How Much Is 1 Solar Panel?
In a world increasingly conscious of the environmental challenges posed by fossil fuels, the shift towards renewable energy sources has become ever-pressing. Solar energy, in particular, has emerged as an attractive option in the fight against climate change. Harnessing the limitless energy of the sun, solar panels have the potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape, reducing dependence on polluting fossil fuels and curbing greenhouse gas emissions. As individuals and businesses seek sustainable alternatives to traditional energy sources, one of the most common questions is a seemingly straightforward one: “How much does 1 solar panel cost?”.
In this article, we will demystify the economics of solar panels. We’ll delve into the numerous factors that influence the cost of 1 solar panel and provide you with a comprehensive overview of the typical price range. Whether you’re a homeowner considering a rooftop solar installation, a business owner looking to invest in clean energy, or simply someone curious about the affordability of going solar, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed choices surrounding solar panels.
The Average Cost Of 1 Solar Panel
So, let’s address a fundamental question: How much does 1solar panel cost? Based on current data for state and national averages in the United States, a single solar panel typically ranges from $150 to $350.
It’s worth noting that while the initial cost of a single solar panel is important to consider, the long-term advantages, such as lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact, establish solar energy as both an eco-friendly and financially prudent choice.
Influencing Price Factors
Type and Quality of Solar Cells
The $150 to $350 range for 1 solar panel mentioned above is a ballpark estimate and can vary significantly based on several factors.
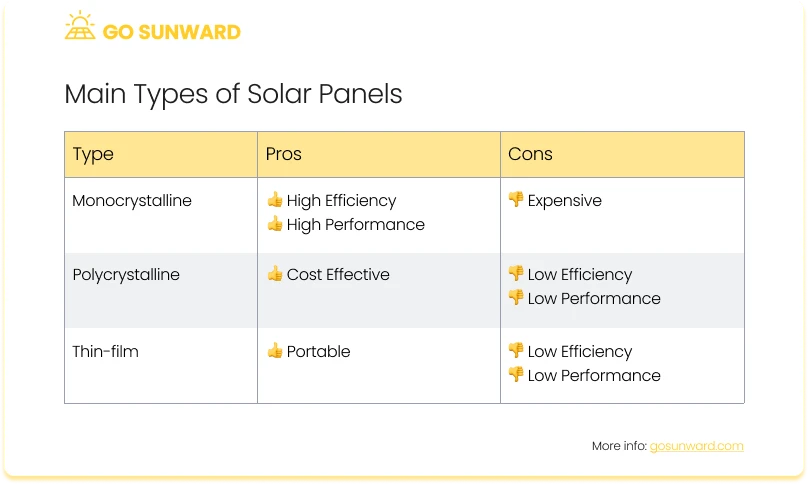
The core component of a solar panel is its solar cells. Panels can be equipped with different types of solar cells, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film.

These vary in price:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Monocrystalline panels are renowned for their exceptional energy efficiency, making them a top choice for those with limited roof space. Typically priced between $1 to $1.50 per watt, these panels are a long-lasting investment, boasting a lifespan of up to 40 years. When compared to polycrystalline panels, monocrystalline panels are the more efficient option.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels : Polycrystalline solar panels, while slightly less energy-efficient than monocrystalline panels, come with an attractive cost advantage, usually ranging from $0.75 to $1 per watt. These panels are commonly used in residential settings due to their affordability. Despite not matching the efficiency of monocrystalline panels, they offer a reliable performance over time, with an average lifespan of 25 to 30 years.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: Thin-film solar panels are the cost-effective choice, with an average price ranging from $0.75 to $1.10 per watt. While budget-friendly, they require more space, making them suitable for industrial applications or smaller projects like RVs or sheds. However, they have a shorter lifespan, lasting approximately 10 to 20 years, and come with a shorter warranty compared to other panel types.
Each panel type has unique strengths and trade-offs, making it essential to consider your specific requirements and budget when choosing the right solar panel for your project.
You can find additional information here if you want to learn more about the diverse range of panels available in the market.
Size and Wattage of the Panel
Solar panels come in various sizes and watts. Larger panels with higher wattage output will generally have a highest price point. The panel size is often tailored to the available home installation space and the user’s energy needs. Larger panels and solar arrays can generate more electricity, but they may only be suitable for some applications and consumers.
