may be slightly less efficient.
For more information on system sizing and working out exactly how many solar panels you would need to run a house, click here.
Practical Tips for Sizing Your System Accurately
Top Tip #1: Consult a Professional
Engage with a solar professional or installer experienced in off-grid systems. They can conduct a comprehensive assessment, considering your location, energy consumption, and specific requirements to recommend the right system size.
Top Tip #2: Use Solar Calculators
Online solar calculators can provide preliminary estimates based on your geographical location, energy consumption, and system preferences. While useful for initial planning, consult with a professional for a more precise assessment.
Top Tip #3: Account for Future Growth
Consider potential changes in your off-grid living arrangements. If you plan to expand your system or add new appliances, ensure your solar system can accommodate these future needs.
Top Tip #4: Budget for Contingencies
Allocate some extra budget for contingencies and unexpected changes. Slight oversizing of your system can provide peace of mind and flexibility.
Budgeting & Financing
Understanding the costs associated with off-grid solar systems is essential for effective budgeting. These costs encompass equipment (solar panels, batteries, inverters, charge controllers), installation, and ongoing maintenance. The total cost can vary widely depending on the system’s size and complexity.
As a rough estimate, the initial investment for a basic off-grid solar system, including solar panels, inverters, charge controllers, and batteries, can range from $5,000 to $15,000.
Financing options play a crucial role in making off-grid solar more affordable. Exploring options like solar loans, leases, or power purchase agreements can help spread the upfront costs over time. Additionally, various incentives and tax credits, offered by governments and utility companies, can significantly offset expenses. These incentives encourage renewable energy adoption and may include rebates, tax credits, or net metering programs that allow you to sell excess energy back to the grid.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving complete off-grid independence through solar power is a viable and sustainable option, but it requires careful planning and sizing. Key takeaways from this guide include the significance of accurately assessing your energy needs, understanding the impact of location and climate, and optimizing your solar system’s components.
It’s crucial to embark on this journey with thorough planning, potentially seeking professional guidance to ensure a reliable and self-sufficient off-grid lifestyle. By doing so, you can embrace the benefits of off-grid living while reducing your environmental footprint and enjoying a higher degree of autonomy.