Brand and Manufacturer
The brand and manufacturer of the solar panel also influence its cost. Well-established, reputable brands tend to command higher prices due to their quality and reliability track record. While cheaper options may be available from lesser-known manufacturers, it’s important to consider the panel’s performance and warranty when making a choice.
Efficiency and Warranty
The efficiency of a solar panel refers to how effectively it converts sunlight into electricity. More efficient panels are often more expensive but can produce more energy for a given area. Additionally, the length and terms of the panel’s warranty can affect its price. Panels with longer warranties typically come at a higher cost but offer greater peace of mind.
Location and Local Market Conditions
The cost of solar panels can vary significantly based on your location and the prevailing market conditions. Areas with high demand for solar installations may have slightly higher prices due to increased competition. Moreover, government incentives, rebates, and tax credits available in your region can impact the final price you pay for a solar panel.
Quantity and Customization
Buying multiple panels as part of a larger solar installation can sometimes lead to cost savings per panel. Additionally, customizations such as advanced monitoring systems or specialized mounting hardware can add to the overall cost of a panel.
To obtain precise pricing information for your specific circumstances, it’s advisable to consult with local solar installers and request quotes tailored to your location and energy needs. They can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed decision regarding your solar panel investment.
A History Of Solar Panel Prices Over Time!
Historical Evolution of Solar Panel Prices
In the early days of solar technology, dating back to the 1950s and 1960s, solar panels were exorbitantly expensive, making them accessible only to specialized industries and space exploration missions. During this nascent stage, the cost of a single watt of solar power was several hundred dollars, a huge difference from today’s prices.
As the decades progressed, solar panel prices began to experience a consistent decline. The 1970s saw the emergence of government-sponsored research and development initiatives aimed at making solar power more affordable. These efforts, coupled with the oil crises of the era, spurred interest in alternative energy sources and played a pivotal role in lowering solar panel costs.
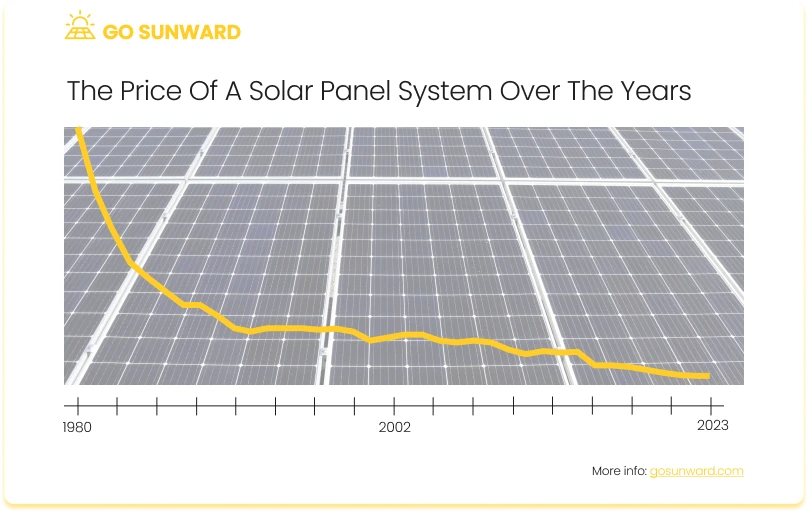
Driving Forces Behind Cost Reduction
Several factors have contributed to the continuous reduction in solar panel prices. Government incentives and policies have been instrumental in promoting the adoption of solar energy. Tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs have incentivized individuals and businesses to invest in solar power systems, driving up demand and encouraging economies of scale in manufacturing.
Technological advancements have also been a key driver of cost reduction. Improved manufacturing processes, innovations in solar cell design, and enhanced materials have all boosted the efficiency of solar panels while simultaneously lowering production costs. This combination of increased efficiency and reduced manufacturing expenses has profoundly impacted the affordability of solar panels.
The concept of economies of scale cannot be overstated when discussing the price trend of solar panels. As the solar industry has grown, production volumes have surged, leading to significant cost savings in manufacturing. This virtuous cycle has enabled manufacturers to produce more panels at lower costs, translating into more affordable consumer prices.
Future Price Trends and Further Cost Reductions
Looking ahead, a key question asked is: will solar panels get cheaper? And in fact, the future of solar panel prices does appear promising. Over the last fee years we can already see a decline in the cost of 1 solar panel. The solar industry continues to innovate, with research focusing on improving the efficiency of solar cells and developing new materials. These advancements can further reduce the cost per watt of solar power.
Government support for renewable energy is expected to persist, with ongoing incentives and policy measures driving continued growth in the solar sector. As solar technology becomes increasingly integrated into mainstream energy systems, economies of scale will continue to drive down costs, making solar power an even more attractive and cost-effective option.
The Cost of a Complete Solar System
While we have effectively answered how much 1 solar panel costs, it is important to take into consideration the other factors influencing the costs of an entire household solar system. In fact, the price of one solar panel represents just a fraction of the total investment required for a functional solar power system.
A comprehensive solar power system has several essential elements, each contributing to its overall functionality and efficiency. One of these crucial components is the inverter, which converts the solar panels’ direct current (DC) electricity generated into alternating (AC) electricity usable in homes and businesses. Inverters come in various types and sizes, and their cost can vary based on capacity and features. Similarly, coupling your solar panel system with energy storage can increase your energy independence and reduce reliance on the grid, but will also increase the initial costs of your solar system.
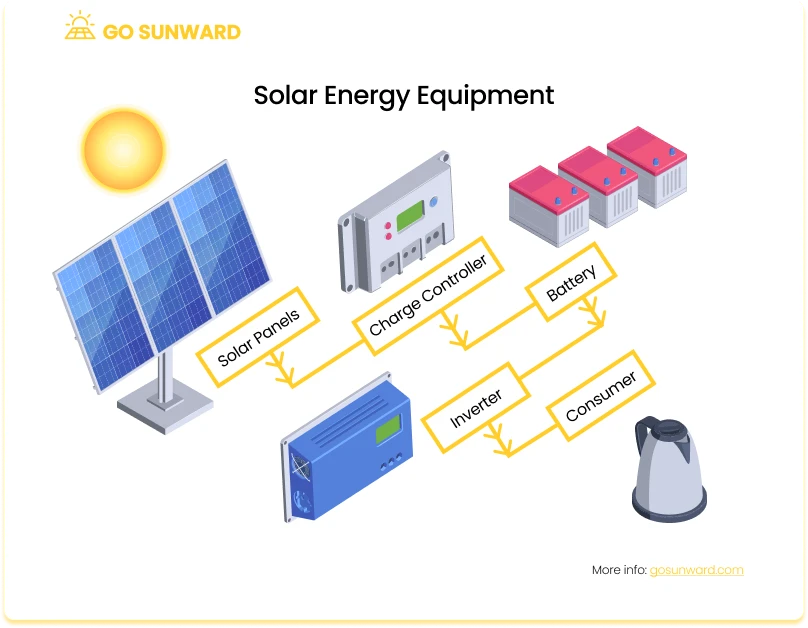
Mounting hardware is another necessary component of a solar installation. These include racks, rails, and brackets that securely hold the solar panels in place, ensuring optimal orientation to the sun for maximum energy capture. The mounting system’s type and complexity can influence the system’s cost and efficiency.
Wiring and electrical components are essential for connecting the solar panels to your home’s electrical system. These include cables, conduits, circuit breakers, and safety mechanisms to protect against electrical issues. Proper wiring is critical to ensure your solar power system’s safe and efficient operation.
Lastly, the installation labor costs should not be overlooked. The expertise and labor required to install solar panels, inverters, and other components, as well as the necessary electrical connections and inspections, contribute significantly to the total system cost.
To make an informed decision on whether solar is the right choice for you and your budget, it’s essential to factor in the costs of inverters, mounting hardware, wiring, and installation labor. Only by considering the overall system cost can you accurately gauge the financial commitment required for your solar installation.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Investing in solar panels offers a range of compelling financial benefits that can result in a positive return on investment (ROI). Understanding these benefits is crucial for making an informed decision about transitioning to solar energy.
The primary financial benefit of solar panels is the significant reduction in electricity costs over the system’s lifespan. Solar panels generate clean, renewable energy from sunlight, offsetting or even eliminating the need to purchase electricity from the grid. This translates into substantial long-term savings on your utility bills, as your reliance on traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources diminishes.
Government incentives and policies play a crucial role in enhancing the financial attractiveness of solar investments. Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs that can offset a significant portion of the initial installation costs. These incentives not only reduce your upfront expenses but also accelerate your path to achieving a positive ROI.
Environmental benefits further contribute to the overall ROI of solar panels. By generating clean, renewable energy, solar panels help reduce carbon emissions and environmental pollution. The positive environmental impact of solar energy can also be leveraged for marketing and branding purposes, potentially benefiting businesses and organizations and their ESG profiles.
What Savings Can You Make?
To illustrate the potential financial gains and payback periods, let’s consider an example. Suppose you install a 6-kilowatt (6kw) solar panel system on your residential property, and the system’s total cost, including installation, is $15,000. With government incentives, you receive a $5,000 rebate, reducing your upfront investment to $10,000.
Assuming that the solar panels generate enough electricity to cover 80% of your household’s energy needs, you could save approximately $1,200 per year on your electricity bill, depending on your location and energy consumption patterns. In this scenario, your payback period would be around 8.3 years ($10,000 initial investment ÷ $1,200 annual savings).
Once the payback period is reached, the electricity generated by your solar panels essentially becomes free, and you continue to enjoy reduced energy costs for the remainder of the system’s lifespan, typically 25 to 30 years. This extended period of energy savings enhances your overall ROI, making solar panels an attractive long-term investment. Want to know exactly what your savings would be? Head over here to estimate your solar savings.
A Note On Maintenance Costs…
Solar panels are renowned for their low maintenance requirements, and their durability and efficiency over time are major selling points. That said, there is some minimal maintenance that is needed for solar panels, and this brings associated costs. For more in-depth information on solar panel maintenance, click here.
1. Regular Cleaning:
Maintenance: The primary upkeep solar panels require is periodic cleaning to ensure they operate at peak efficiency. Dust, dirt, bird droppings, and debris can accumulate and reduce sunlight absorption.
Cost: Cleaning is a straightforward task that can often be done by homeowners using water, a soft brush, and mild detergent. This DIY approach typically incurs minimal to no cost. Alternatively, professional cleaning services are available, usually at a modest fee.

2. Visual Inspection:
Maintenance: Routine visual checks allow homeowners to identify any visible damage or issues such as cracks, loose connections, or physical harm.
Cost: Visual inspections can be conducted by the owner at no additional cost. For those who prefer professional inspections, there may be a nominal fee involved.
3. Monitoring System Performance:
Maintenance: Solar panel systems often come equipped with monitoring tools that track energy production and system health. Regularly reviewing these reports can help detect performance issues early.
Cost: Monitoring software and services are often included with the initial installation or require minimal subscription fees.
4. Inverter Maintenance:
Maintenance: Inverters, a crucial component of solar panel systems, may require occasional maintenance or replacement during their lifespan.
Cost: Maintenance or replacement costs vary depending on the type and size of the inverter but generally range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars.
5. Professional Inspections:
Maintenance: Periodic professional inspections carried out by certified technicians provide more comprehensive system assessments.
Cost: Professional inspections may come with a cost, typically a few hundred dollars, but they are generally infrequent, often needed every few years.
6. Storm and Weather Damage:
Maintenance: Solar panels are designed to withstand various weather conditions, but in the event of severe storms or hail, there may be damage that requires repairs.
Cost: Repair expenses for weather-related damage can vary widely based on the extent, but insurance coverage may assist in offsetting these costs.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the factors that influence the cost of a single solar panel and the broader context of solar energy systems. While we’ve established that the cost of 1 solar panel can vary widely, typically falling within the range of $150 to $350 per panel, it is crucial to understand that numerous factors influence this price. These include the type and quality of solar cells, the panel’s size and wattage, the brand, efficiency, and local market conditions. How much is 1 solar panel is an essential consideration, it represents only a portion of the overall investment required for a complete solar power system.
We encourage readers to take proactive steps towards exploring the feasibility of solar energy for their specific needs. Obtaining multiple quotes from local solar installers is an essential part of the decision-making process, as it ensures you receive accurate pricing information tailored to your location and requirements. It is also essential to consider the long-term benefits of solar energy, which include substantial savings on electricity bills, reduced environmental impact, and a step towards a more sustainable energy future.
Solar power offers a practical solution as we work to address climate change and shift towards cleaner, sustainable energy sources. By grasping the cost factors of solar panels and looking at the broader context of solar energy systems, you can make a smart investment that saves you money and supports a greener, more sustainable global energy system.




